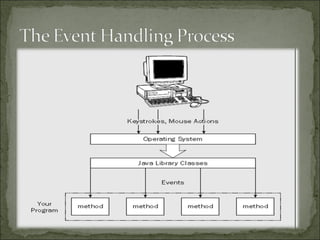
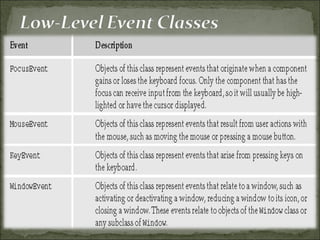
The document discusses event handling in Java, describing different types of events like window, mouse, and keyboard events. It explains the event handling process and different event classes. Various listener interfaces are described that can be implemented to handle specific events, such as WindowListener, MouseListener, and KeyListener.