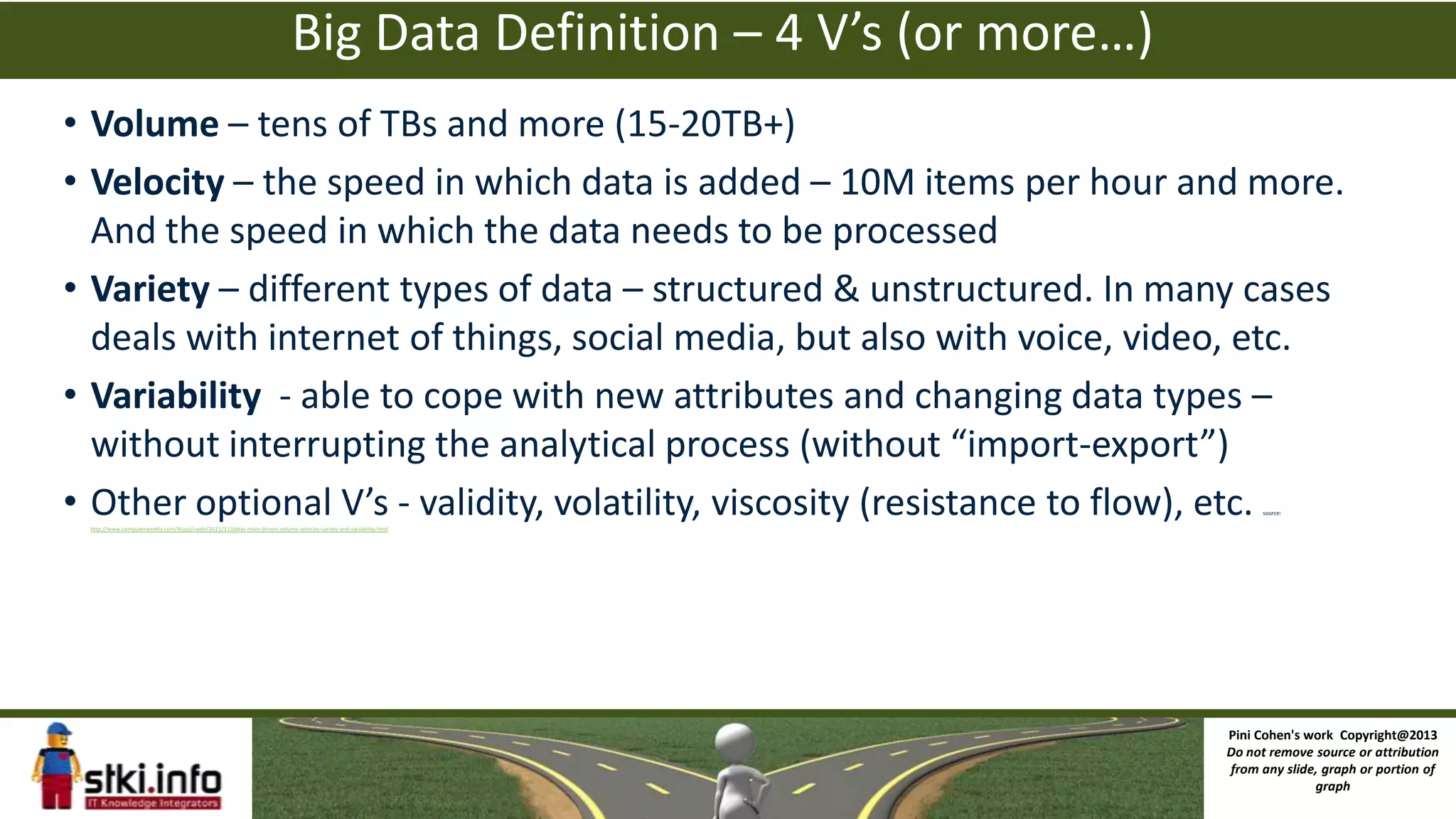
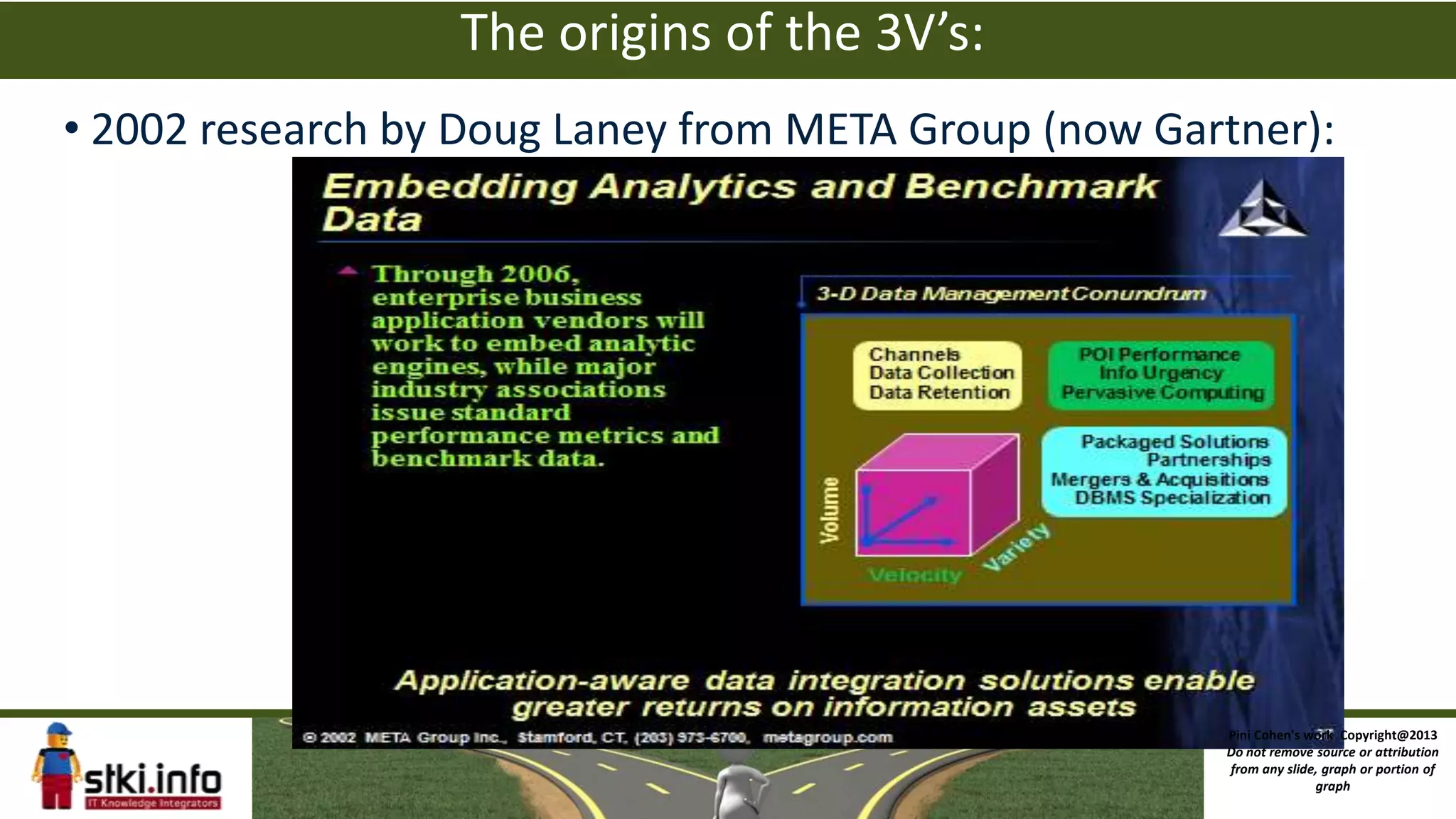
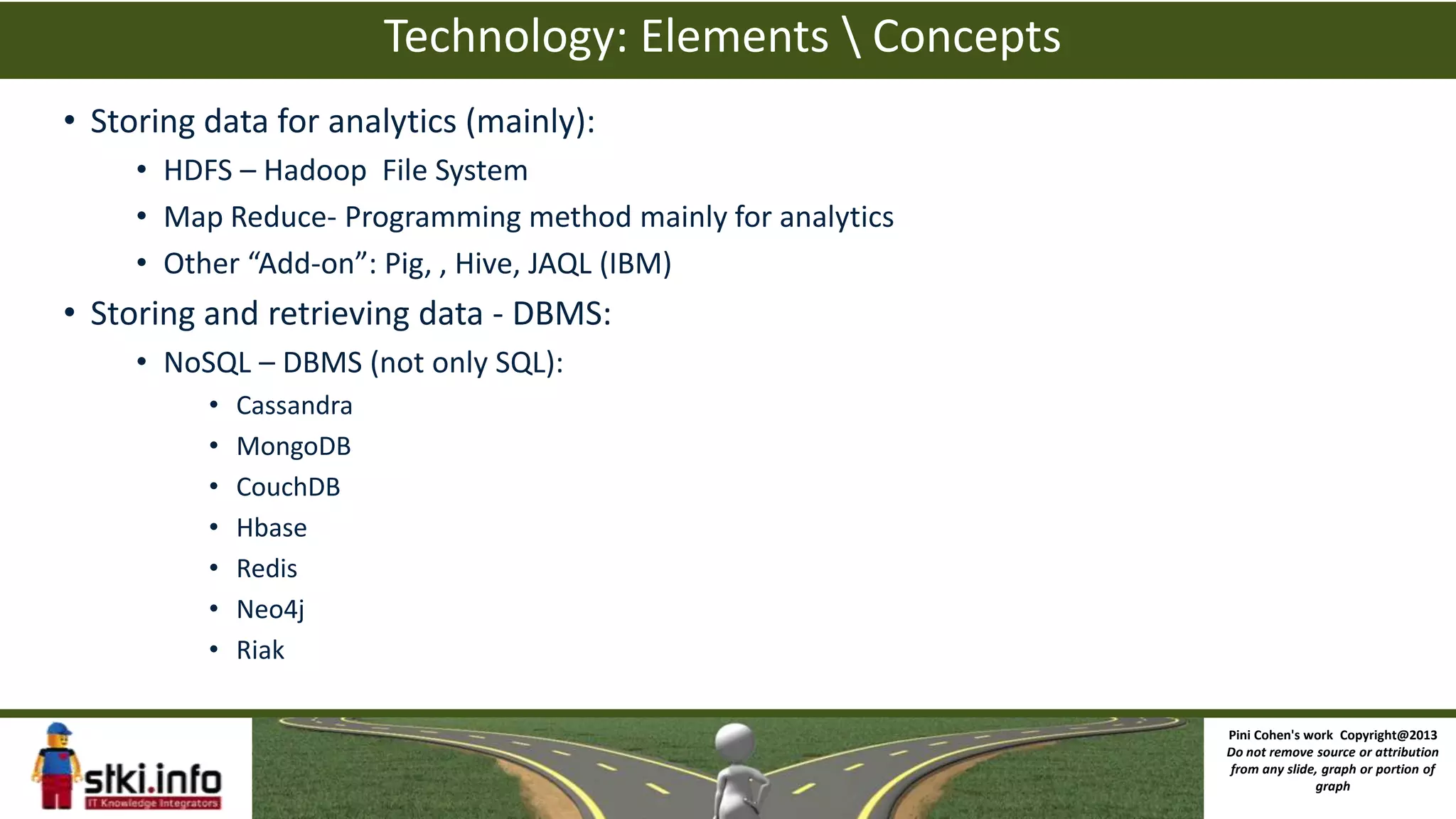
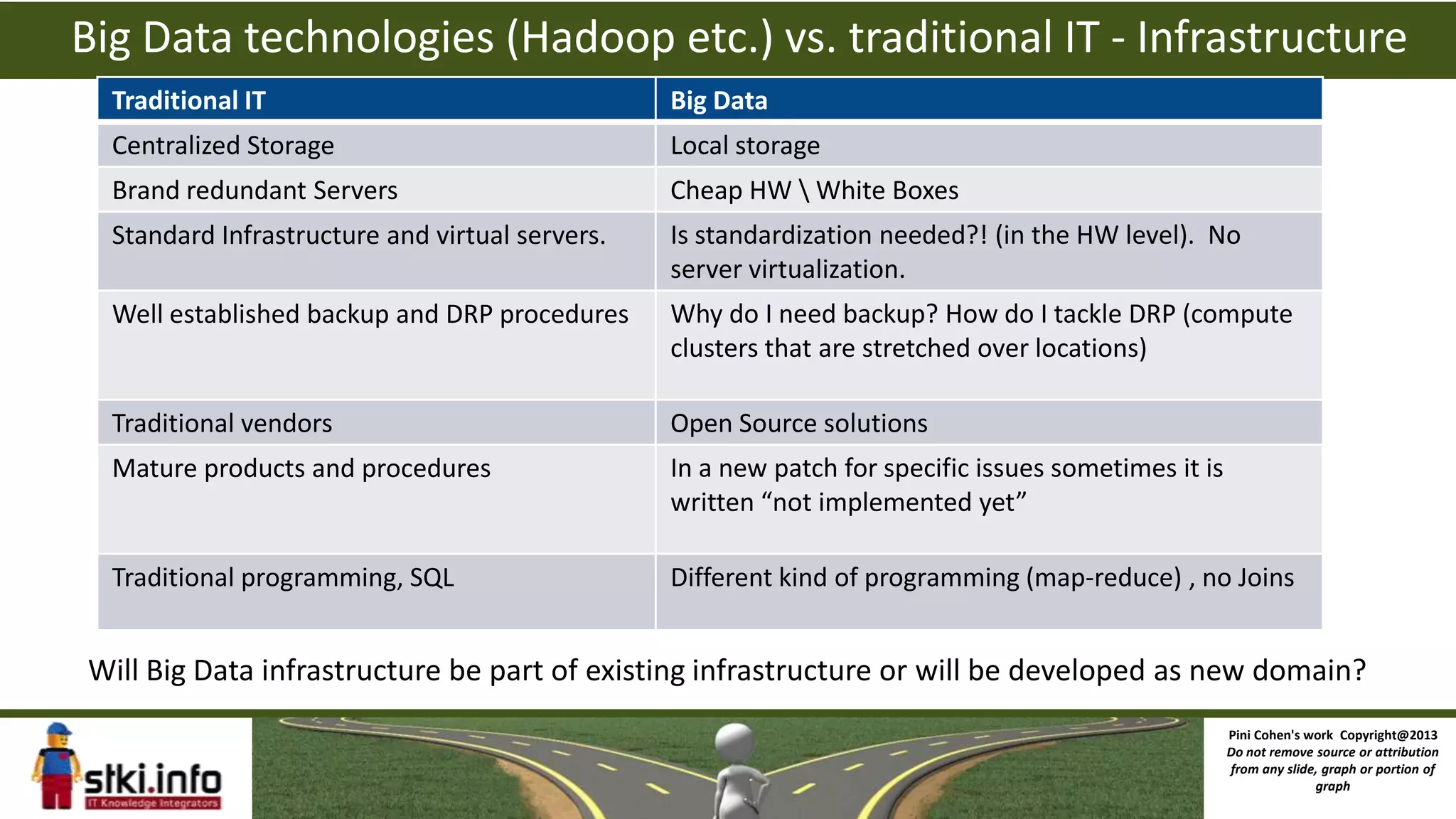
