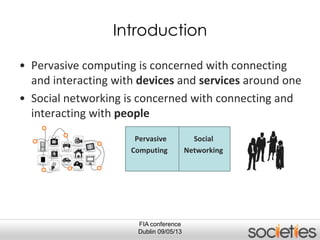
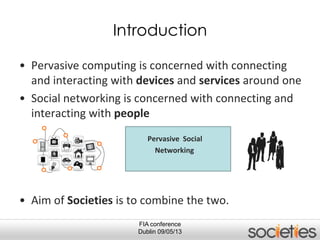
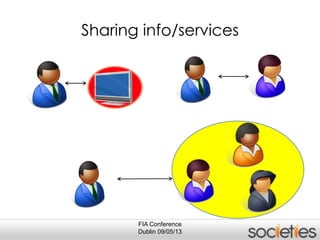
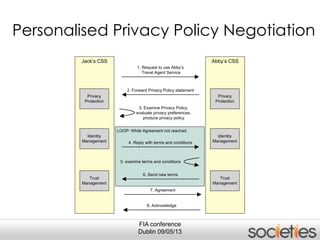
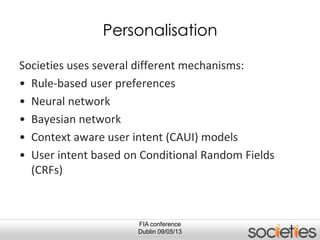
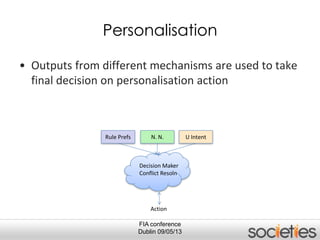
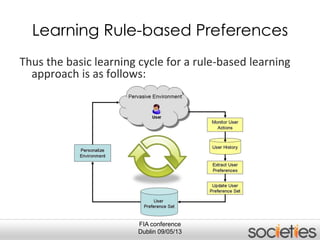
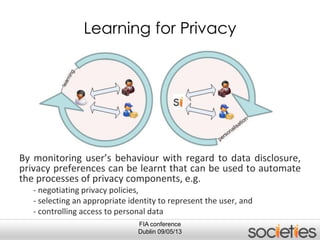
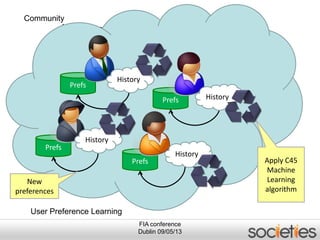
The document discusses enabling privacy and personalization for a pervasive social networking system. It proposes combining pervasive computing, which connects devices and services, with social networking, which connects people. Two key supporting processes are privacy and personalization, both of which are data-driven and rely on learning. The system uses personalized privacy policy negotiation to allow users to control what personal data is disclosed. It also personalizes services for individuals and communities using various learning mechanisms like rules and neural networks to adapt to users' needs.