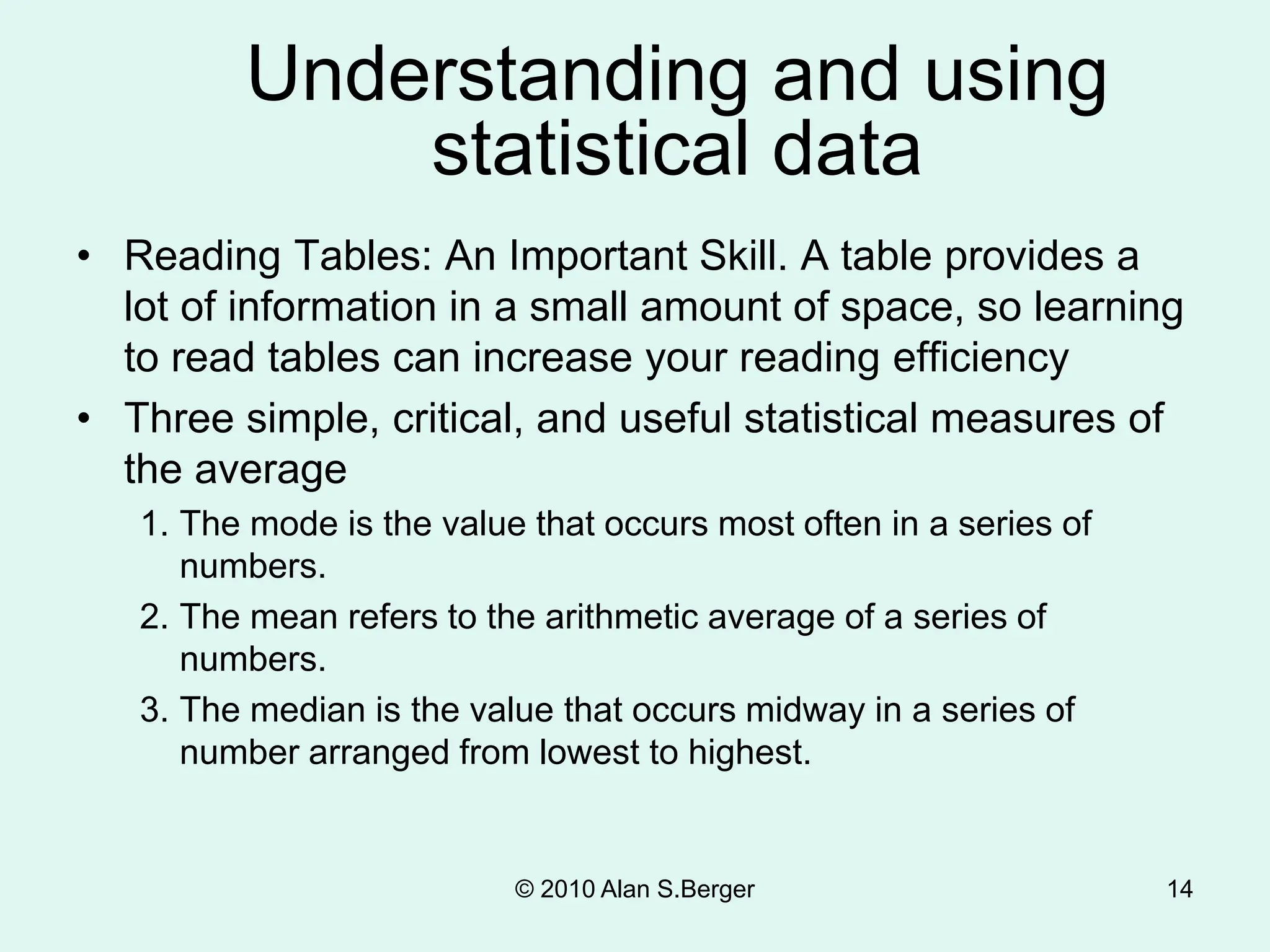
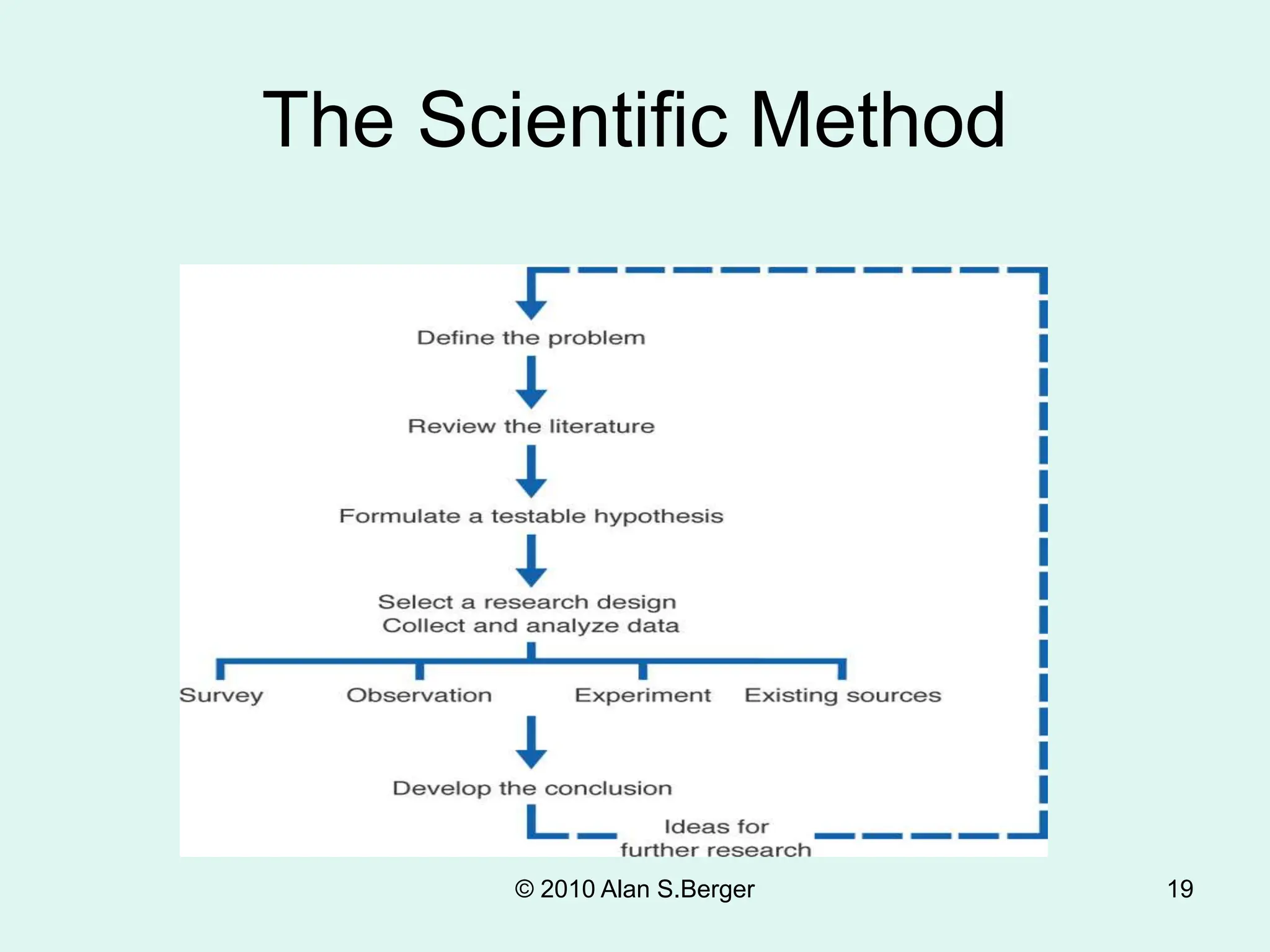
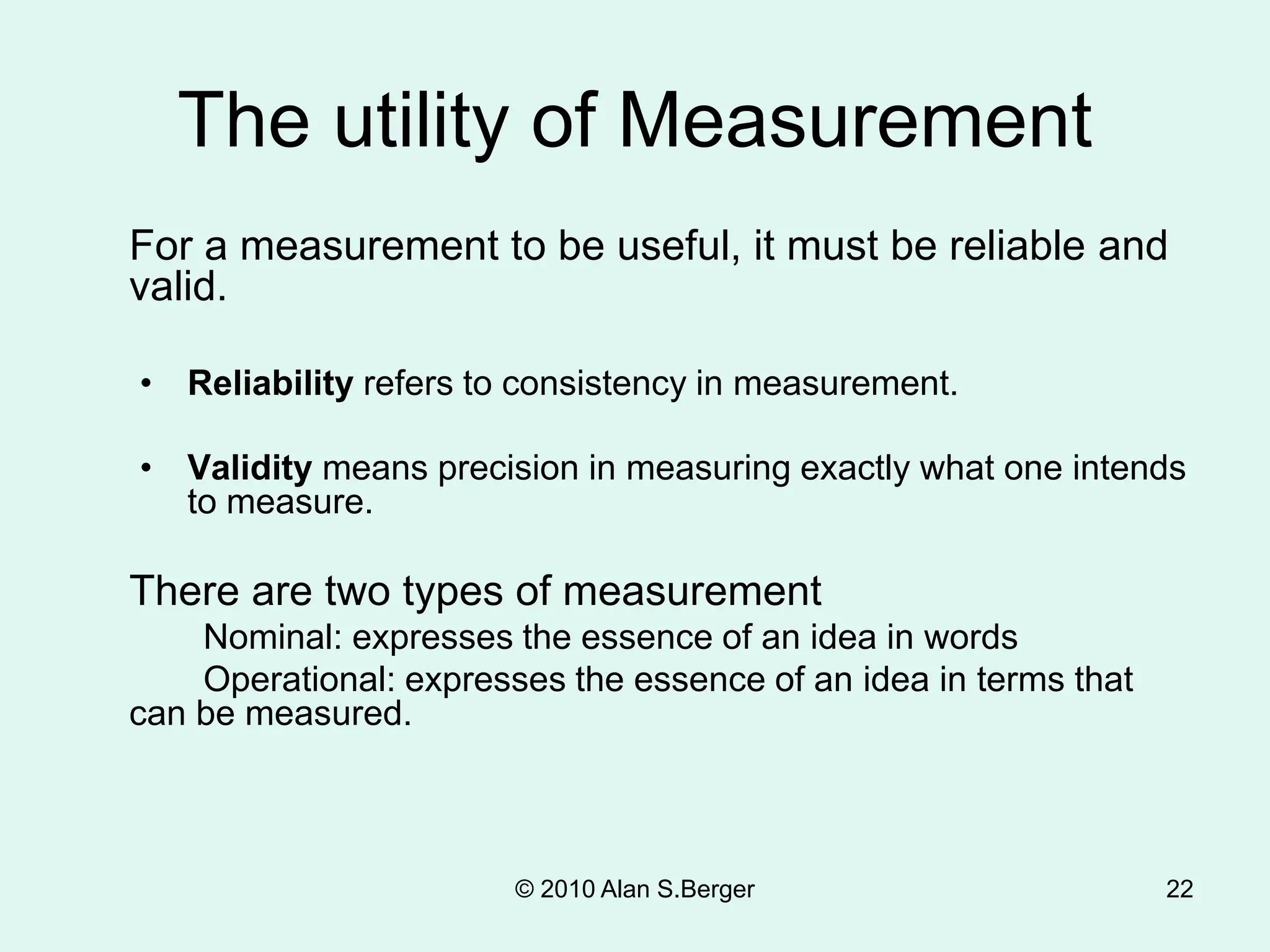
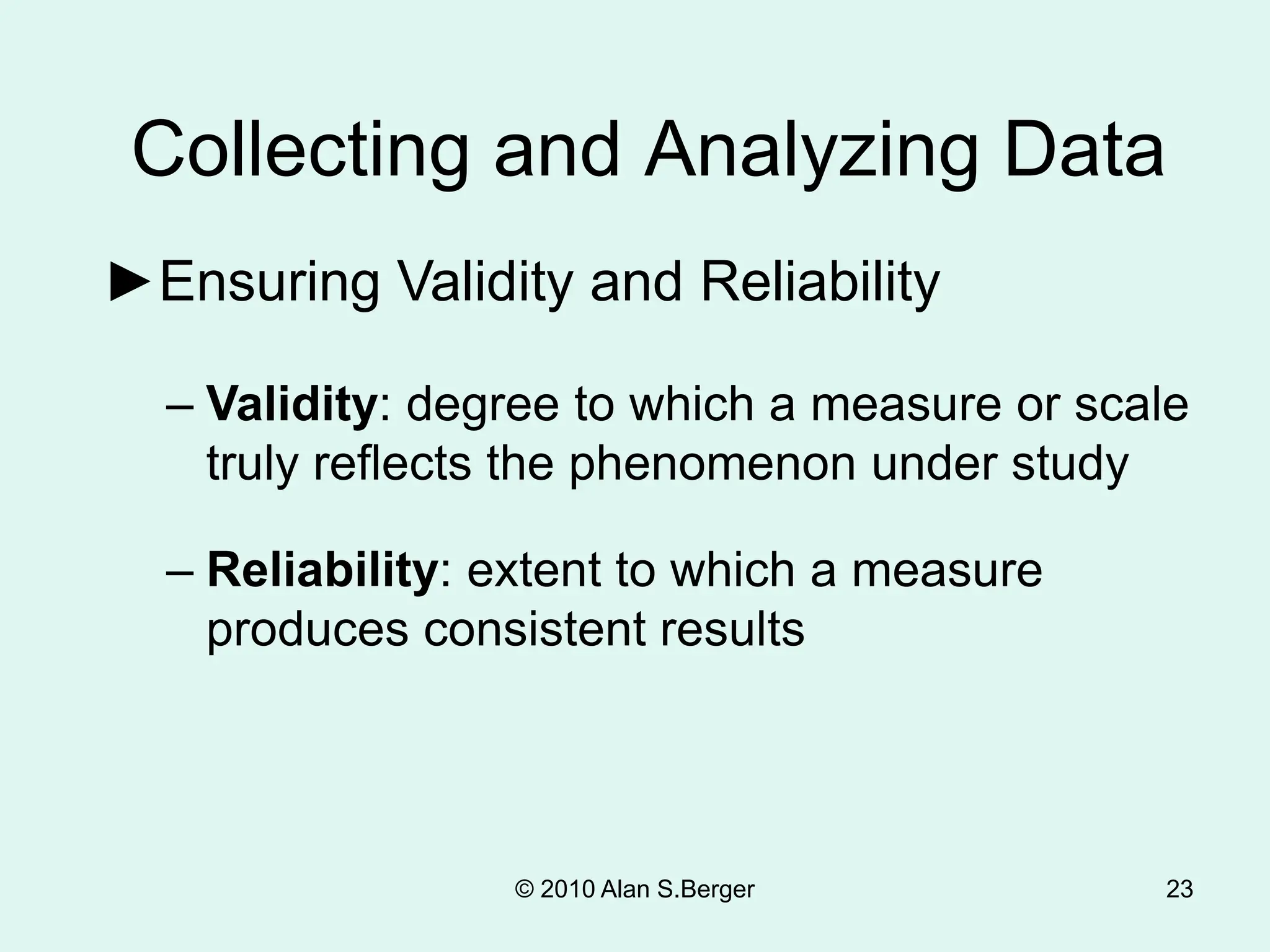
This document discusses sociological research methods. It covers topics like how sociologists seek to understand society's influence on people and how people shape society. Unlike common sense, sociological findings are tested and evaluated using scientific methods and sociological theory. Sociological research follows steps like selecting a topic, reviewing literature, formulating hypotheses, choosing a research design, collecting and analyzing data, and reporting conclusions. It discusses methods such as surveys, experiments, participant observation, and secondary analysis. It also covers issues like research ethics, biases, and ensuring objectivity.