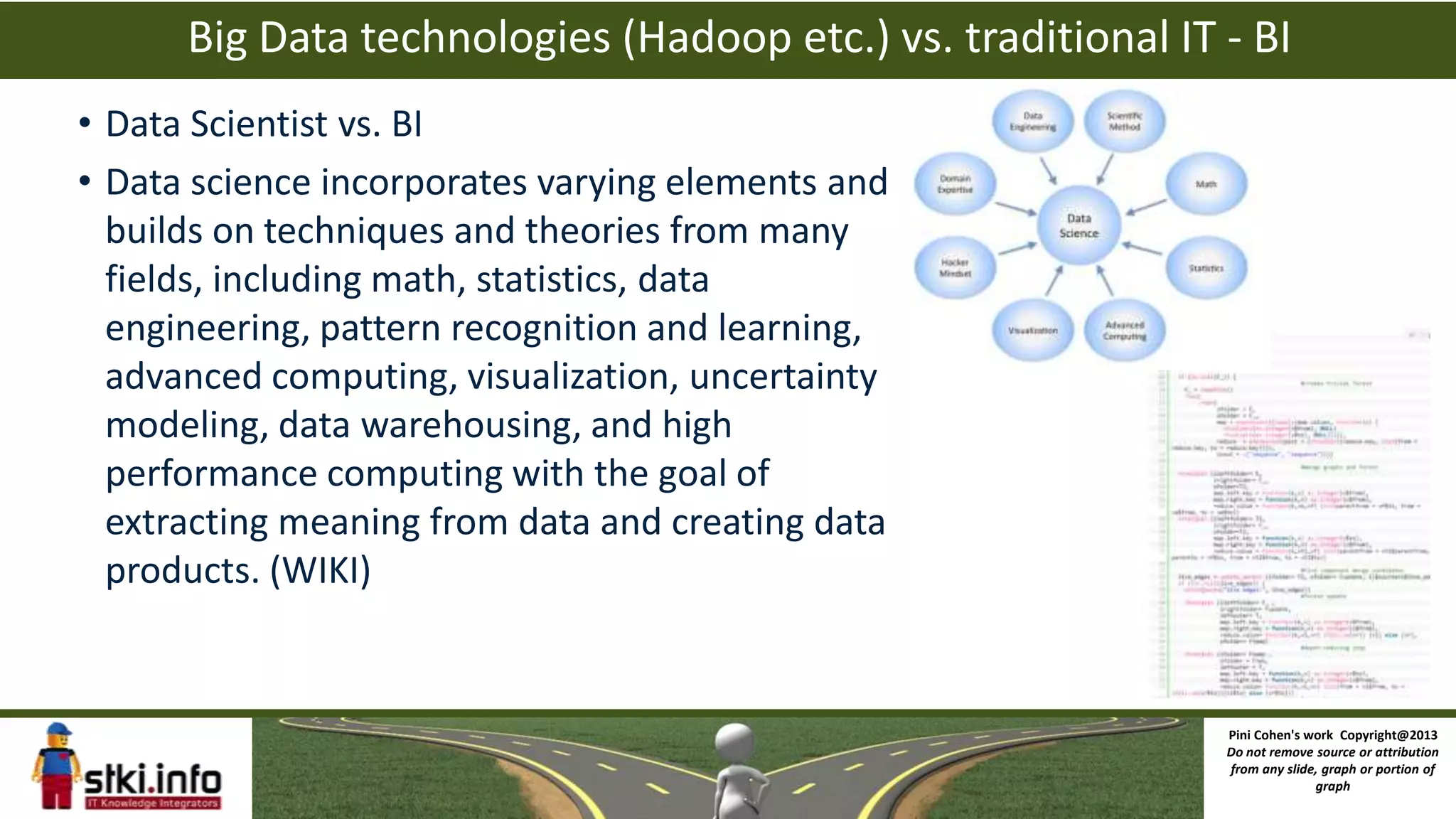
The document discusses big data and how it differs from traditional IT approaches. It defines big data using the four V's - volume, velocity, variety, and variability. Technologies used for big data like Hadoop, MapReduce, and NoSQL databases are outlined. Differences between big data infrastructure and traditional IT infrastructure and BI are explored. Examples of how Orbitz and the DoD use big data are provided. The business value of big data analytics is discussed as enabling new types of analysis and insights not previously possible.