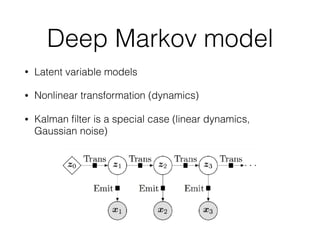
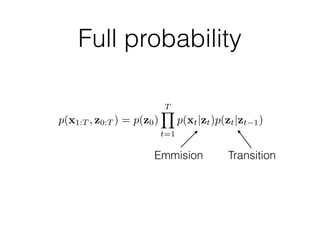
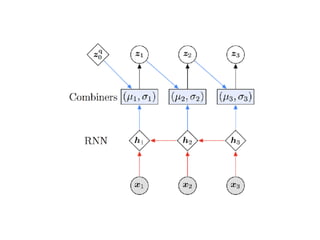
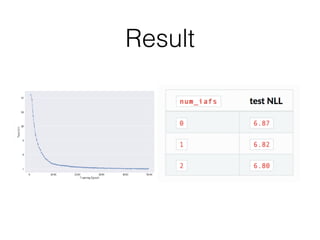
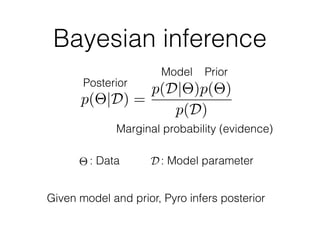
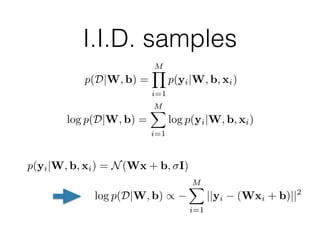
Probabilistic programming with Pyro (1) introduces Pyro, a probabilistic programming language based on PyTorch that allows defining probabilistic models and performing Bayesian inference; (2) discusses Bayesian modeling and inference using linear regression as an example; (3) presents an example of using Pyro to build a deep Markov model for modeling music sequences.






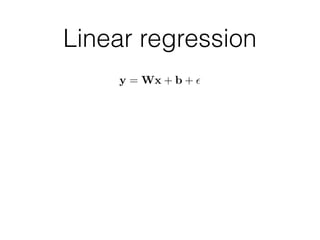
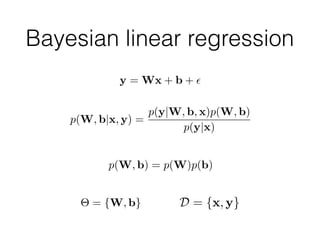

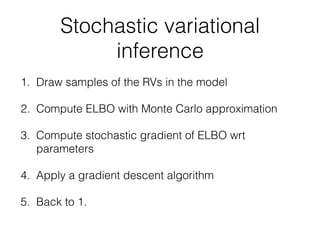
![Posterior approximation
• Referred to as variational distribution (‘guide’ in Pyro)
• Minimize wrt
p(W, b|D) ⇡ q (W, b)
p(W, b|D) ⇡ q W
(W)q b
(b)Simple version
KL [q (W, b)||p(W, b|D)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180722-pyro-180722015547/85/20180722-pyro-14-320.jpg)
![Evidence lower bound
(ELBO)
L( ) = Eq (⇥) [log p(D, ⇥) log q (⇥)]
= log p(D) KL [q (W, b)||p(W, b|D)]
log p(D)
Maximizing ELBO implies minimizing KL-divergence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180722-pyro-180722015547/85/20180722-pyro-15-320.jpg)
![Monte Carlo (MC)
approximation
Eq (⇥) [log p(D, ⇥) log q (⇥)]
= N 1
NX
i=1
[log p(D, ⇥i) log q (⇥i)] ⇥i ⇠ q (⇥i)
• Reparametrization is applied to reduce the variance of
stochastic gradient: https://stats.stackexchange.com/
questions/199605](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180722-pyro-180722015547/85/20180722-pyro-16-320.jpg)