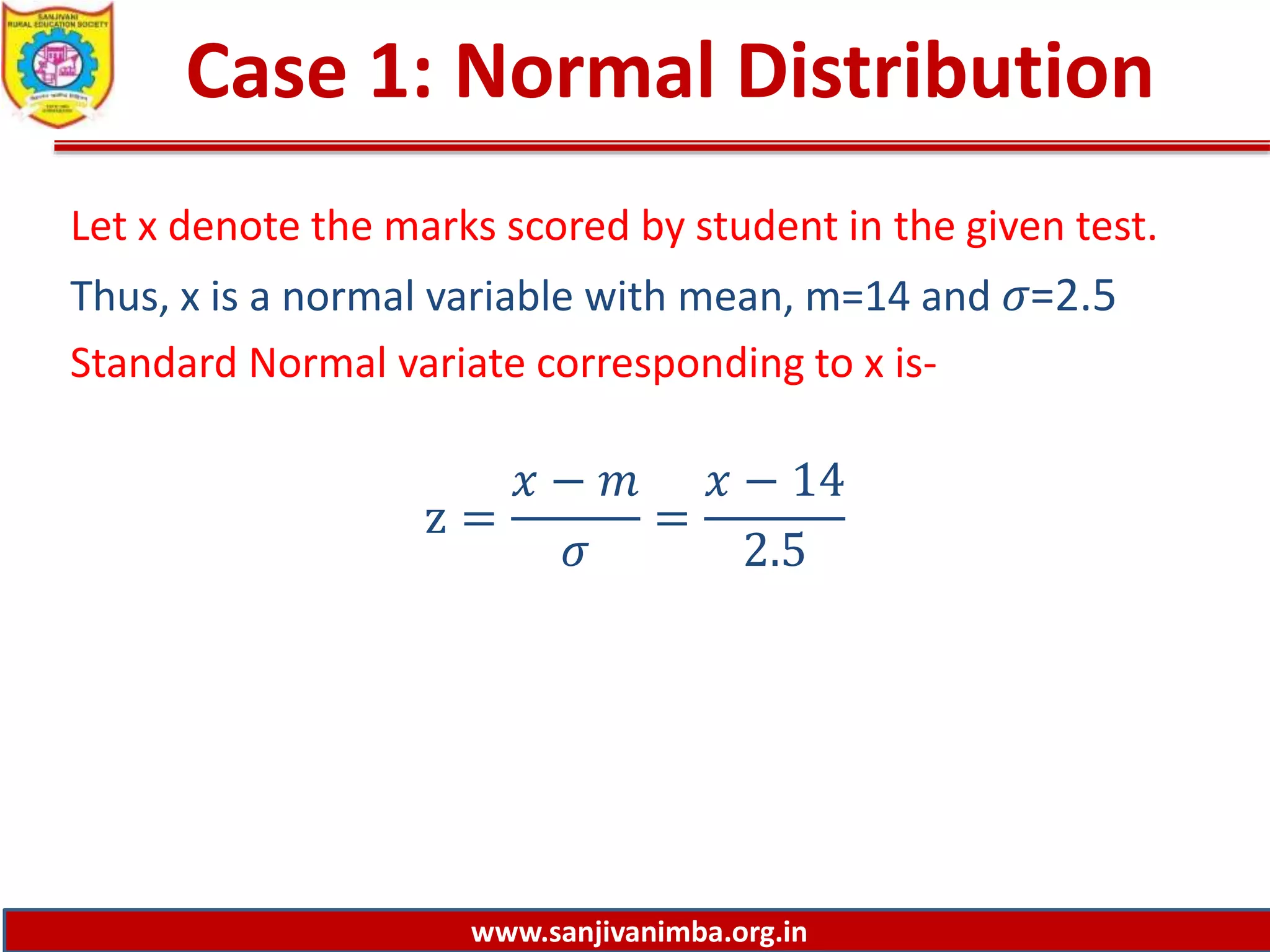
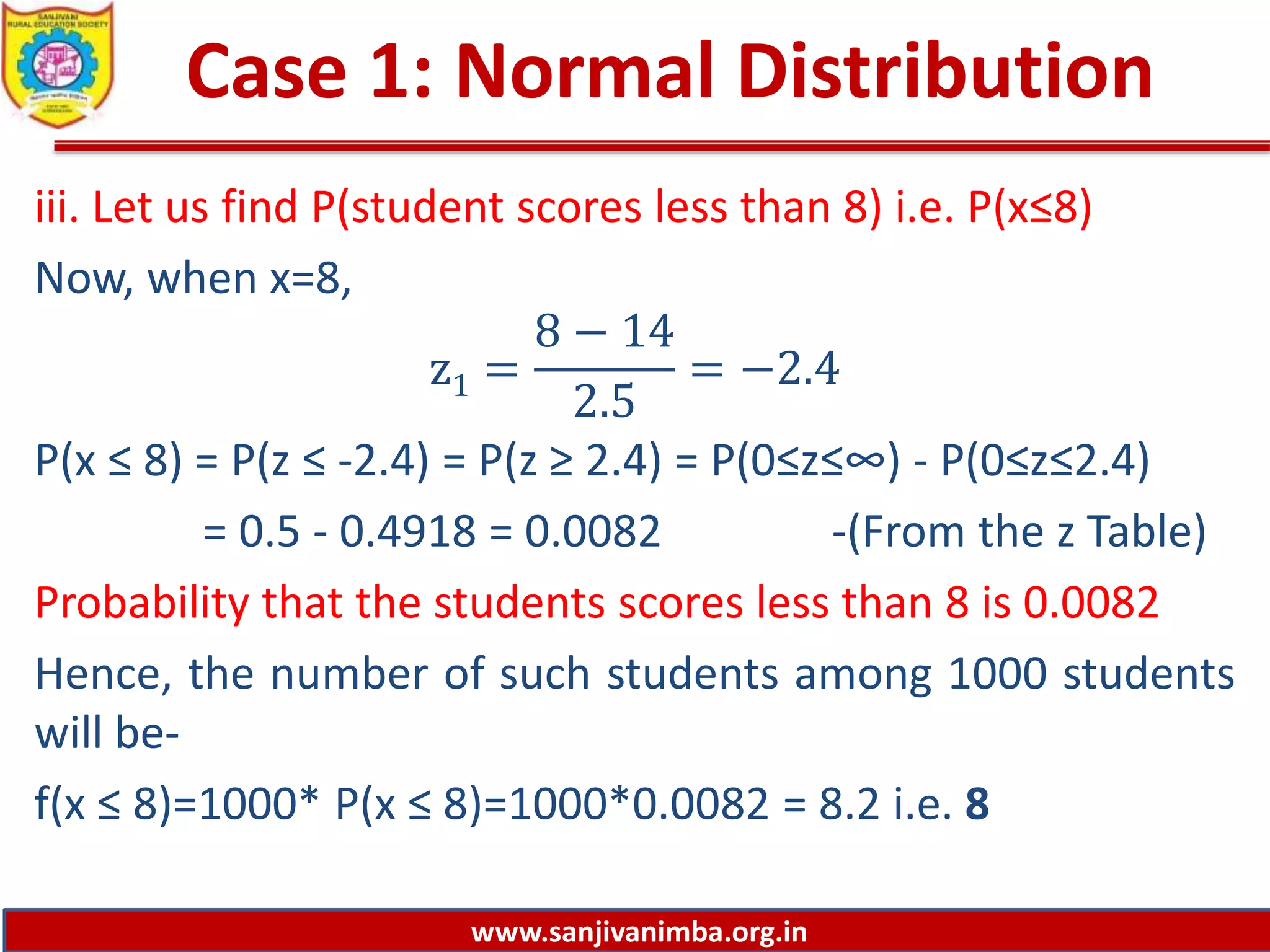
This document discusses solving probability problems