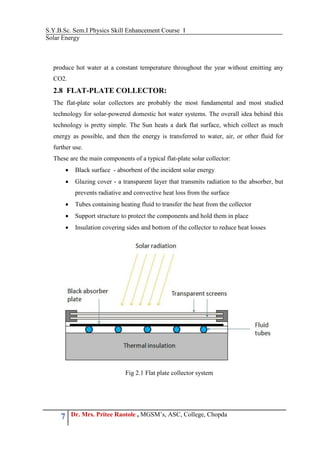
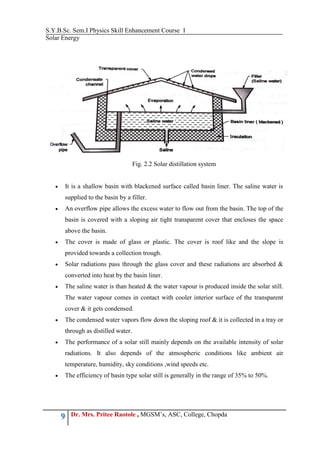
The document outlines a physics skill enhancement course focused on solar energy, covering topics such as photovoltaic systems, solar heating methods, and various types of solar applications including solar ponds and cookers. It emphasizes the environmental benefits of solar energy as a clean, renewable resource and provides details on energy storage techniques, particularly in photovoltaic systems. Practical applications of solar technology, such as solar water heating and distillation, are also discussed, highlighting their significance in sustainable energy practices.