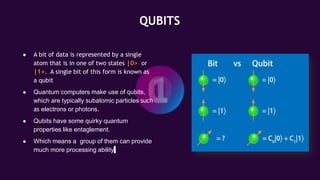
This document provides an overview of quantum computing. It discusses key concepts like qubits, superposition, and entanglement. Qubits can exist in superposition of states |0> and |1> allowing quantum computers to perform multiple calculations in parallel. Entanglement links the states of qubits. The document also covers applications in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. Quantum cryptography uses principles of quantum mechanics for encryption but has limitations like short communication ranges and high costs.