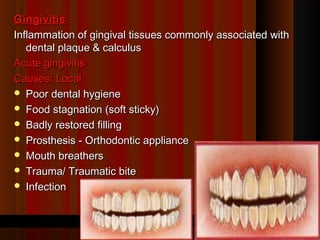
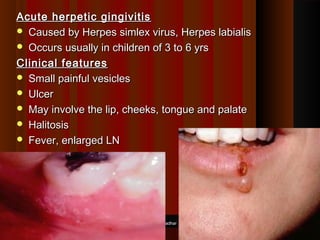
This document discusses different types of gingivitis, including acute and chronic gingivitis. Acute gingivitis can be caused by local factors like poor oral hygiene or systemic diseases. It commonly presents with pain, bleeding, and halitosis. Treatment involves maintaining oral hygiene and using antiseptics. Chronic gingivitis is caused by long-term plaque and calculus buildup and presents as red, swollen gums that bleed easily. Treatment for chronic gingivitis includes scaling, oral hygiene maintenance, and antibiotics in some cases.