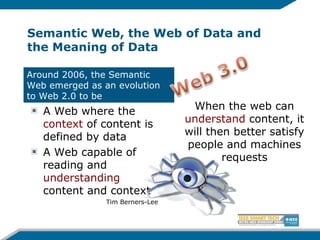
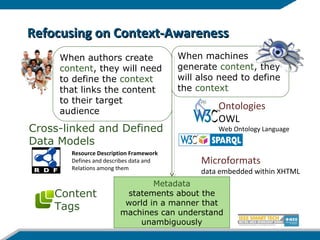
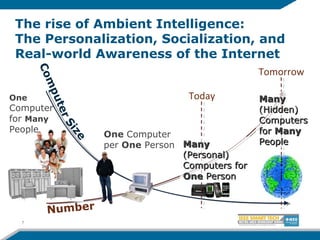
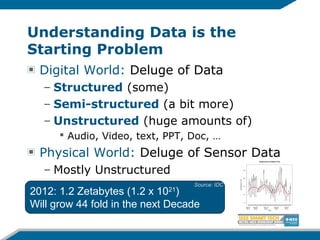
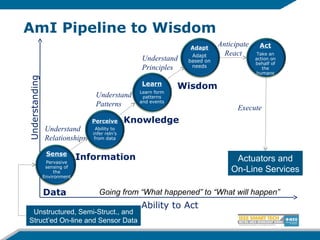
The document discusses the evolution from the Internet to the Internet of Things (IoT) and the role of ambient intelligence, emphasizing the integration of everyday devices into smart environments that enhance personalization and responsiveness. It highlights challenges in data management, interoperability, and the need for intelligent systems that can self-adapt and learn from their surroundings. Key technologies in this evolving landscape include machine learning, the semantic web, and various innovative programming languages.
![The Internet of Things,
Ambient Intelligence and the
Move Towards Intelligent
Systems
Santa Clara (IEEE Region 6) Event
September [28 or 29], 2012
Dr. George Vaněček, Jr.
Senior Principal Scientist, FutureWei Technologies, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/512-r6maw-sat-21stcent-vanecek-140327042808-phpapp02/75/The-Internet-of-Things-Ambient-Intelligence-and-the-Move-Towards-Intelligent-Systems-1-2048.jpg)









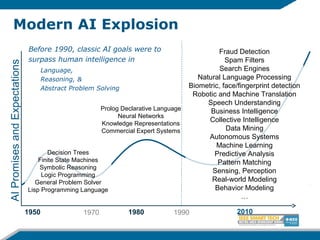

![Machine Learning
Supervised Learning Algorithms
– K-Nearest Neighbor
– Naïve Bayes
– Support Vector Machines
– Decision Tree Induction
– Etc.
Unsupervised Learning Alg.s
– K-Means
– Expectation Maximization
– Etc.
16
ML refers to a statistical suite of algorithms and
paradigms for finding patterns in data.
Training
Set {x}
Training
Algorithm:
X’
D
{[Patterni,Di]}
{D}
{}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/512-r6maw-sat-21stcent-vanecek-140327042808-phpapp02/85/The-Internet-of-Things-Ambient-Intelligence-and-the-Move-Towards-Intelligent-Systems-16-320.jpg)