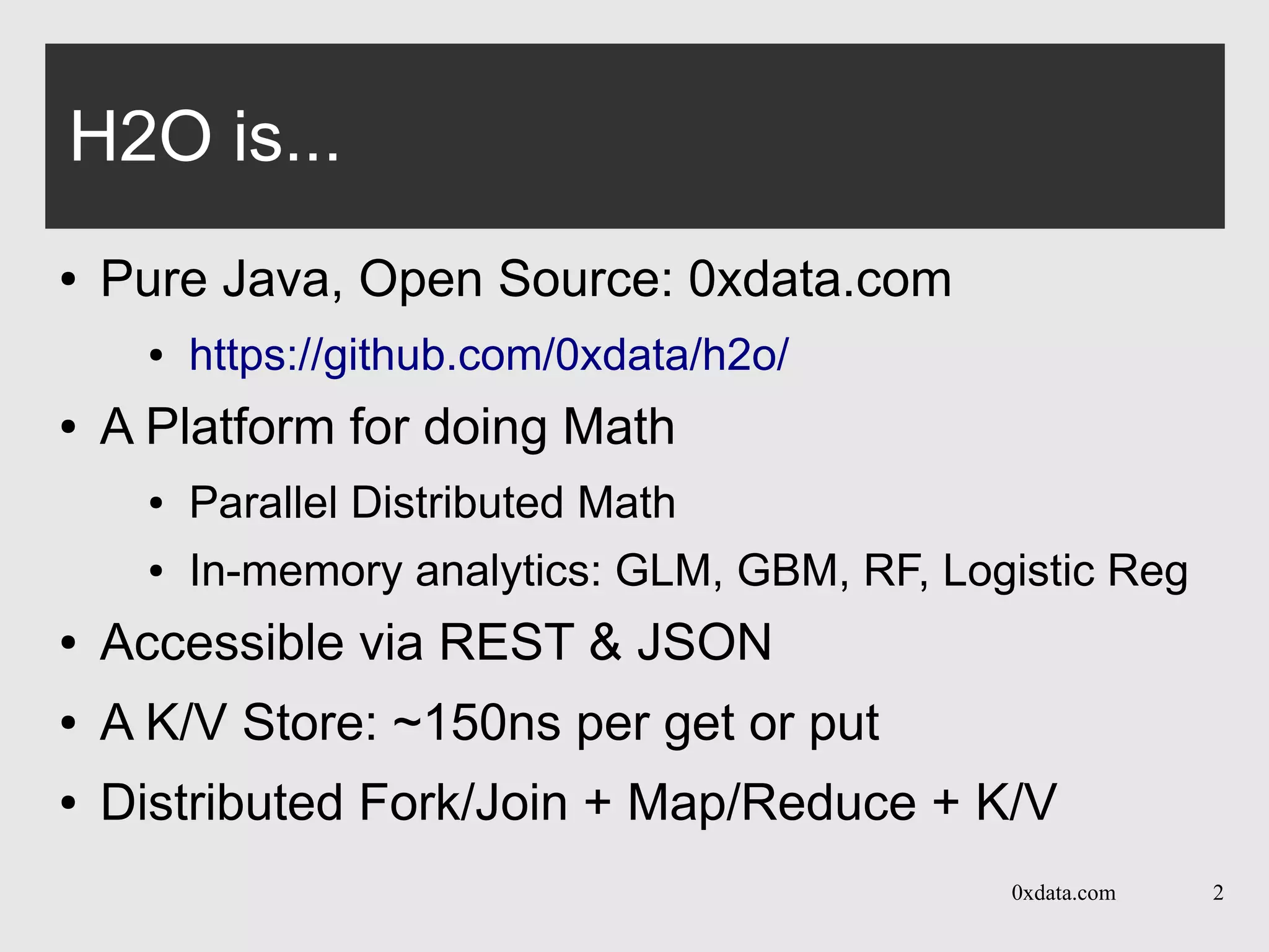
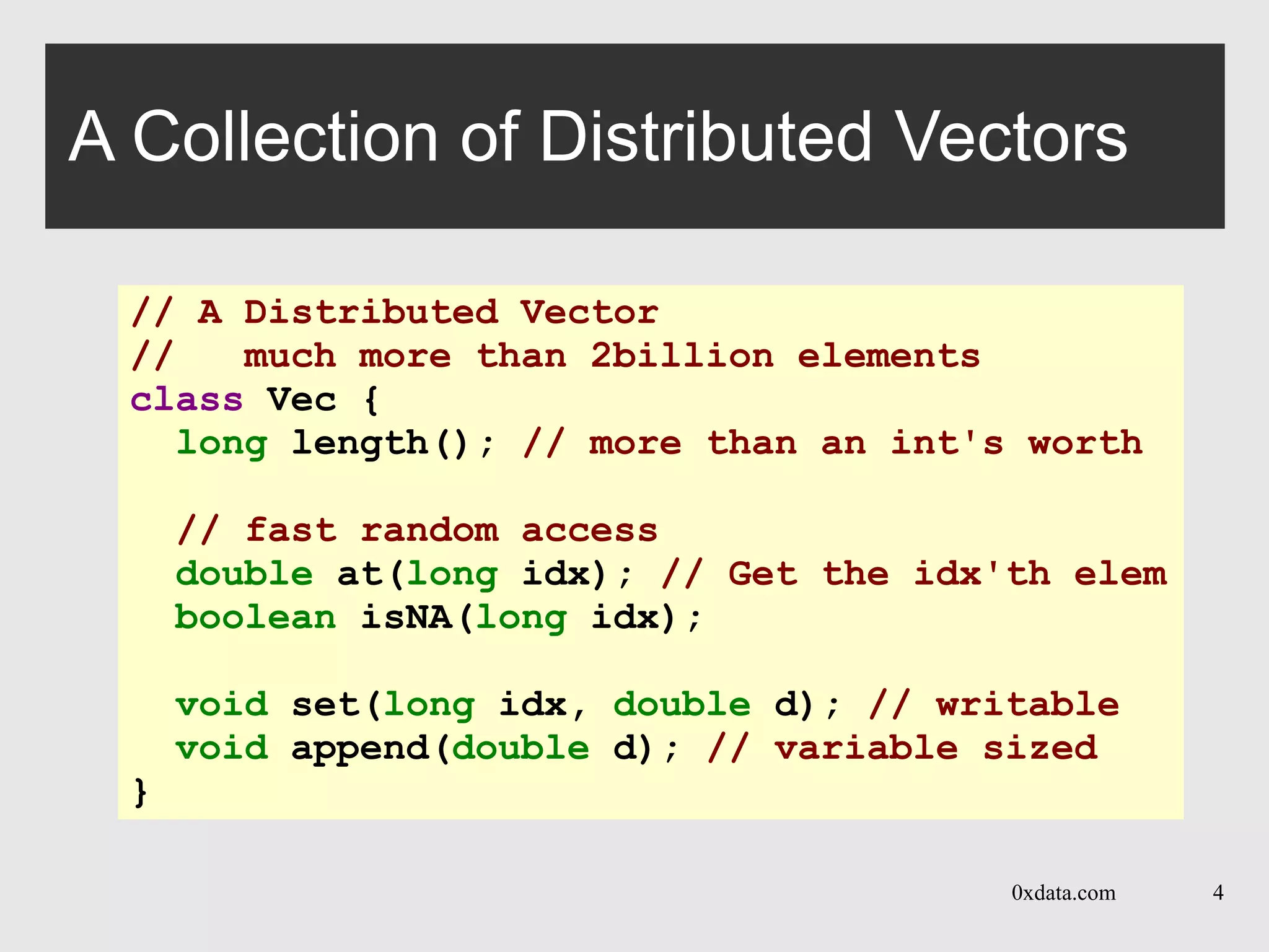
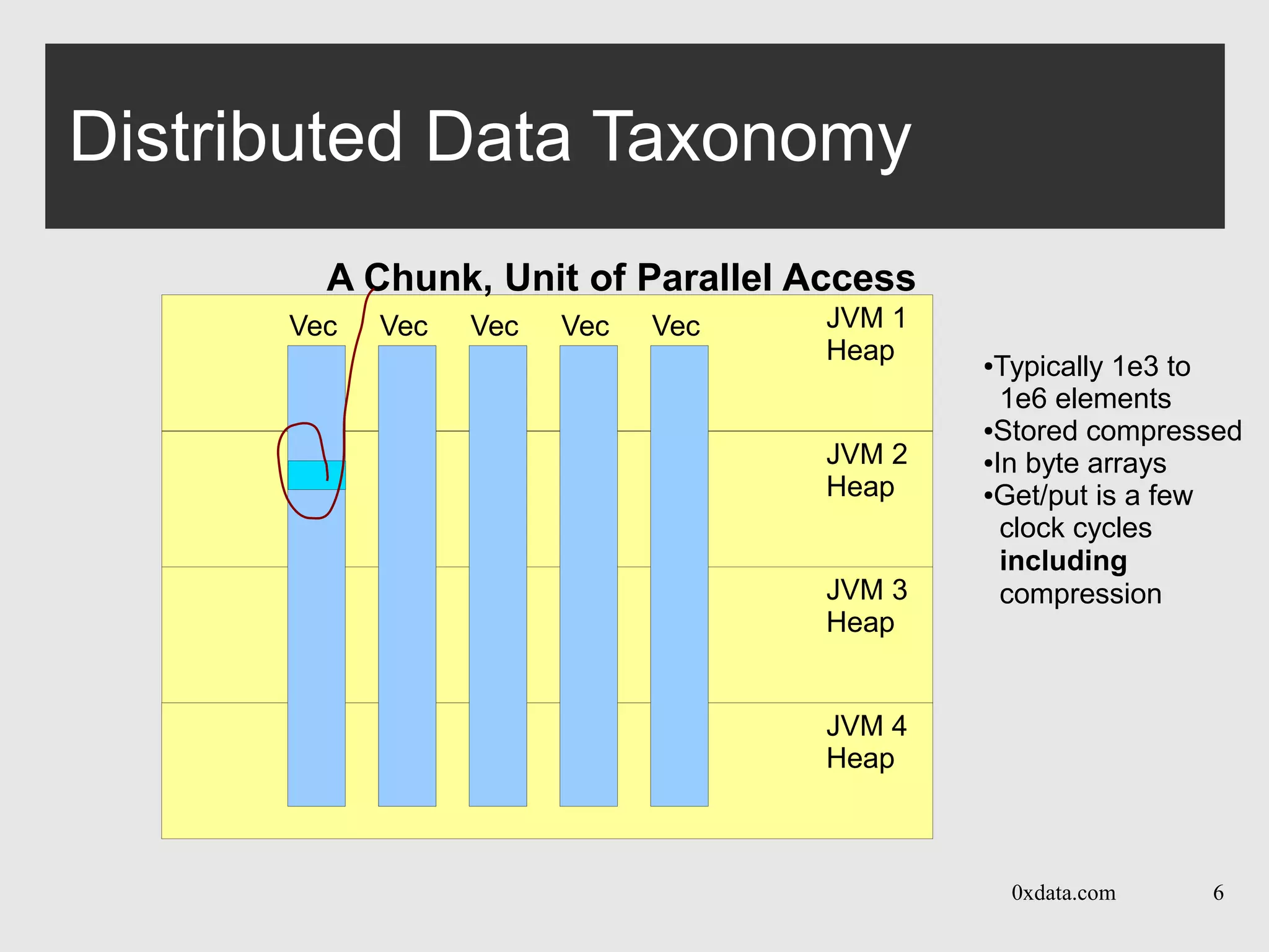
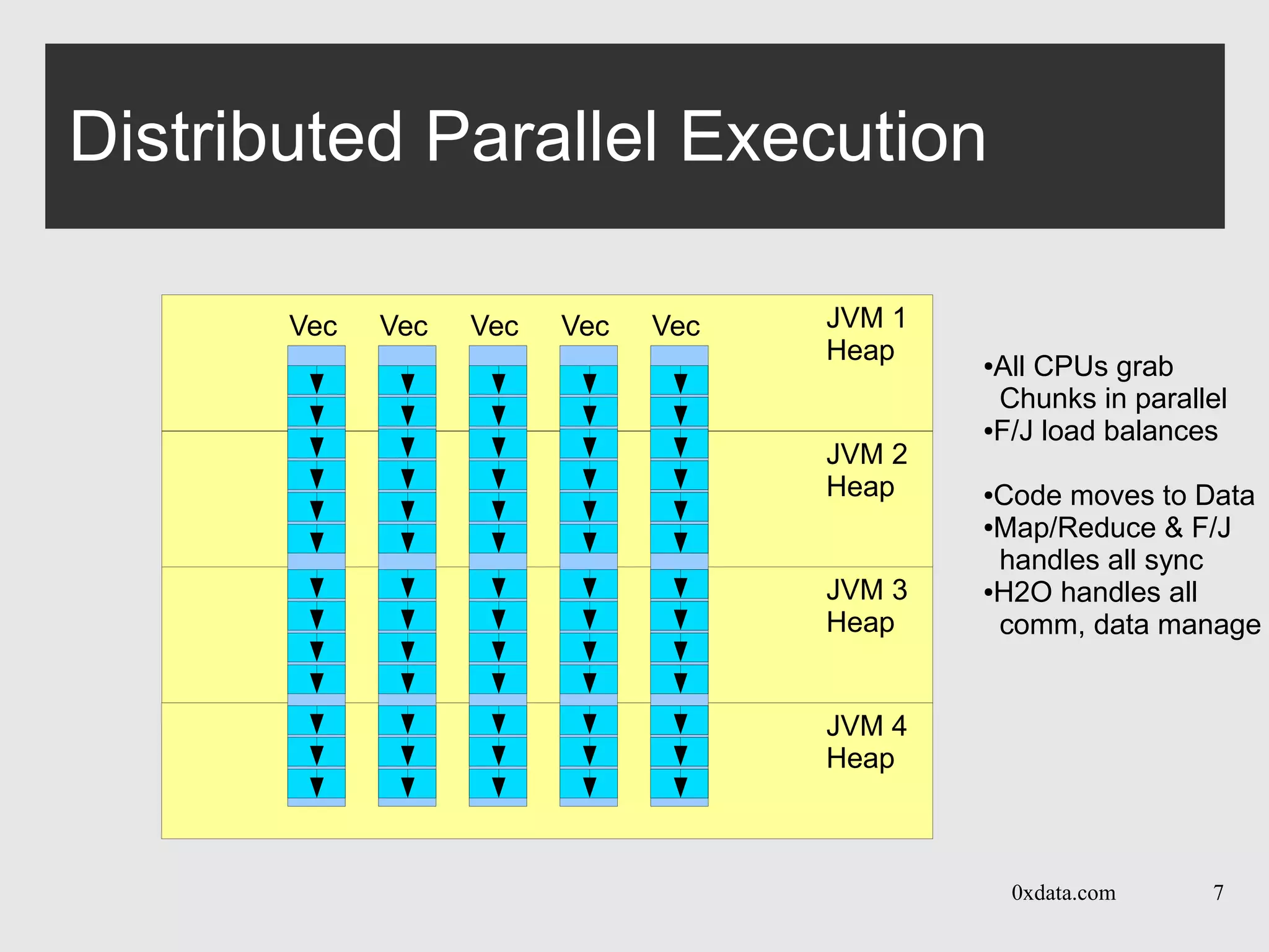
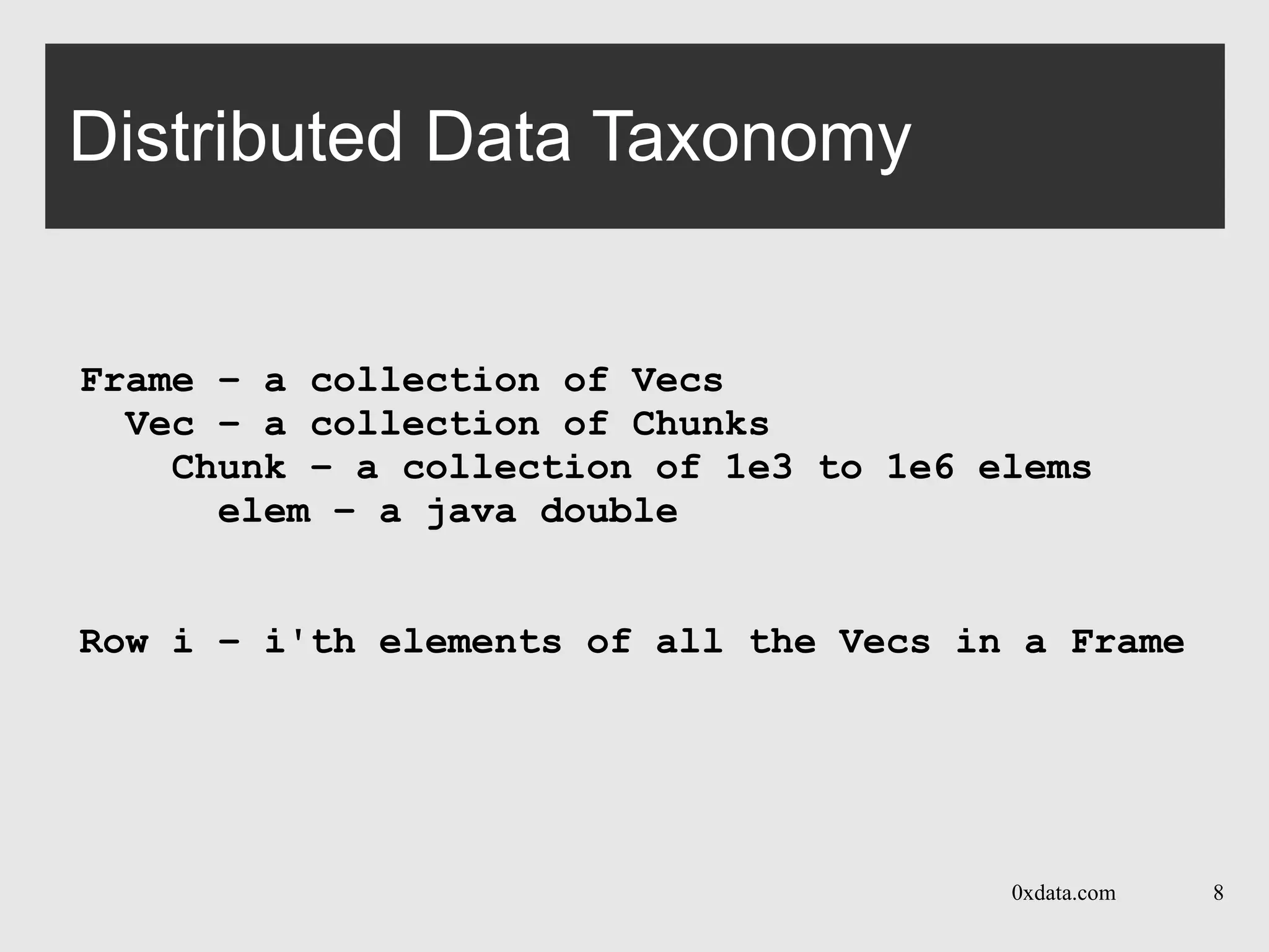
