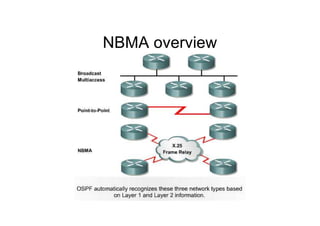
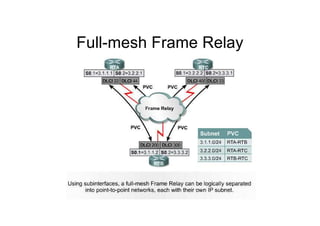
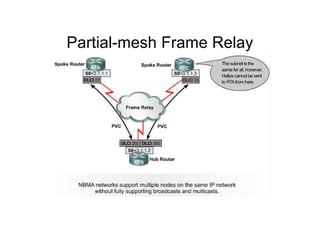
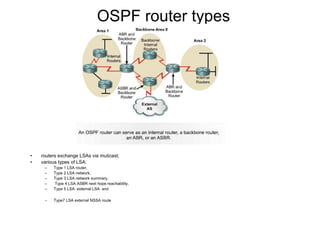
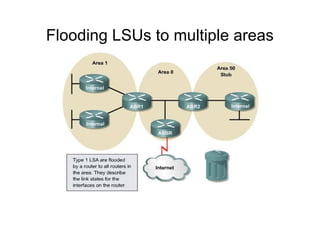
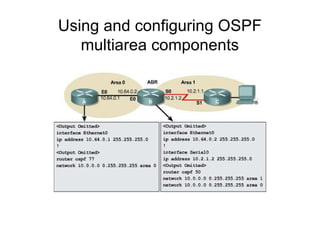
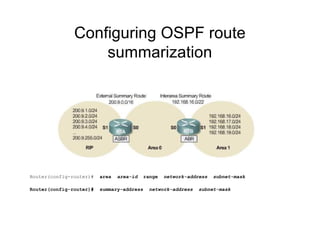
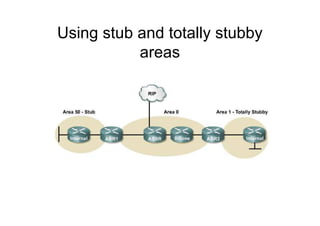
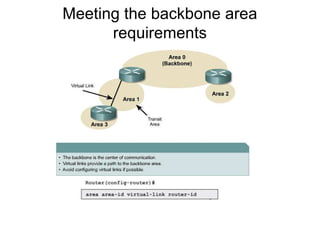
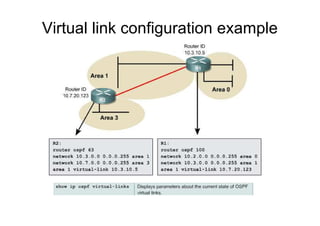
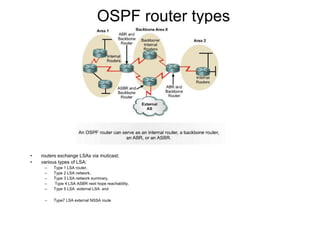
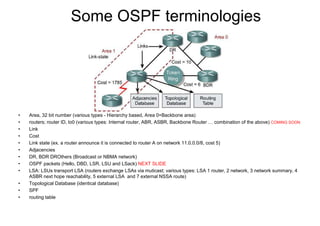
This document provides an overview of OSPF including terminology, router types, link state advertisements (LSAs), network types, and the steps of OSPF operation. It discusses establishing adjacencies, electing designated routers, discovering routes, selecting routes, and maintaining routing information. It also covers configuring and verifying OSPF within a single area, over non-broadcast multi-access (NBMA) networks, and across multiple areas. Special area types like stub, totally stubby, and not-so-stubby areas are explained as well as using virtual links.









![Optional configuration commands
(continued)
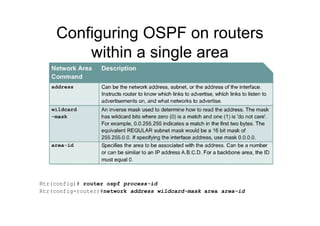
CISCO Routers use the formula = 108/bandwidth
Rtr(config-if)# bandwidth 64 = Rtr(config-if)# ip ospf cost 1562
Rtr(config-if)# bandwidth kilobits
Rtr(config-if)# ip ospf authentication-key passwd
Rtr(config-router)# area “area” authentication
Rtr(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key key-id md5 password
Rtr(config-router)# area area authentication [message-digest]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20407473-ospf-170422234506/85/20407473-ospf-19-320.jpg)