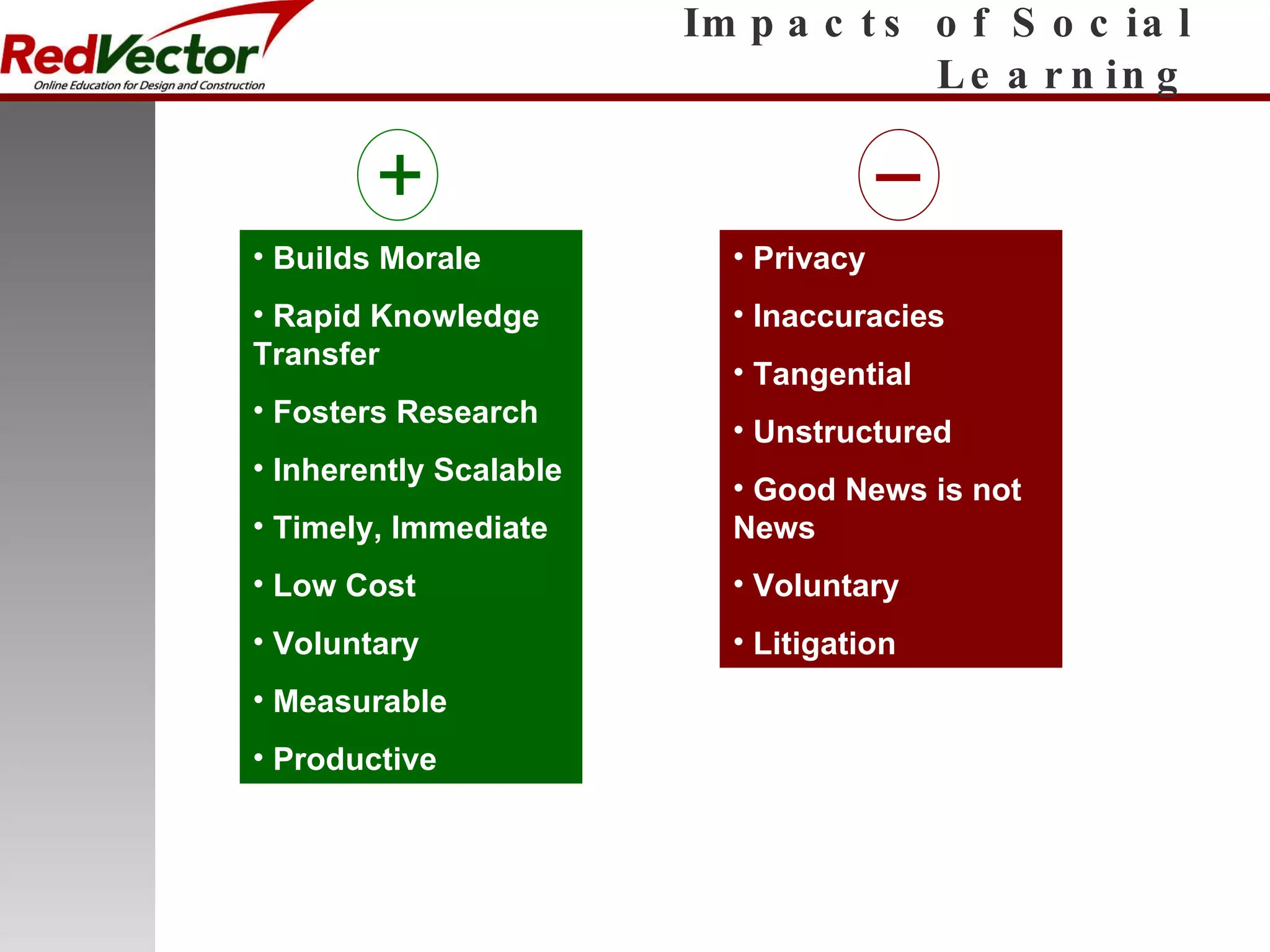