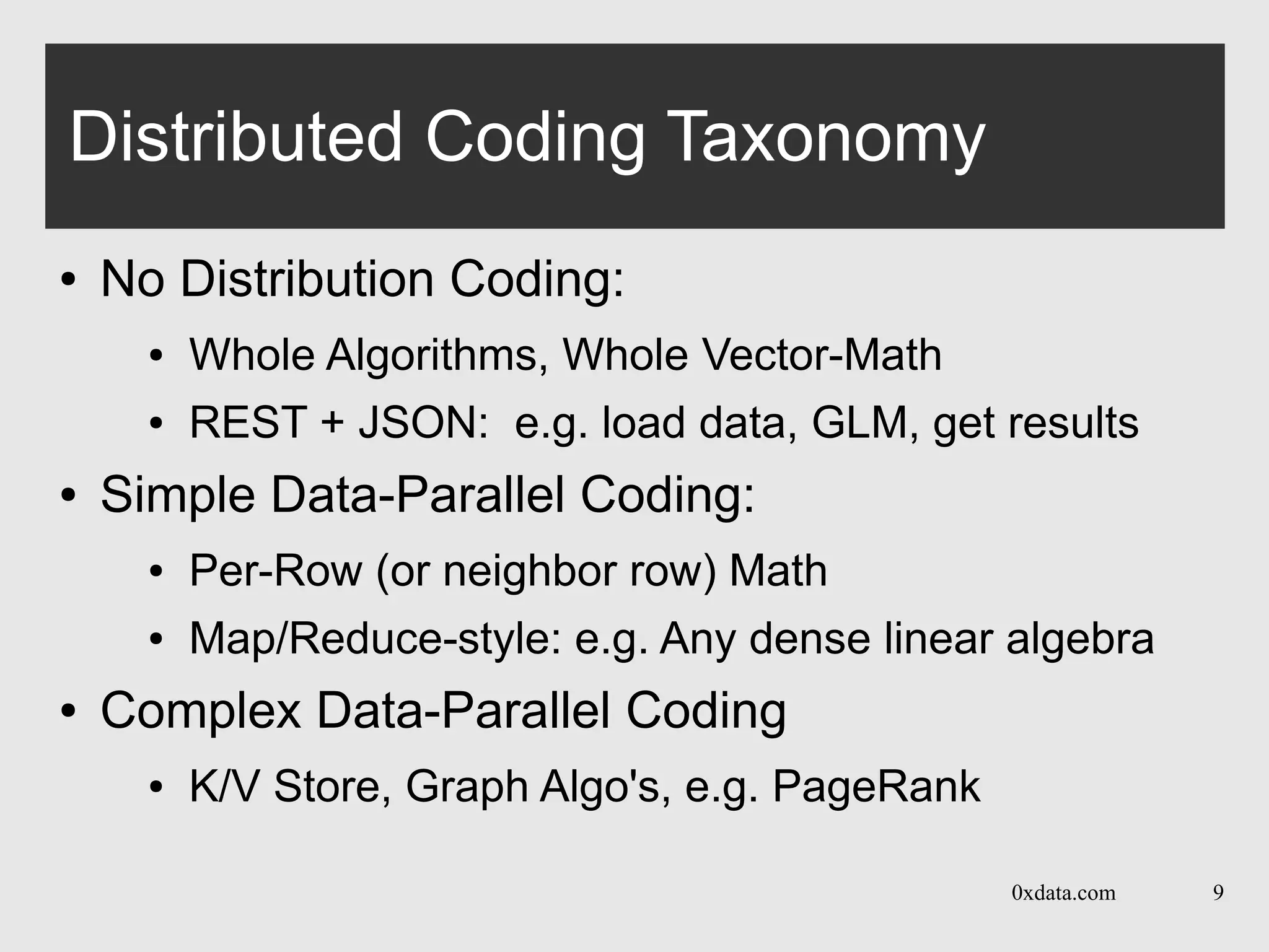
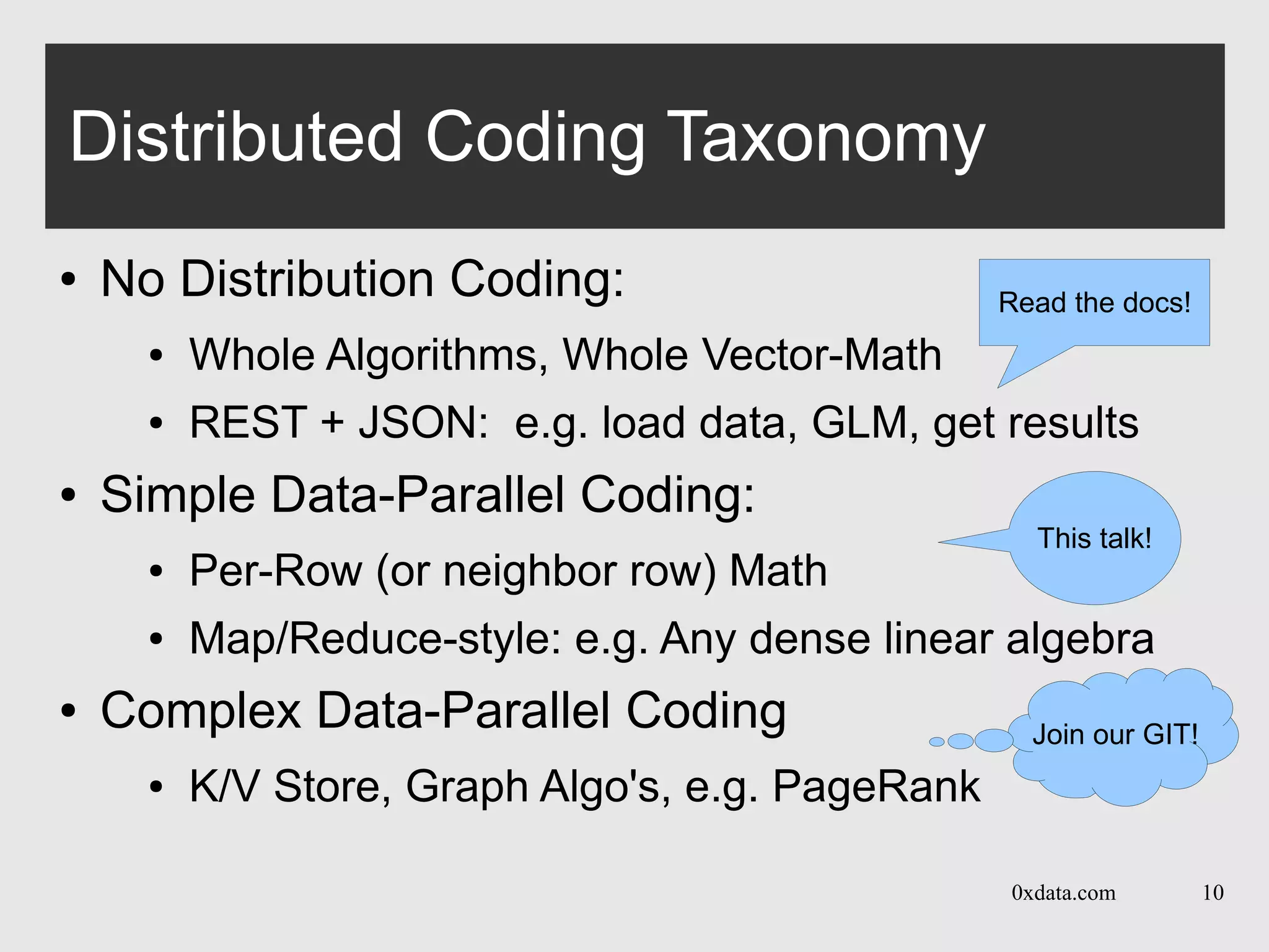
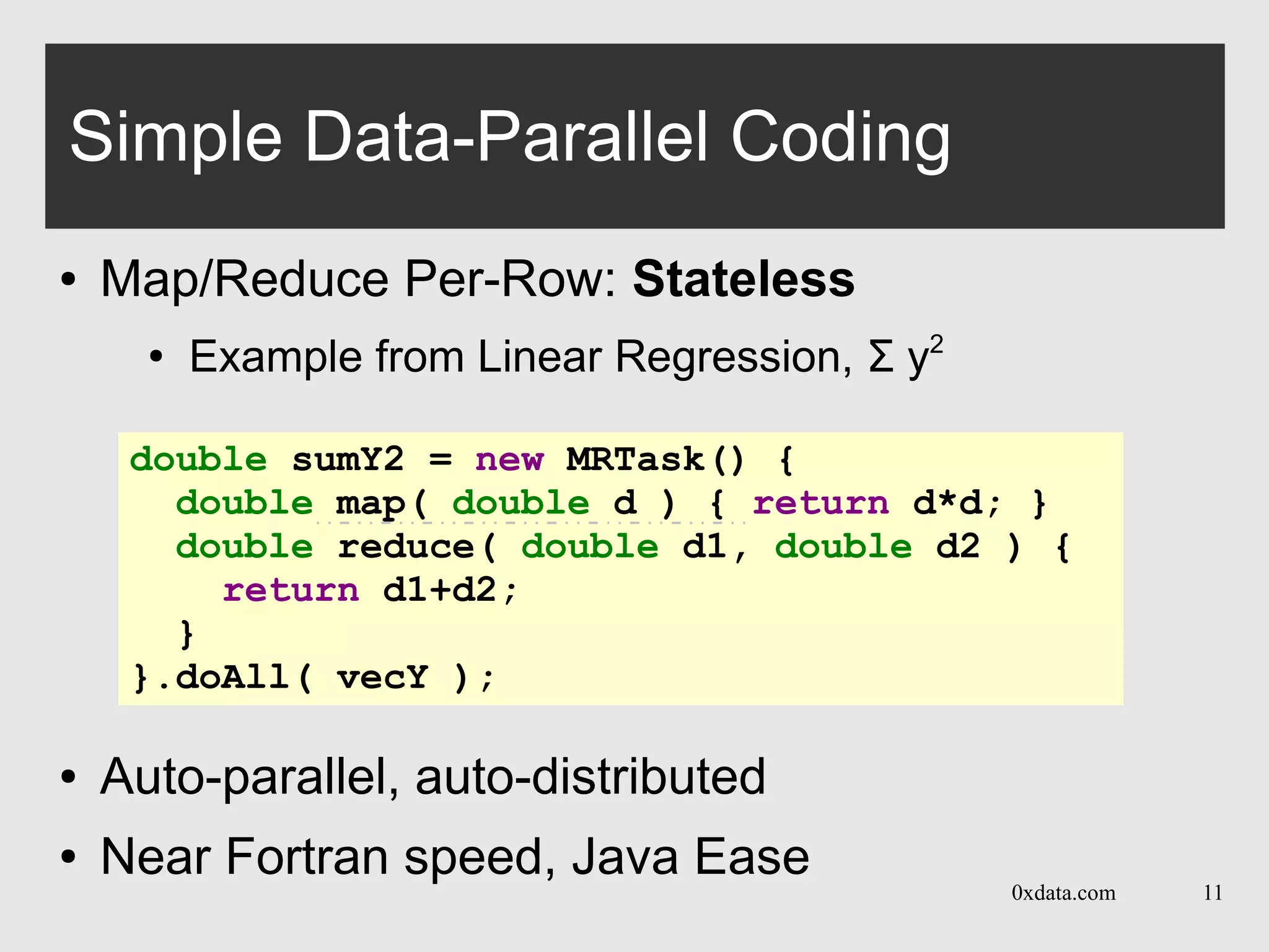
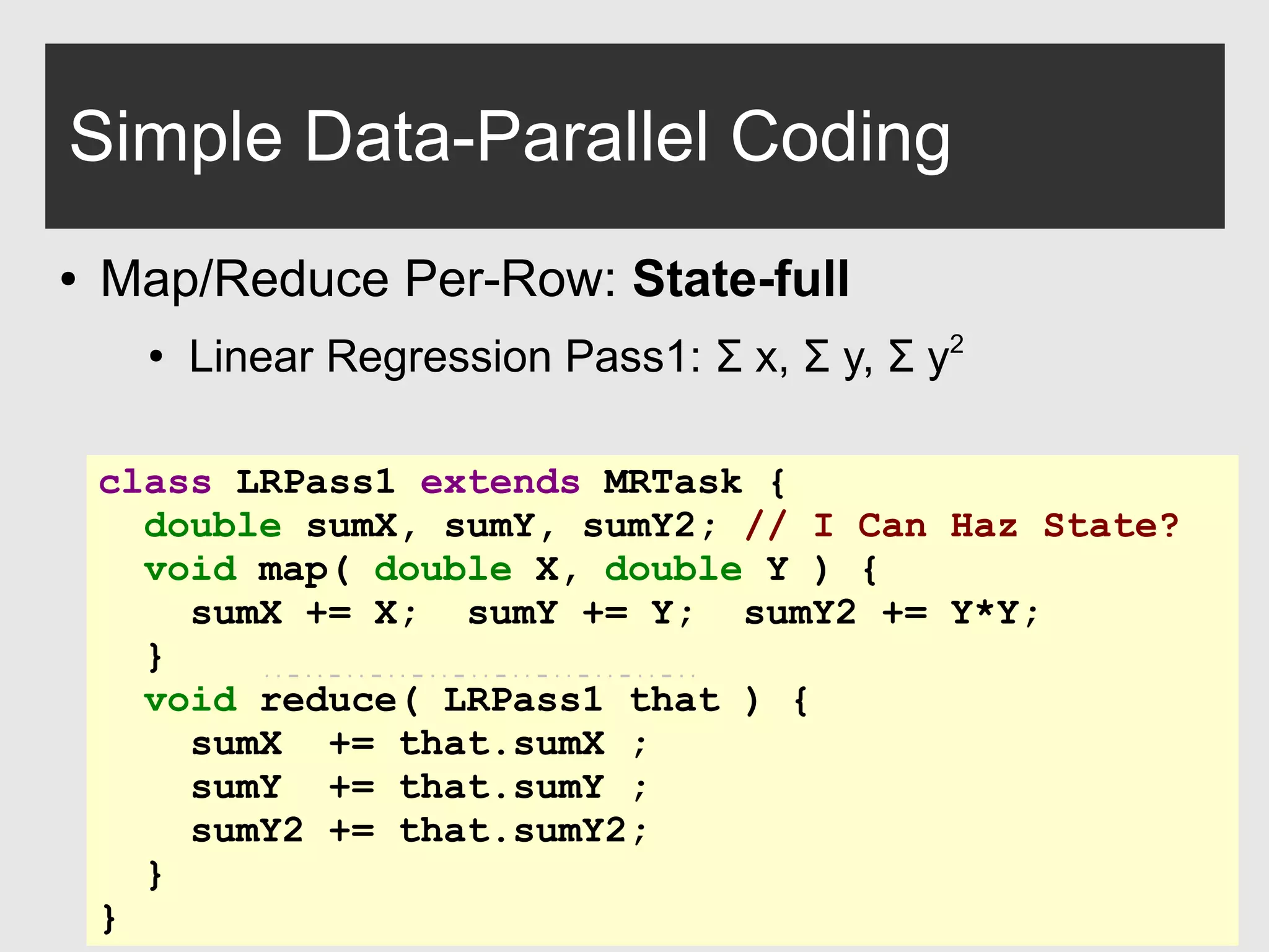
