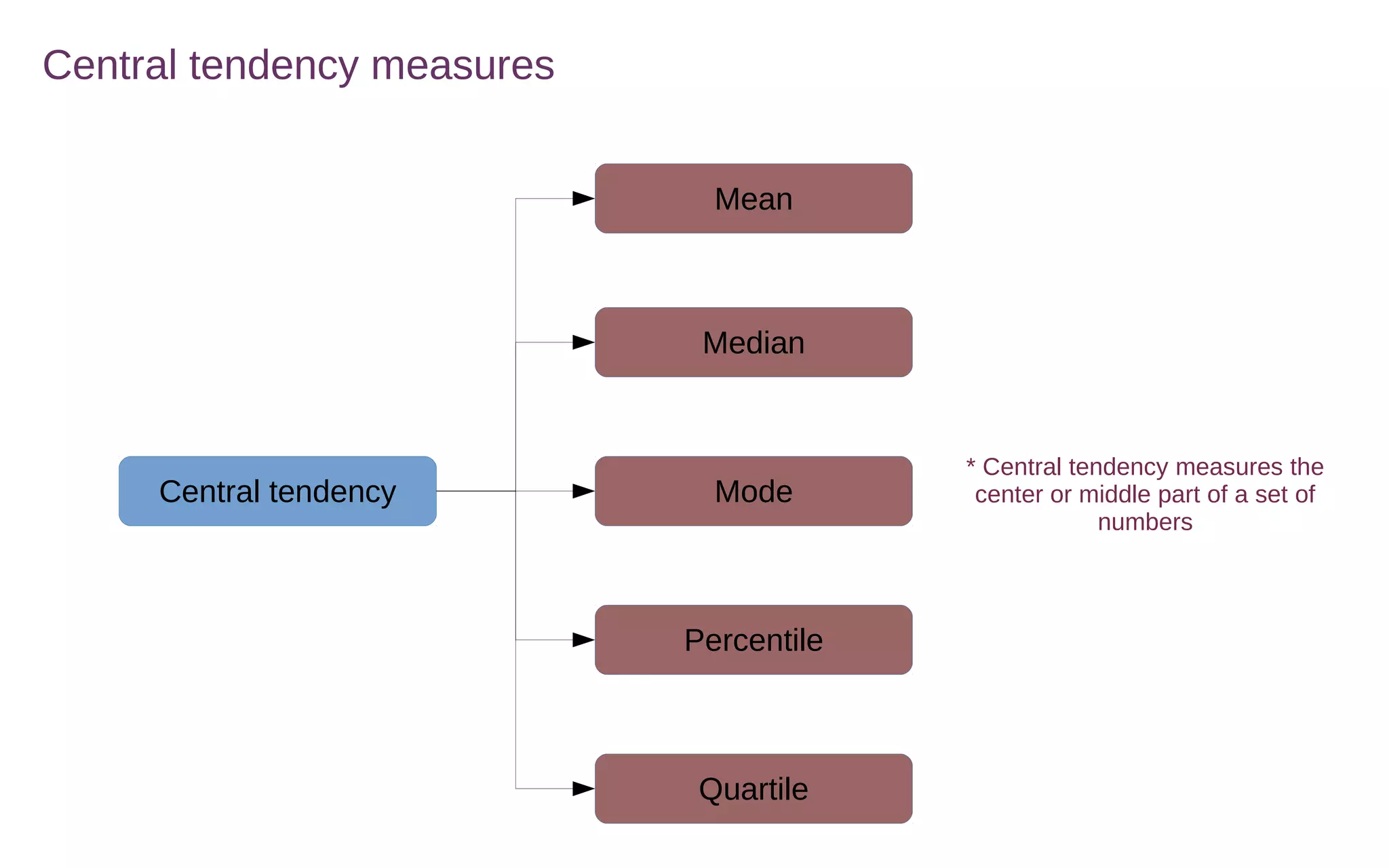
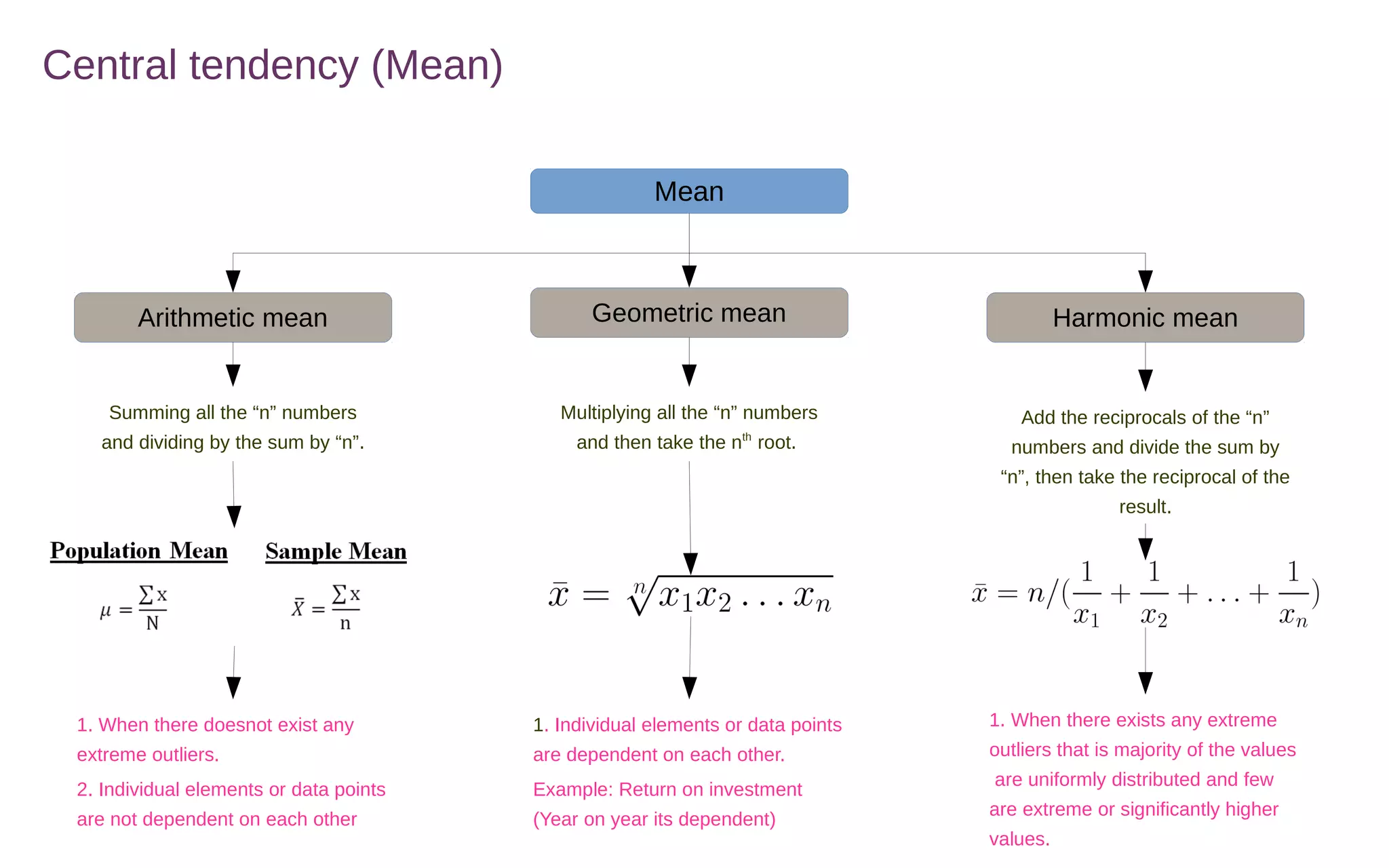
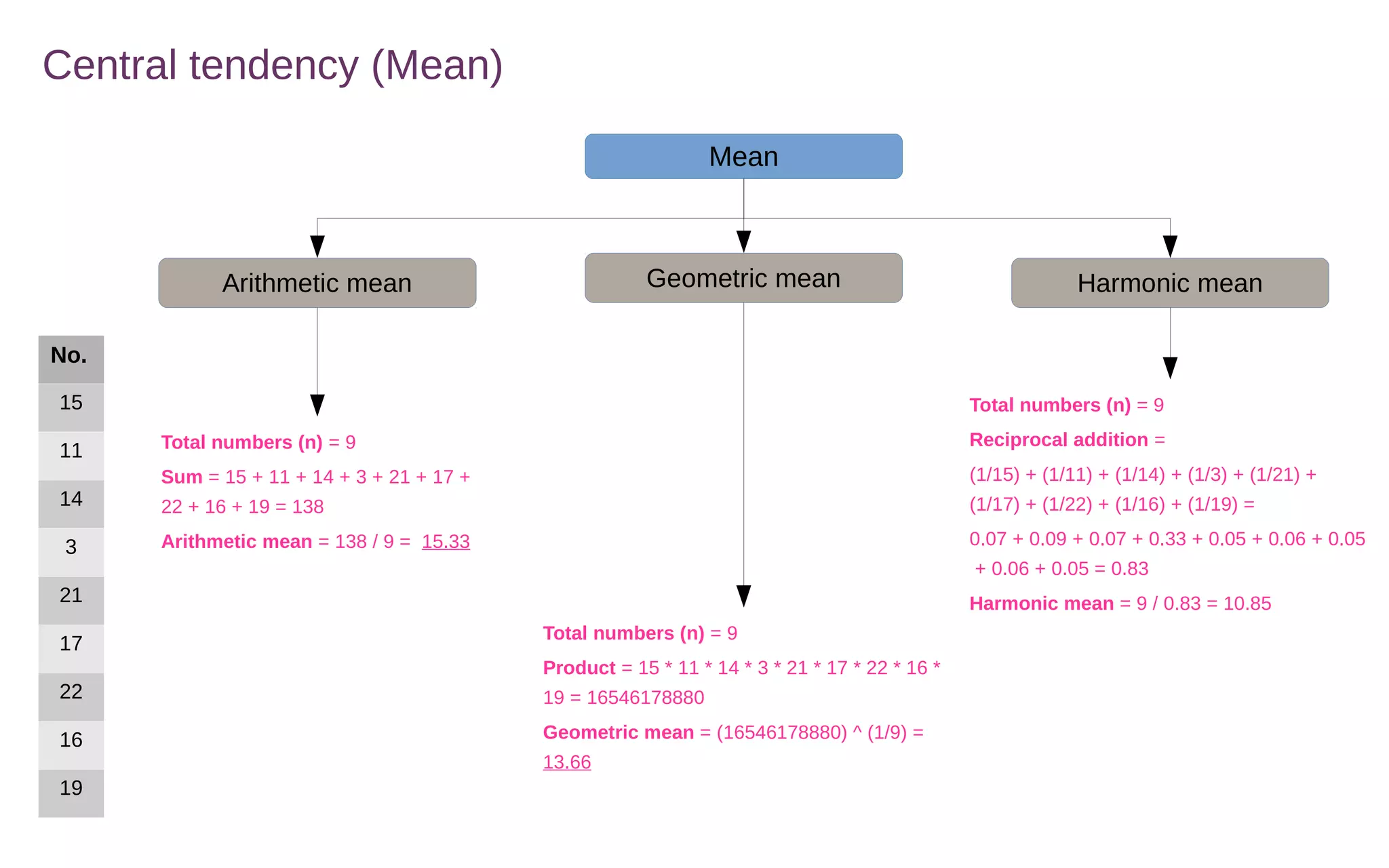
