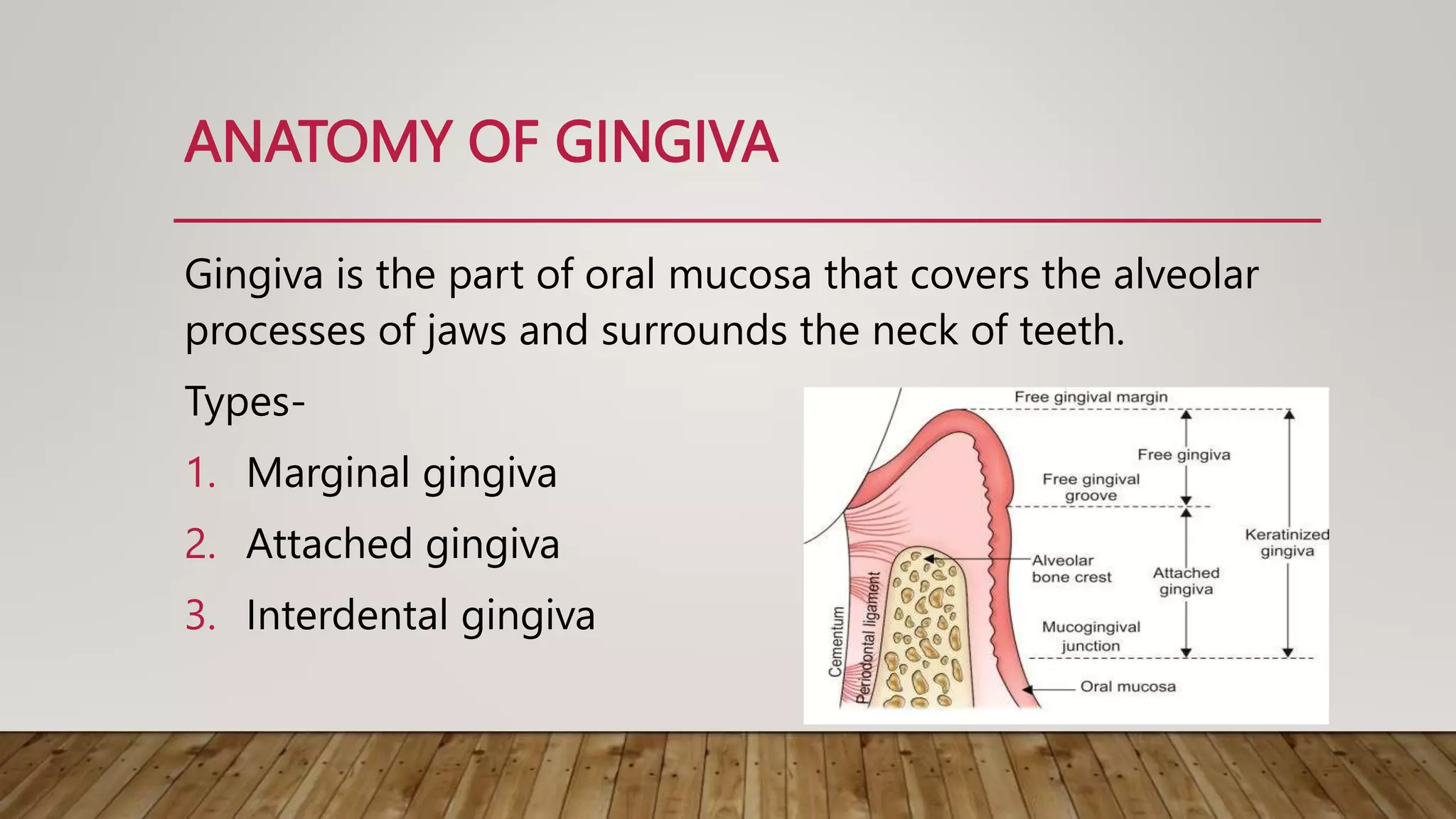
The document presents a paper on gingivitis, detailing its definition, pathogenesis, and risk factors associated with poor oral hygiene, bacteria, hormonal changes, and malnutrition. It describes clinical findings such as color changes, bleeding, and variations in gingiva, while also outlining complications if left untreated, including potential progression to periodontitis. A treatment protocol is provided, highlighting the importance of local factor removal, systemic disease correction, scaling, and oral hygiene practices.