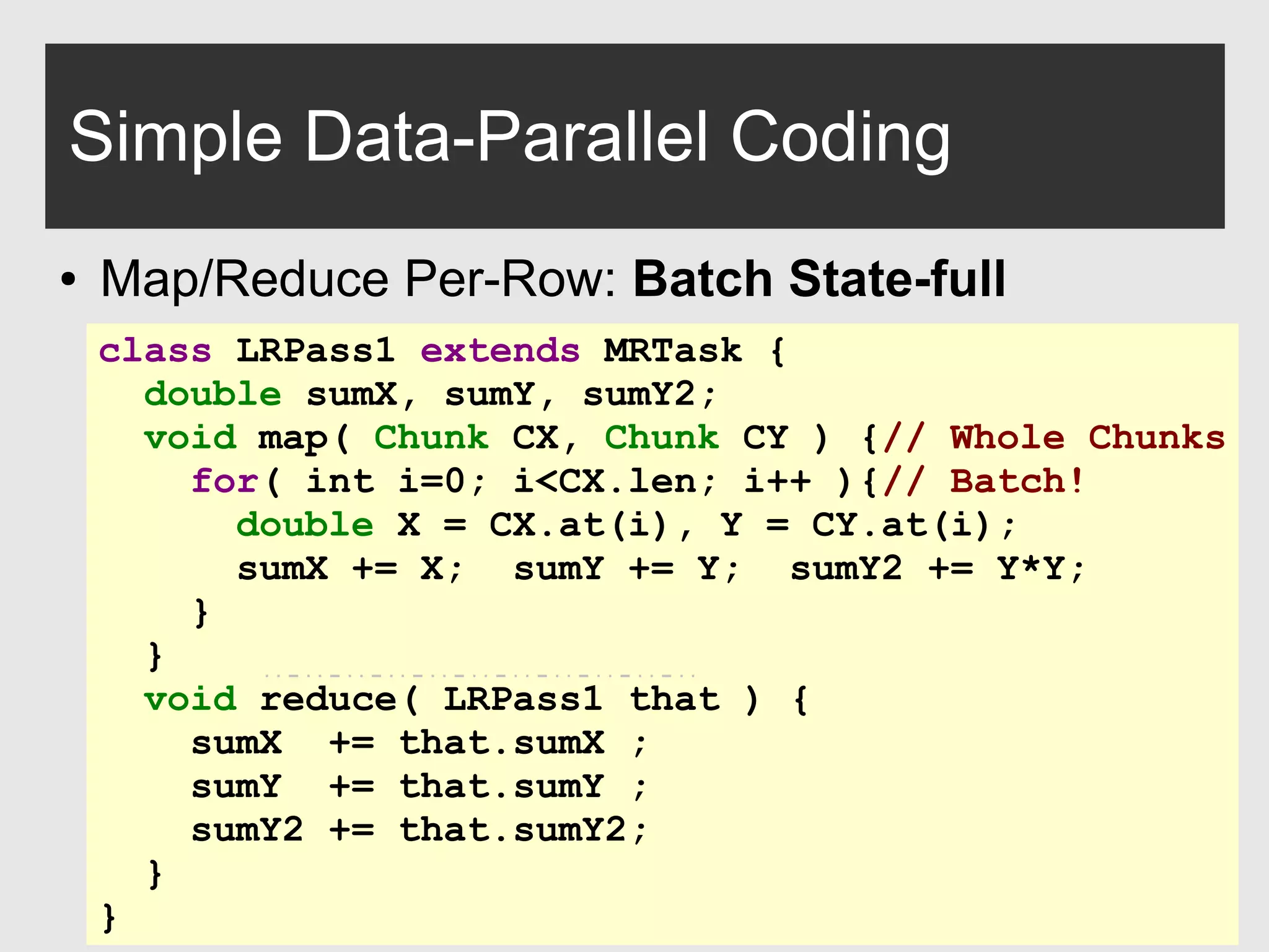
The document discusses H2O, a pure Java open-source platform for distributed data analytics that supports various algorithms including generalized linear models and gradient boosting machines. It details the architecture of distributed vectors and frames, highlights tree-based algorithm execution, and showcases parallel execution patterns for efficient data handling. Additionally, it explains coding taxonomies and provides examples of data processing tasks using map/reduce methods in a distributed computing environment.

