This document provides an overview and summaries of key concepts from sociology including:
- Sociology is the systematic study of human society and social interaction. It helps reveal connections between individual lives and larger social patterns.
- Mills' concept of the sociological imagination, which is using history and social context to understand how personal experiences are shaped by broader social forces.
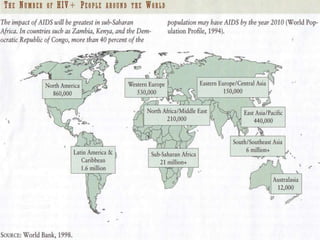
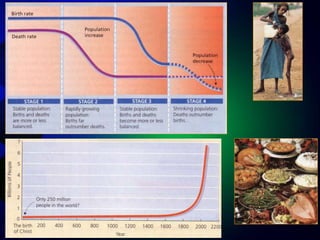
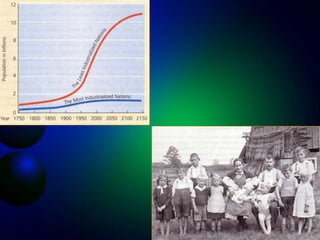
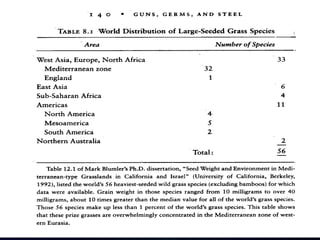
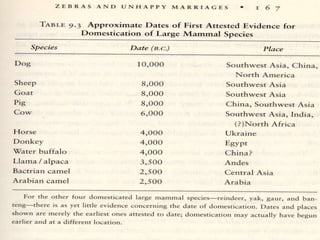
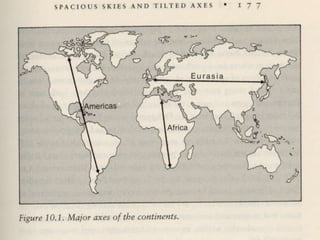
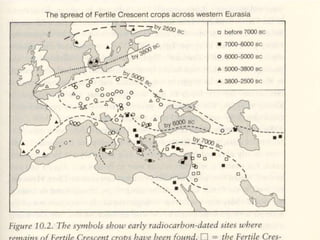
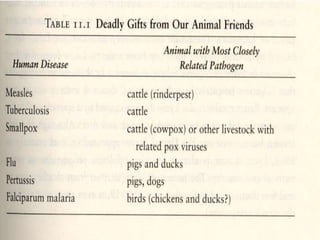
- Diamond's theory that Western societies became dominant due to geographic and environmental factors that gave them earlier starts with agriculture, animal domestication, and resistance to diseases, allowing greater technological advances.