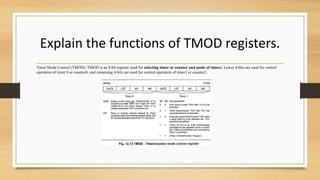
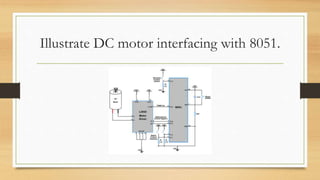
The TMOD register is an 8-bit register used to select the timer or counter mode for timers 0 and 1. The 8051 has 32 bytes set aside for 4 register banks of 8 registers each (R0-R7) that can be used for temporary data storage and the stack. An LED can be interfaced with an I/O port on the 8051 by first configuring the port as an output and then writing a 0 to turn the LED on or a 1 to turn it off. Ports 0 and 2 have a dual role, with port 0 also functioning as the lower 8 address lines and port 2 functioning as the upper 8 address lines when accessing external memory up to 64KB.