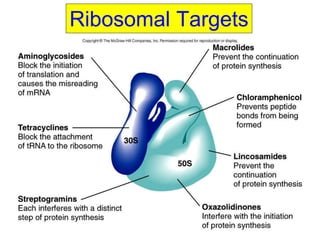
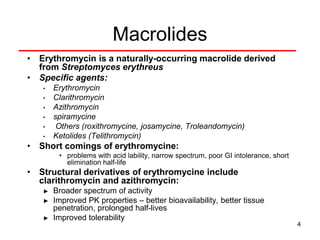
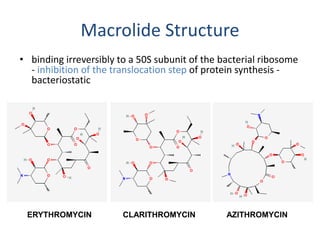
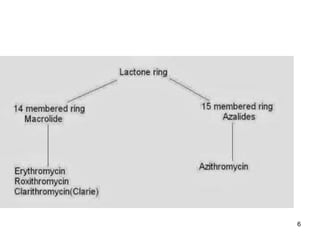
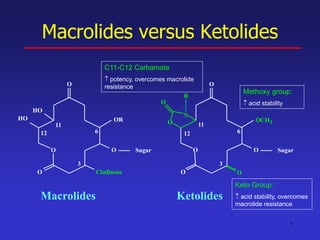
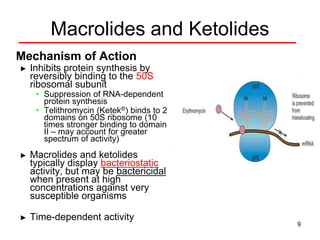
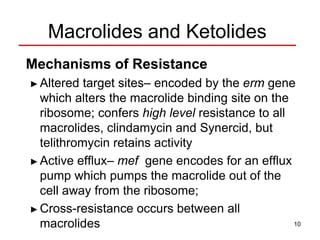
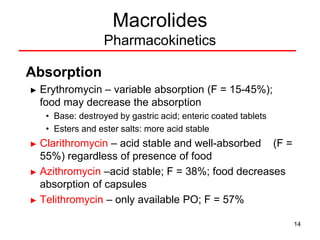
This document discusses macrolide antibiotics, including erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, and telithromycin. It describes their mechanisms of action as protein synthesis inhibitors that bind reversibly to the 50S ribosomal subunit. It outlines their spectra of activity against various gram-positive and -negative bacteria as well as atypical pathogens. It also covers their pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, adverse effects, drug interactions, and mechanisms of resistance.