![0xdata.com 5
JVM 4
Heap
JVM 1
Heap
JVM 2
Heap
JVM 3
Heap
Frames
A Frame: Vec[]
age sex zip ID car
●Vecs aligned
in heaps
●Optimized for
concurrent access
●Random access
any row, any JVM
●But faster if local...
more on that later](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201310gbm-130927131031-phpapp01/75/GBM-in-H2O-with-Cliff-Click-H2O-API-5-2048.jpg)

![0xdata.com 18
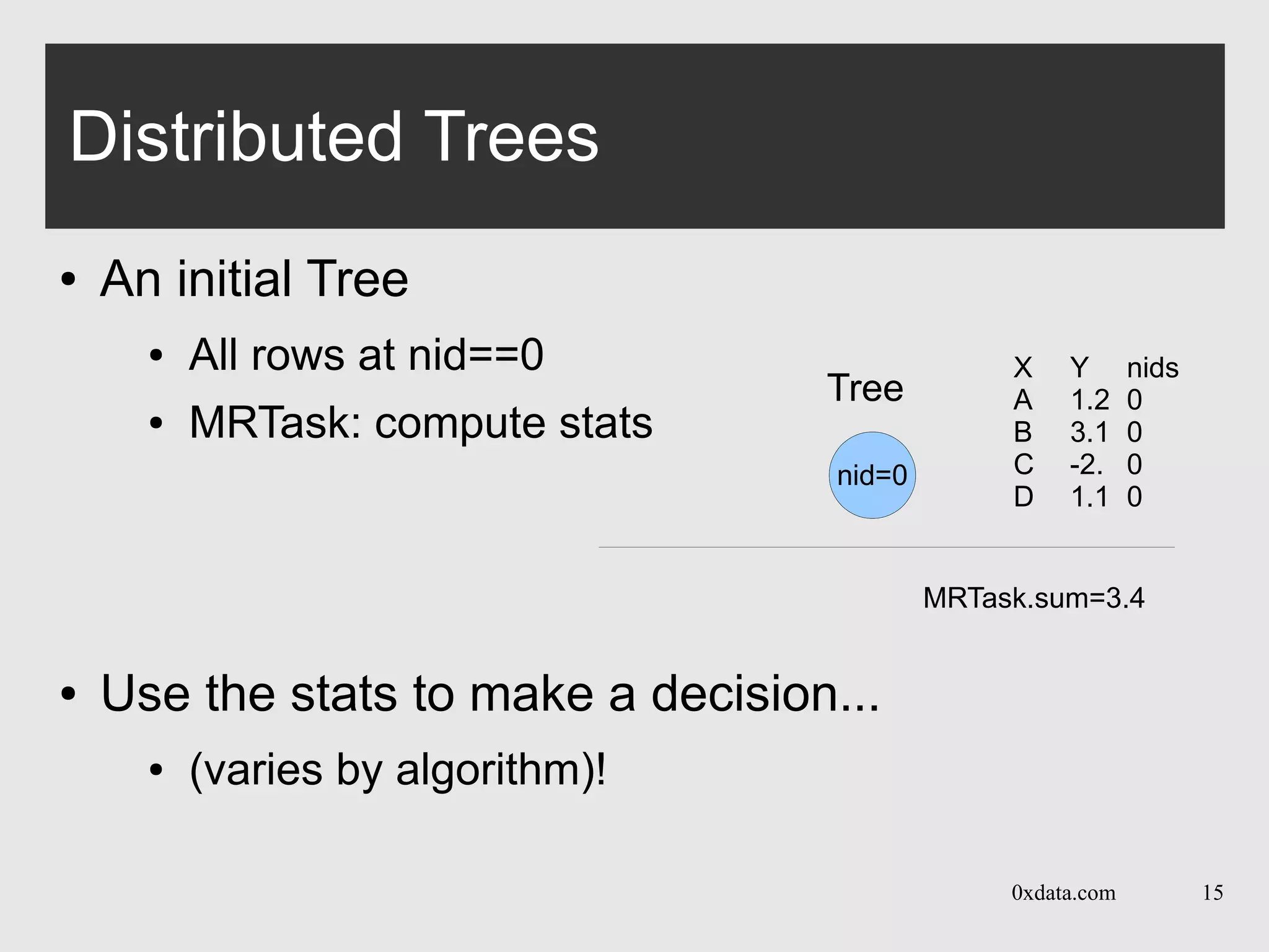
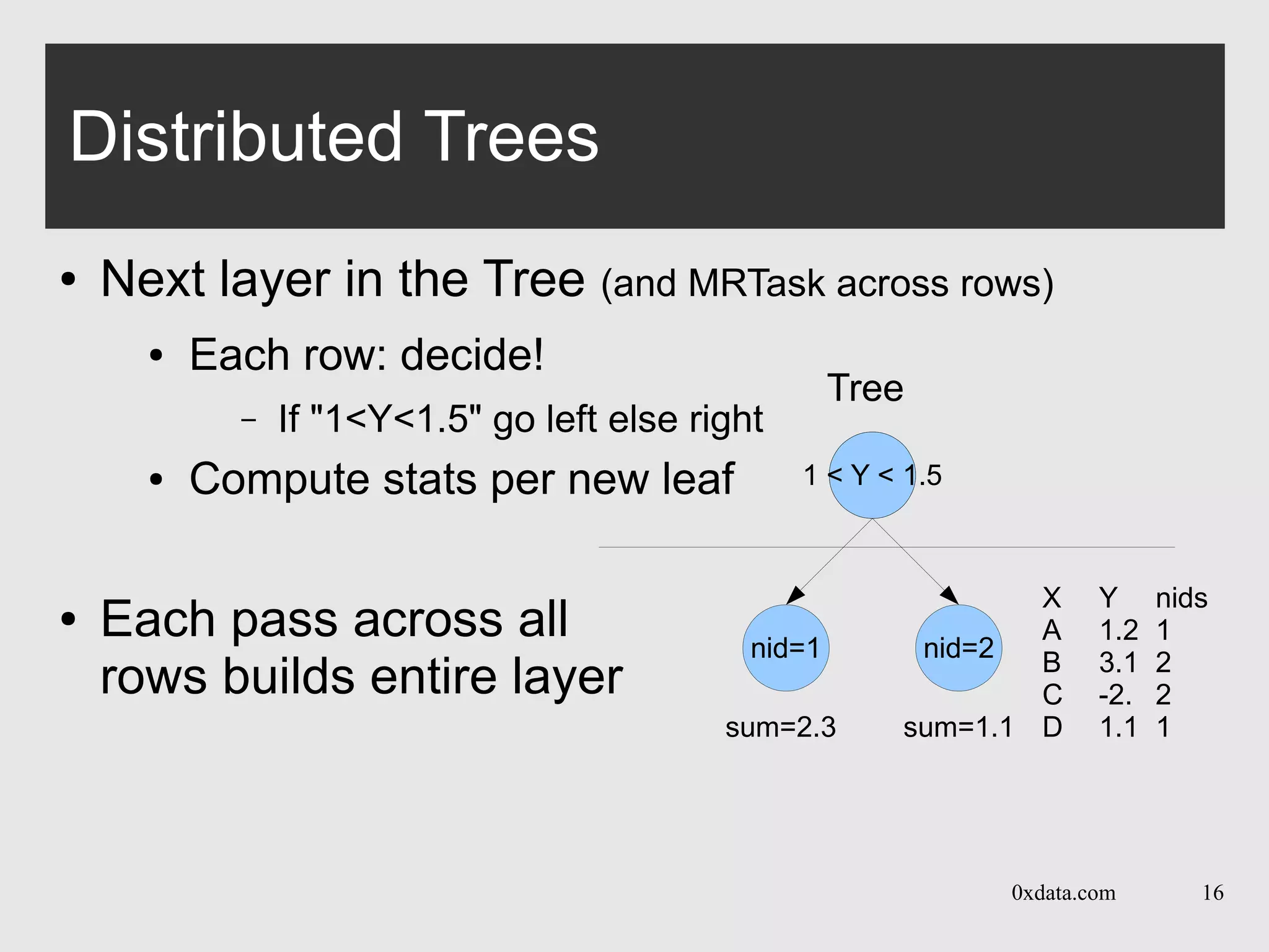
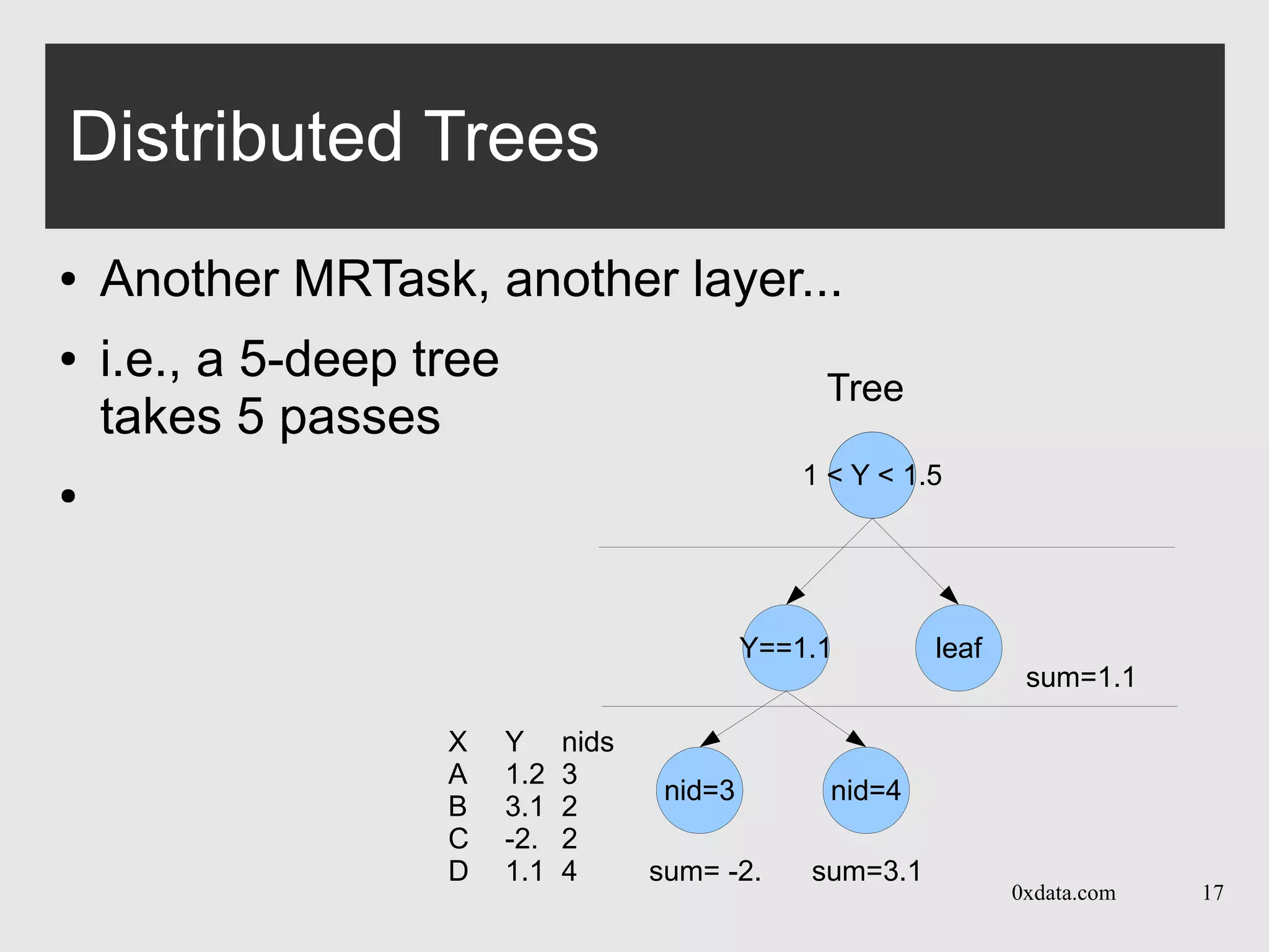
Distributed Trees
● Each pass is over one layer in the tree
● Builds per-node histogram in map+reduce calls
class Pass extends MRTask2<Pass> {
void map( Chunk chks[] ) {
Chunk nids = chks[...]; // Node-IDs per row
for( int r=0; r<nids.len; r++ ){// All rows
int nid = nids.at80(i); // Node-ID THIS row
// Lazy: not all Chunks see all Nodes
if( dHisto[nid]==null ) dHisto[nid]=...
// Accumulate histogram stats per node
dHisto[nid].accum(chks,r);
}
}
}.doAll(myDataFrame,nids);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201310gbm-130927131031-phpapp01/75/GBM-in-H2O-with-Cliff-Click-H2O-API-18-2048.jpg)

![0xdata.com 20
Distributed Trees: utilities
● “score+build” in one pass:
● Test each row against decision from prior pass
● Assign to a new leaf
● Build histogram on that leaf
● “score”: just walk the tree, and get results
● “compress”: Tree from POJO to byte[]
● Easily 10x smaller, can still walk, score, print
● Plus utilities to walk, print, display](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201310gbm-130927131031-phpapp01/75/GBM-in-H2O-with-Cliff-Click-H2O-API-20-2048.jpg)



![0xdata.com 27
The Platform
NFS
HDFS
byte[]
extends Iced
extends DTask
AutoBuffer
RPC
extends DRemoteTask D/F/J
extends MRTask User code?
JVM 1
NFS
HDFS
byte[]
extends Iced
extends DTask
AutoBuffer
RPC
extends DRemoteTask D/F/J
extends MRTask User code?