using the normal distribution. It provides an example of test scores that are normally distributed with a mean of 14 and standard deviation of 2.5. It then calculates:
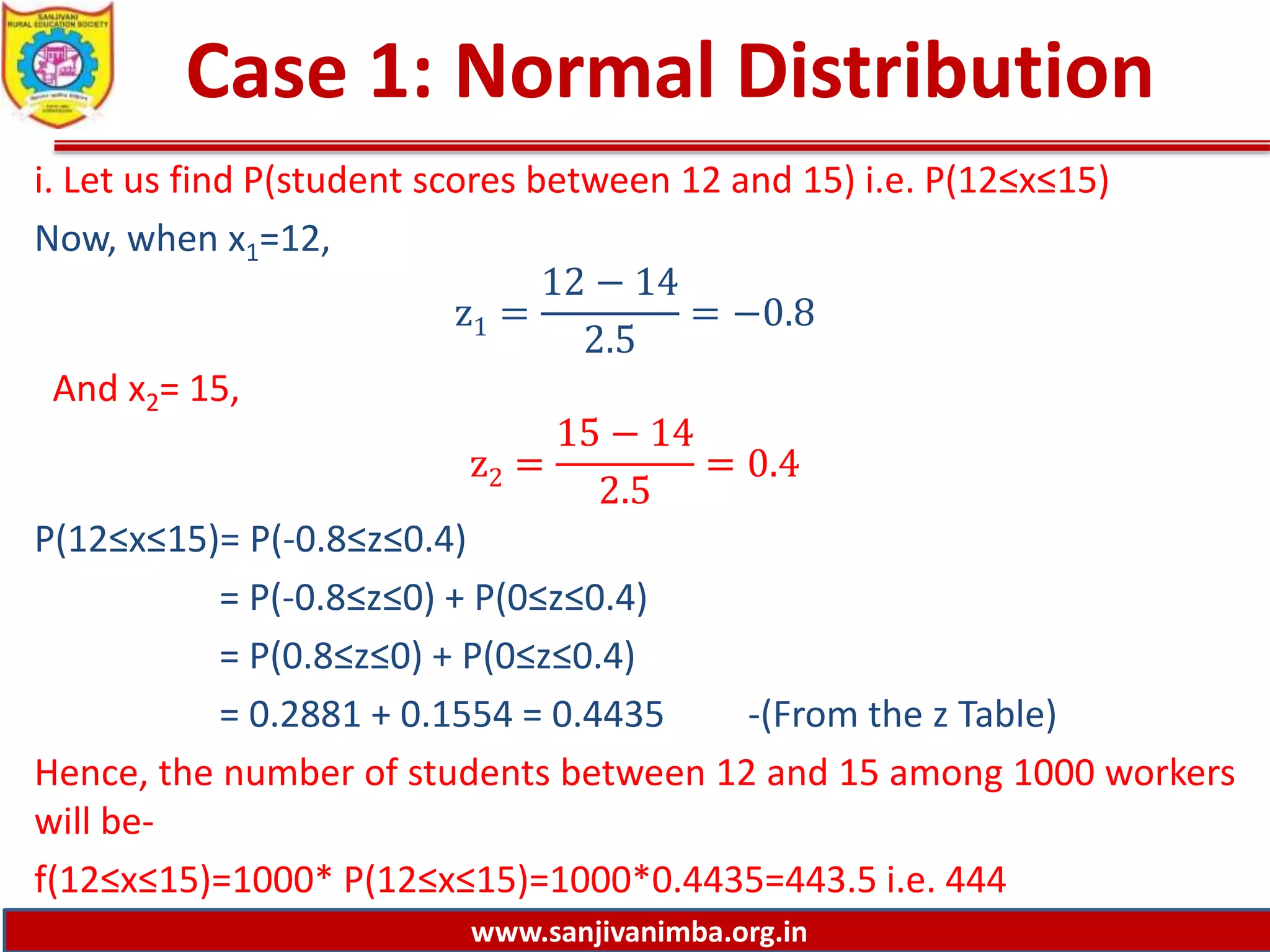
1) The number of students who scored between 12 and 15, which is 444.