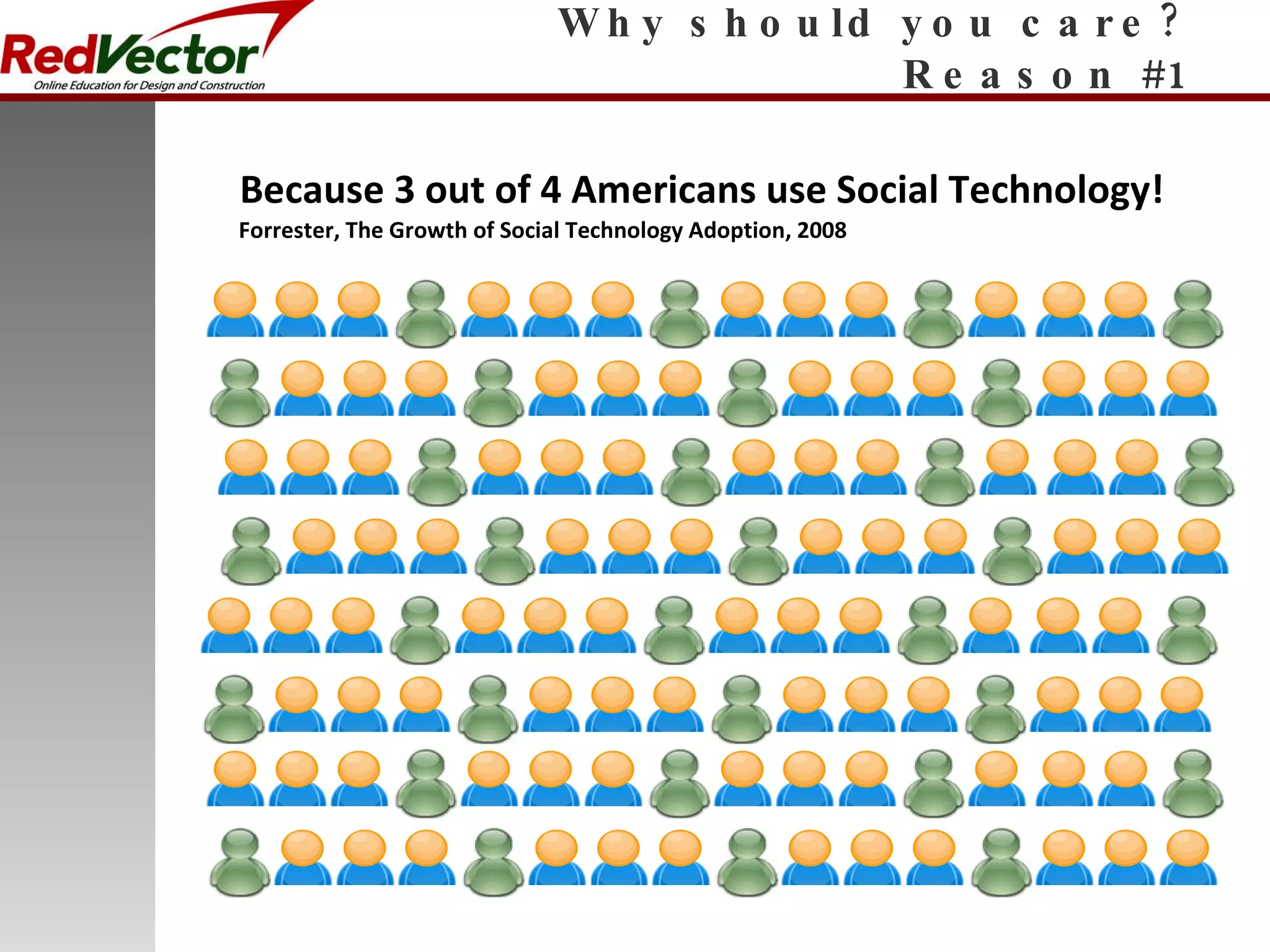