JVM 2
K/V get/put
UDP / TCP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201310gbm-130927131031-phpapp01/75/GBM-in-H2O-with-Cliff-Click-H2O-API-27-2048.jpg)


![0xdata.com 31
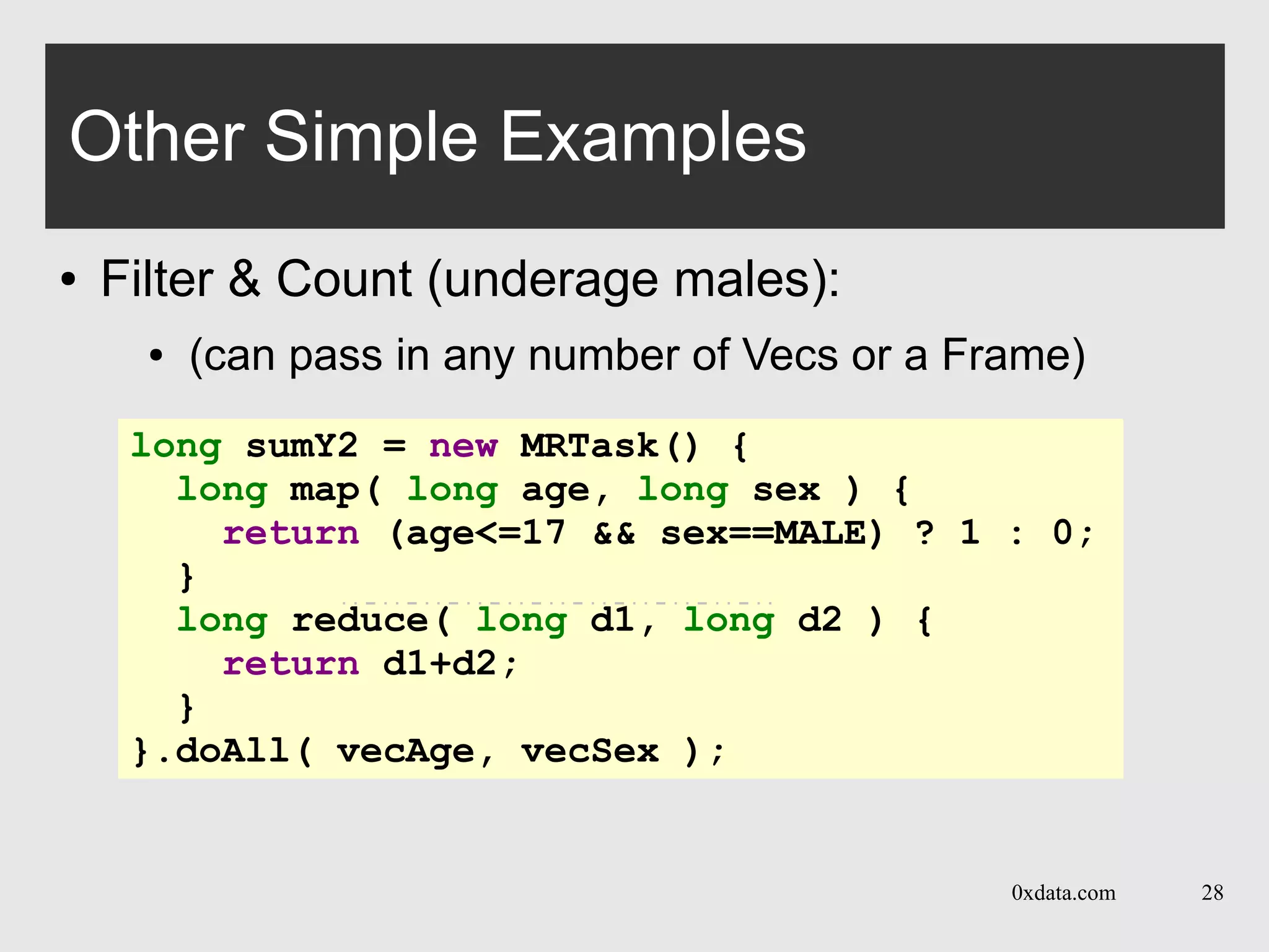
Other Simple Examples
● Group-by: count of car-types by age
class AgeHisto extends MRTask {
long carAges[][]; // count of cars by age
void map( Chunk CAge, Chunk CCar ) {
carAges = new long[numAges][numCars];
for( int i=0; i<CAge.len; i++ )
carAges[CAge.at(i)][CCar.at(i)]++;
}
void reduce( AgeHisto that ) {
for( int i=0; i<carAges.length; i++ )
for( int j=0; i<carAges[j].length; j++ )
carAges[i][j] += that.carAges[i][j];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201310gbm-130927131031-phpapp01/75/GBM-in-H2O-with-Cliff-Click-H2O-API-31-2048.jpg)
![0xdata.com 32
class AgeHisto extends MRTask {
long carAges[][]; // count of cars by age
void map( Chunk CAge, Chunk CCar ) {
carAges = new long[numAges][numCars];
for( int i=0; i<CAge.len; i++ )
carAges[CAge.at(i)][CCar.at(i)]++;
}
void reduce( AgeHisto that ) {
for( int i=0; i<carAges.length; i++ )
for( int j=0; i<carAges[j].length; j++ )
carAges[i][j] += that.carAges[i][j];
}
}
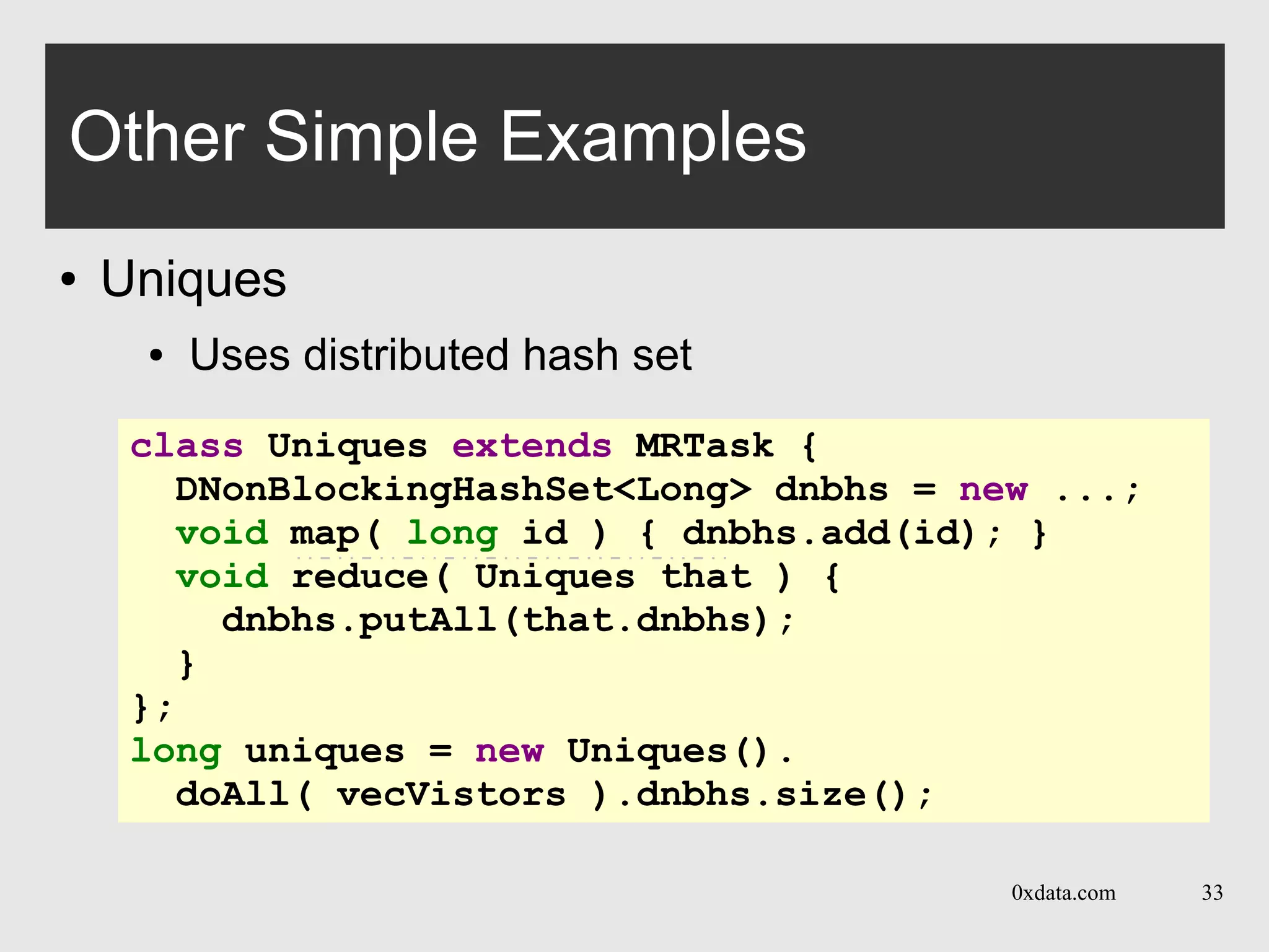
Other Simple Examples
● Group-by: count of car-types by age
Setting carAges in map() makes it an output field.
Private per-map call, single-threaded write access.
Must be rolled-up in the reduce call.
Setting carAges in map makes it an output field.
Private per-map call, single-threaded write access.
Must be rolled-up in the reduce call.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/201310gbm-130927131031-phpapp01/75/GBM-in-H2O-with-Cliff-Click-H2O-API-32-2048.jpg)