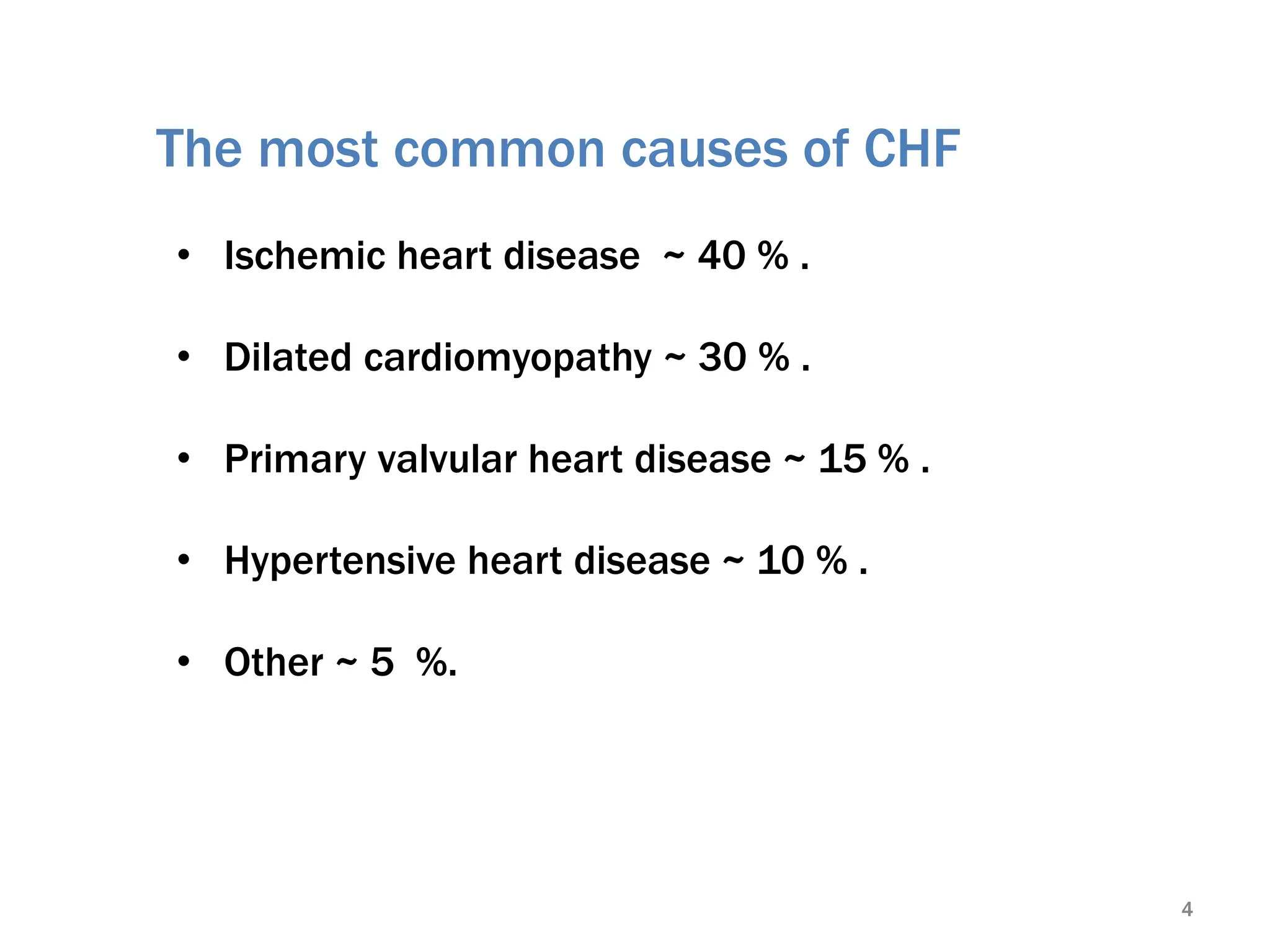
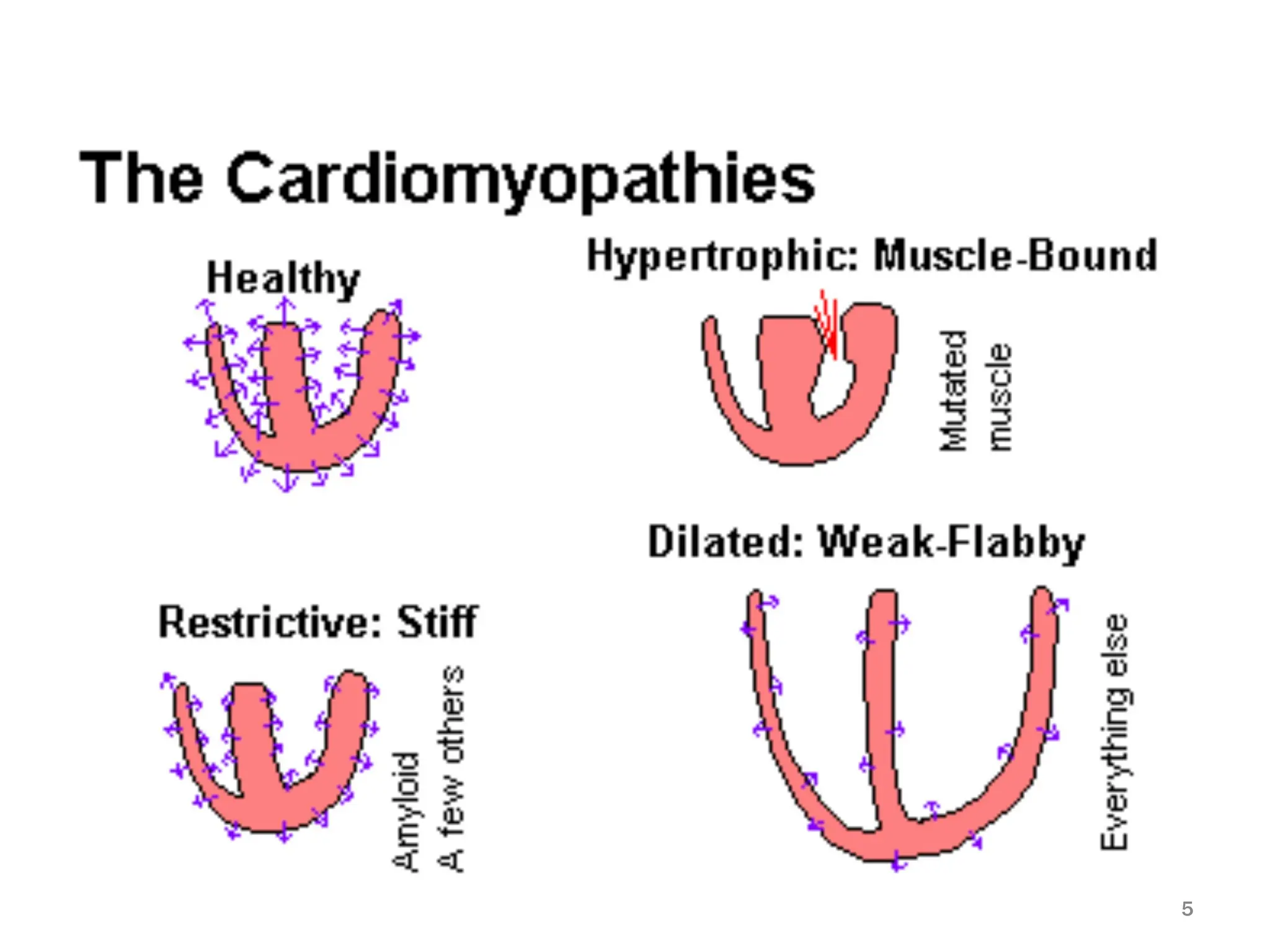
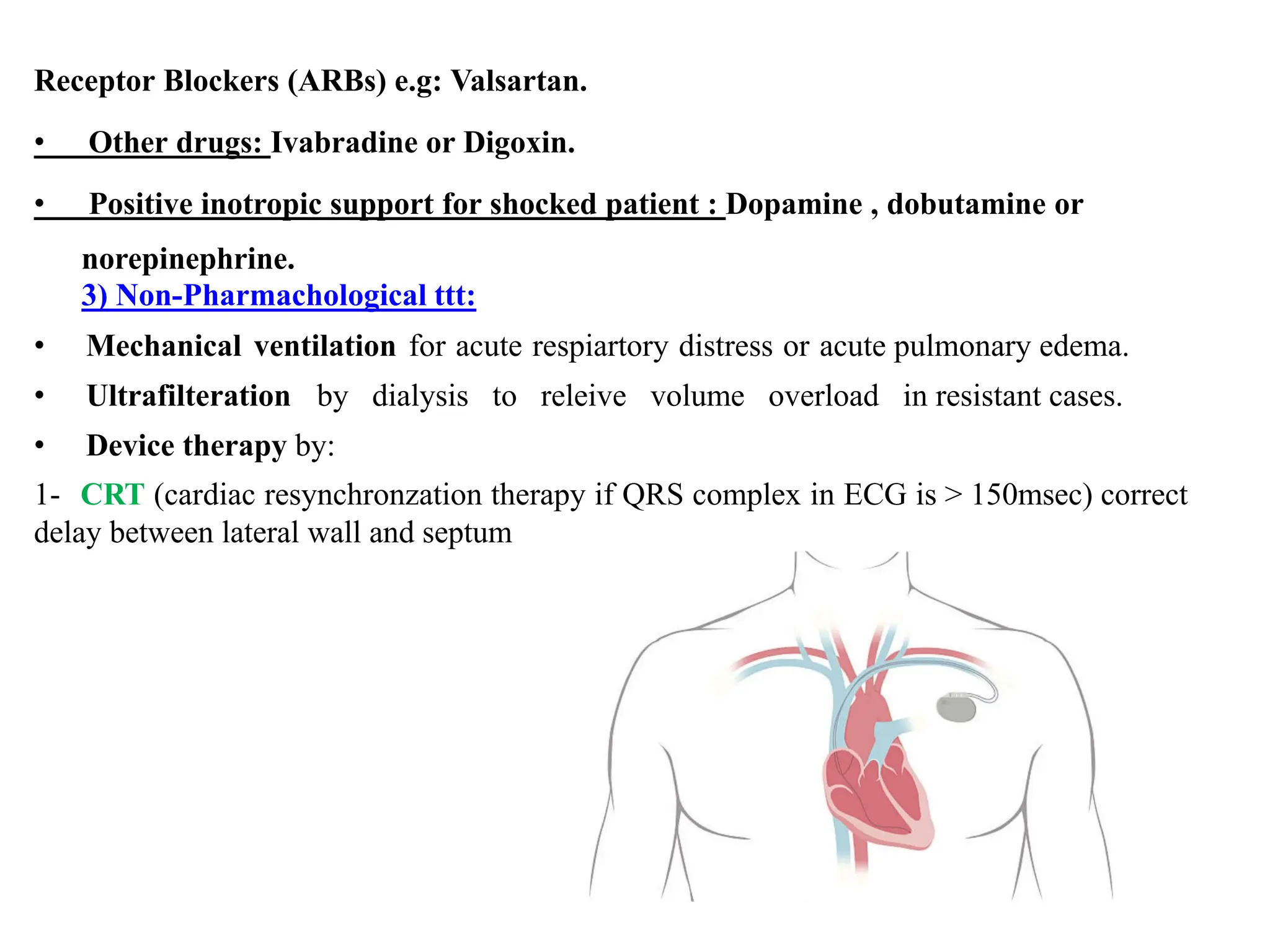
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome defined as the heart's inability to maintain adequate output to meet the body's metabolic demands, affecting 1-2% of the population and causing significant hospital admissions, especially in those over 65. It can be categorized into various types such as acute vs. chronic, left sided vs. right sided, and systolic vs. diastolic heart failure, with common causes including ischemic heart disease and dilated cardiomyopathy. Treatment involves addressing reversible causes, pharmacological options like diuretics and ACE inhibitors, as well as non-pharmacological interventions and potential surgical options.