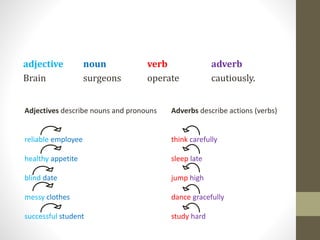
This document provides information about foundational words used in writing simple English sentences. It discusses nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions. For nouns, it defines concrete, abstract, and proper nouns as well as pronouns. For verbs, it discusses action, linking, and helping verbs. It provides examples of adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositional phrases. The document also demonstrates how to construct simple and compound sentences using these foundational words.





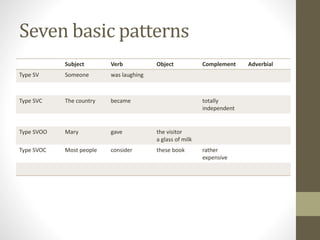
![A typical SVO pattern
• In most cases a verb must be followed by another noun to
make sense and express a complete thought.
• The verb bellow is an example of action verbs
Noun Verb Noun
Teachers Give _______________ [What?]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningenglish-160517185427/85/5182016-7-320.jpg)