1. An iterative algorithm is proposed for jointly estimating SNR and the frequency selective channel for OFDM systems.
2. The algorithm estimates the channel using LMMSE estimation and estimates the noise variance using MMSE estimation at each iteration. SNR is then derived from the noise variance estimate.
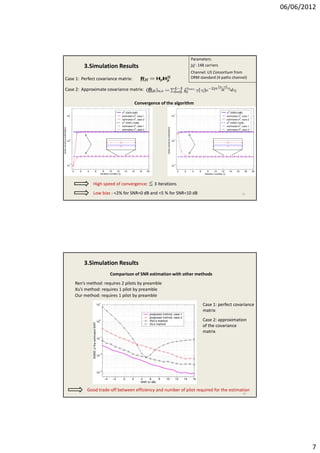
3. Simulation results show the algorithm converges quickly within 3 iterations with low estimation bias for SNR and channel. SNR estimation accuracy is better than other methods using fewer pilots.


![06/06/2012
3
1.Background
Estimation Methods ‐ Signal to noise ratio (SNR, noted )
, with the second moment‐order of the received signal
[1]: estimated thanks to the subtraction of two consecutive received
signal vectors
[2]: estimated thanks to the subspace properties of the estimated
covariance matrix of the received signal
5
G. Ren, H. Zhang, and Y. Chang, “SNR Estimation Algorithm Based on the Preamble for OFDM Systems in Frequency Selective
Channels,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 57, no. 8, August 2009.
X. Xu, Y. Jing, and X. Yu, “Subspace‐Based Noise Variance and SNR Estimation for OFDM Systems,” in IEEE Mobile Radio
Applications Wireless Communication Networking Conference, March 2005, pp. 23 –26.
[1]
[2]
Our solution: estimated thanks to the MMSE criterion
1.Background
Estimation Methods ‐ Noise estimation
MMSE criterion performed on the pilot (index )
‐=
22
6
In practice: approximation of MMSE criterion
The noise variance estimation depends on the channel estimation quality](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-04-26savaux-160417233206/85/2012-04-26-savaux-3-320.jpg)