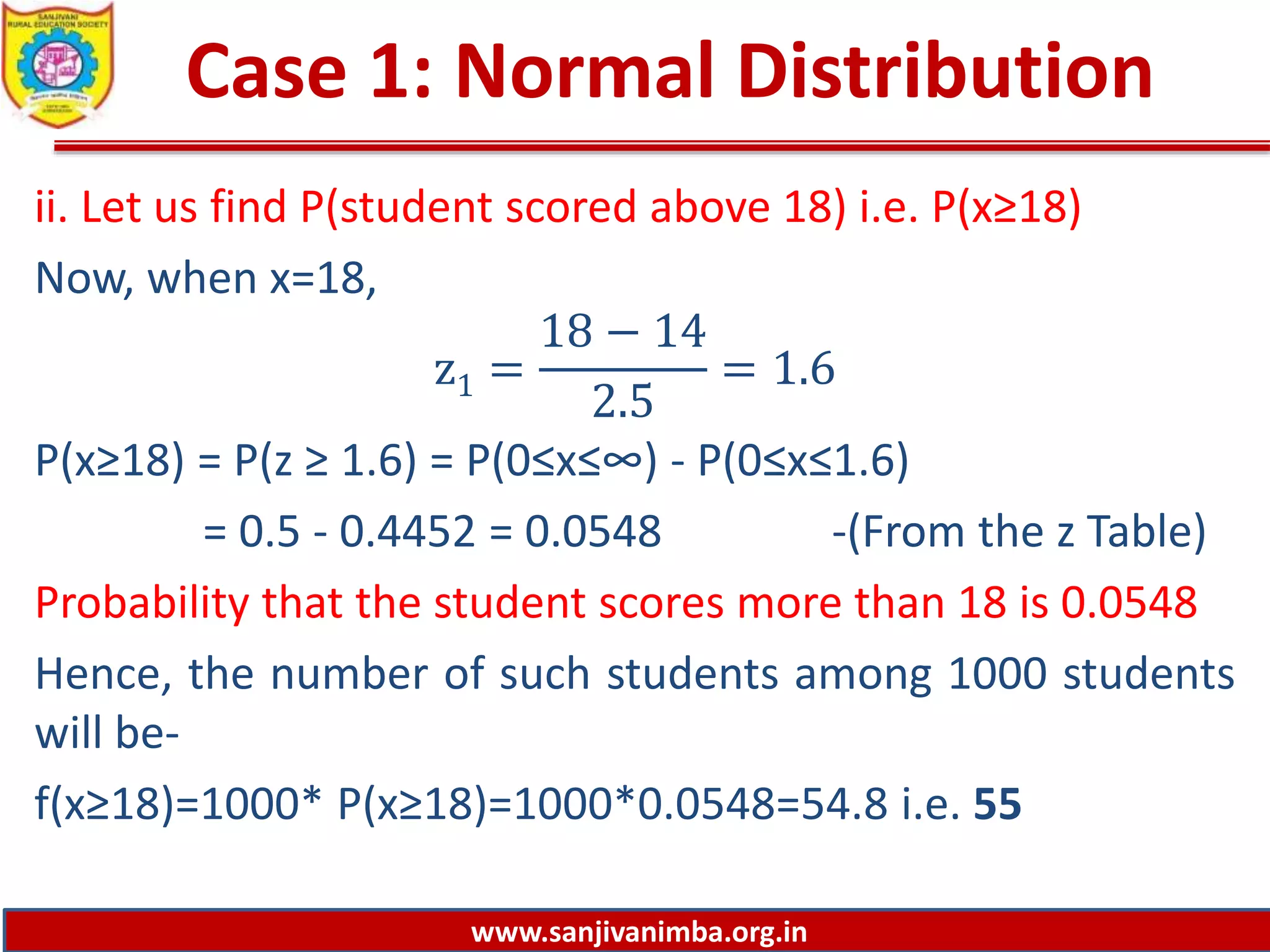
2) The number of students who scored above 18, which is 55.
3) The number of students who scored below 8, which is 8.
The calculations are shown by converting the data values to standard normal variables and looking them up in a z-table.