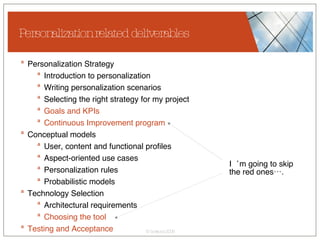
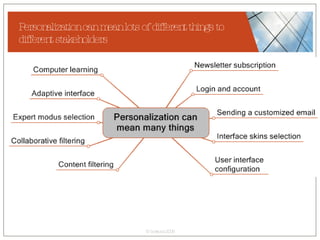
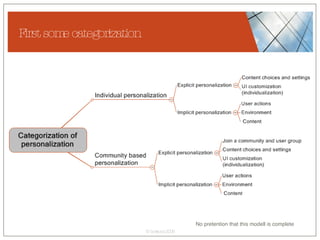
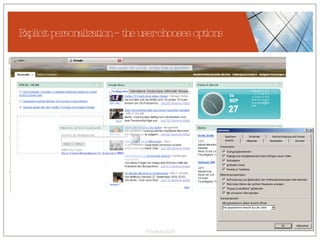
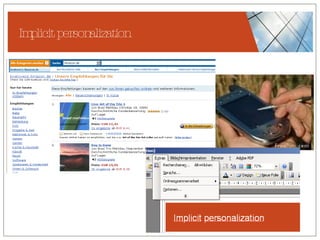
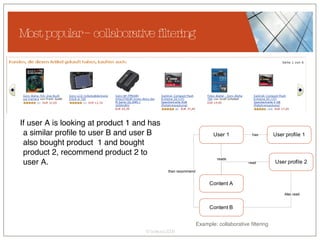
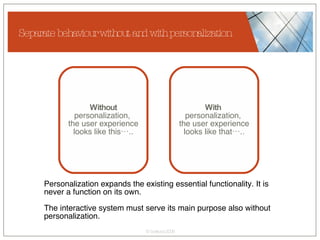
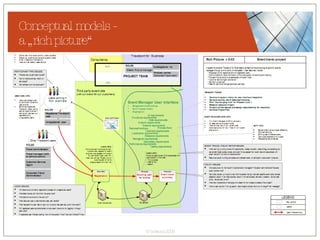
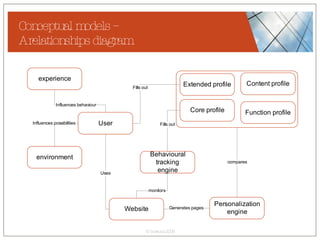
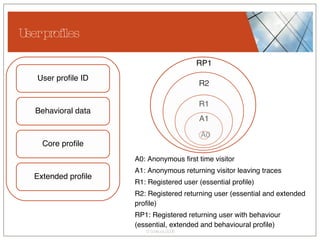
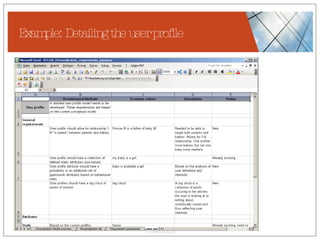
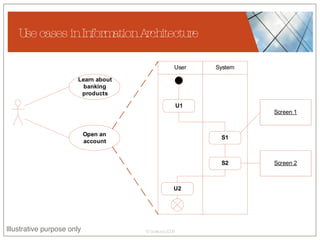
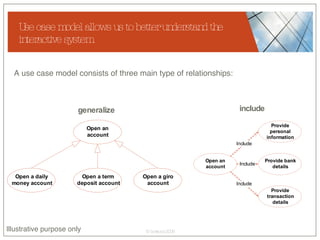
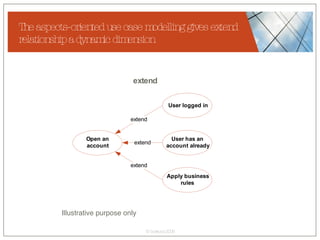
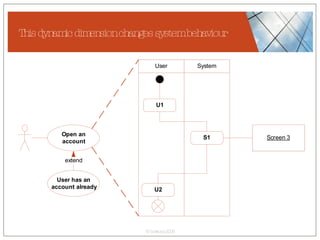
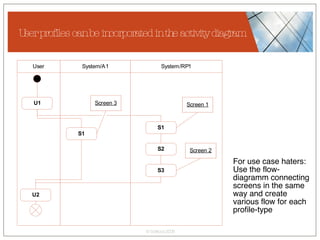
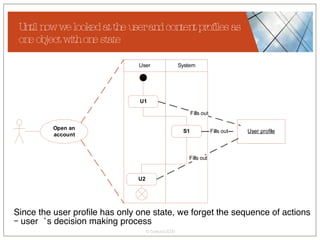
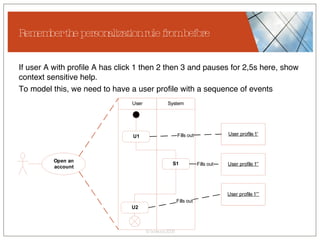
The document discusses conceptualizing personalization in information architecture. It covers personalization strategies, scenarios, profiles, use cases, rules, and architectural requirements. Personalization is modeled using various techniques like conceptual models, relationships diagrams, aspects-oriented use cases, and rules to specify conditions for personalization. Tracking user behavior over time and probabilistic models are discussed to enable adaptive interfaces. The key is to separately describe user experiences with and without personalization and align personalization with business goals.