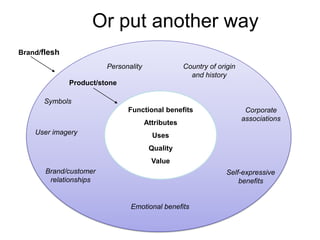
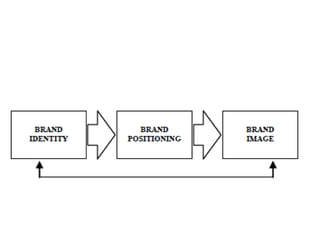
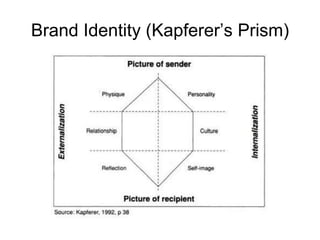
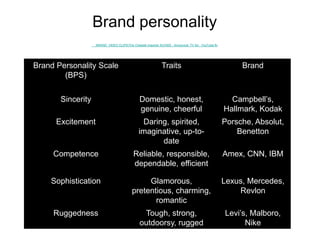
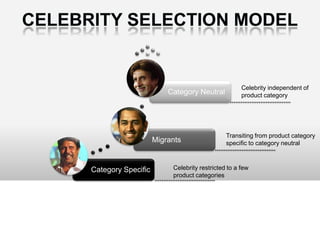
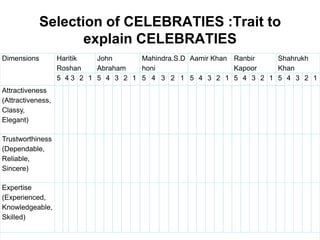
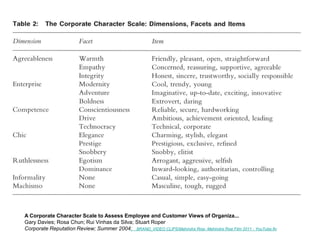
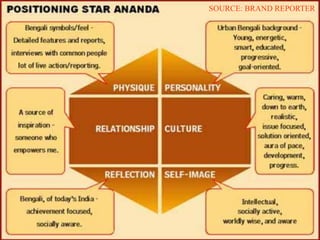
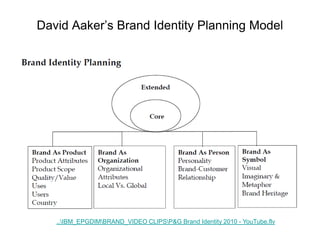
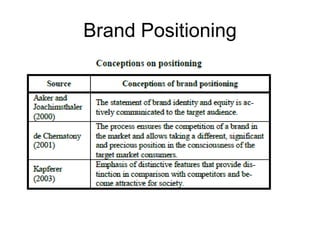
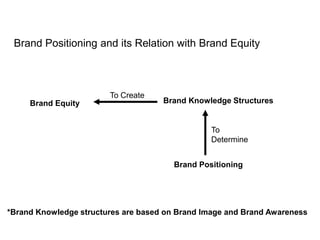
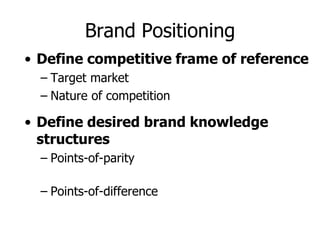
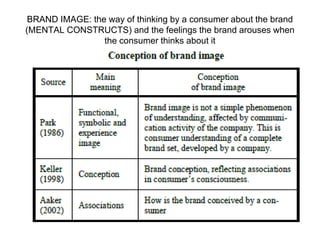
Brand identity is the unique set of brand associations that the brand strategist aspires to create or maintain. These associations represent what the brand stands for and imply a promise to customers. A brand's identity includes its moral image, aim, values, and personality that differentiate it. However, a brand's actual image perceived by customers may differ from its intended identity. Identifying any gaps between a brand's identity and image helps strategists align marketing efforts to close those gaps.