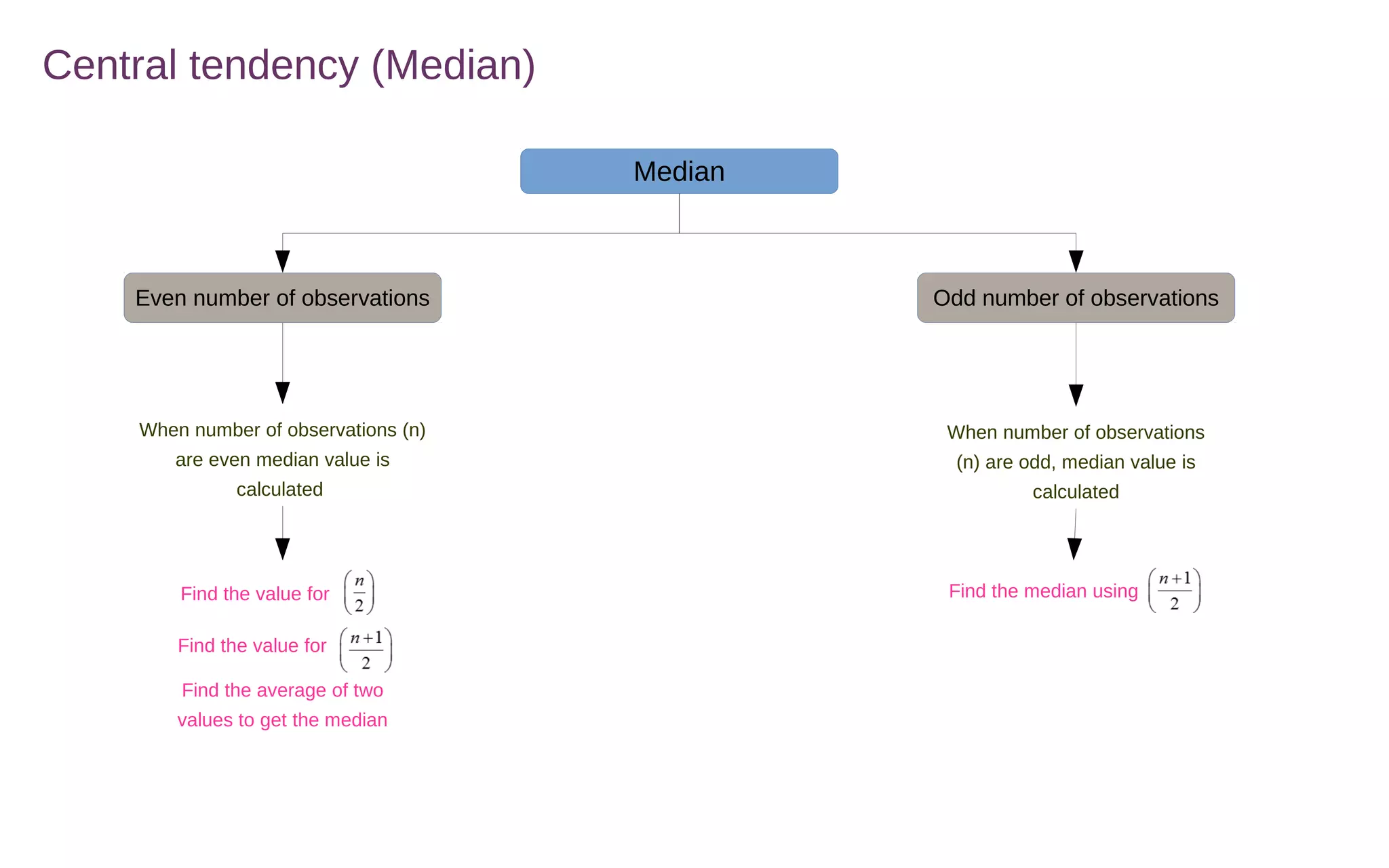
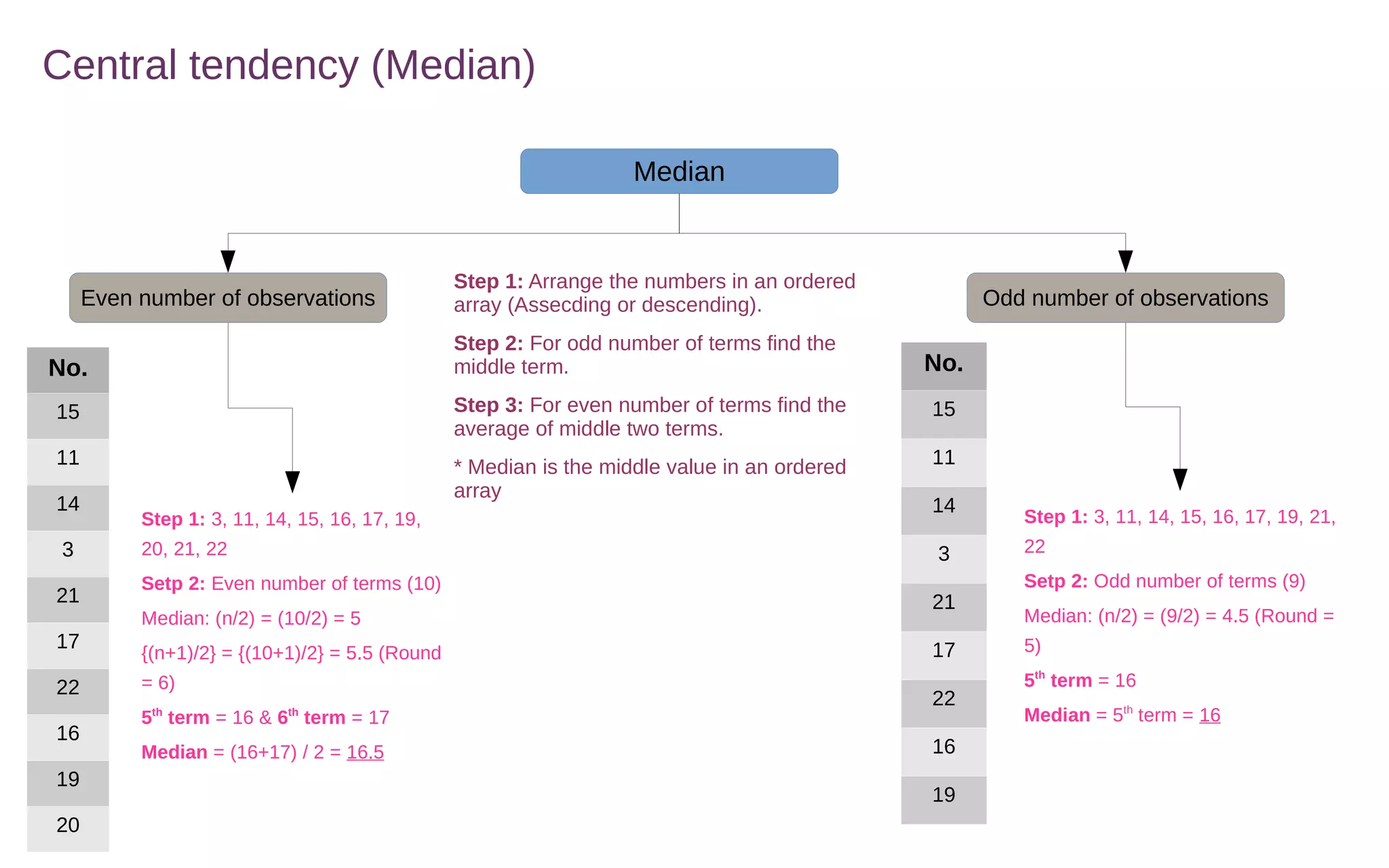
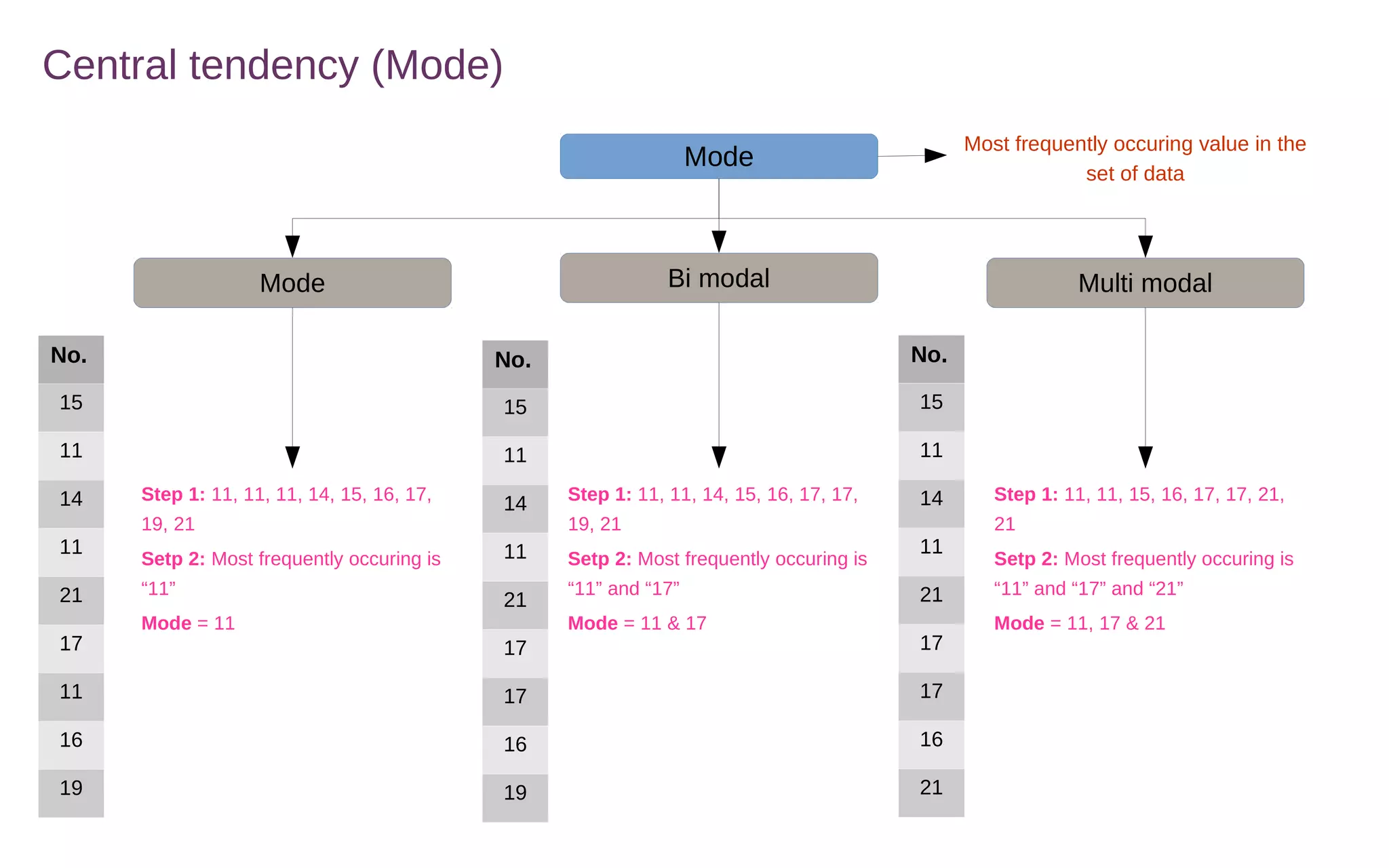
Central tendency measures describe the middle or center of a dataset. The three main measures are the mean, median, and mode.
The mean is calculated by adding all values and dividing by the total number of values. The median is the middle value of a sorted list of values. The mode is the most frequently occurring value.
Percentiles and quartiles divide a dataset into 100 and 4 equal parts, respectively. The 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles are called the first, second and third quartiles and describe the divisions of the data.