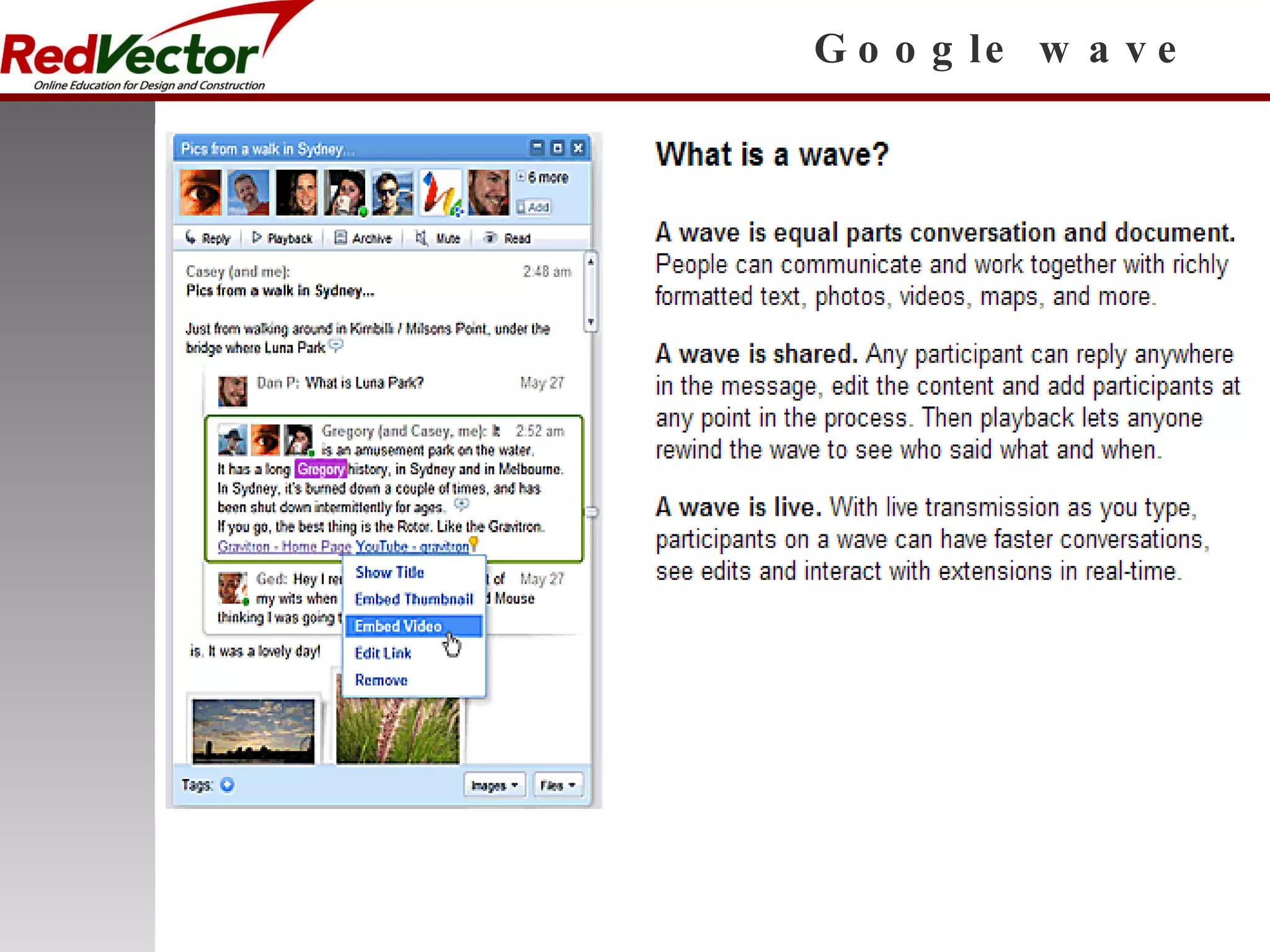
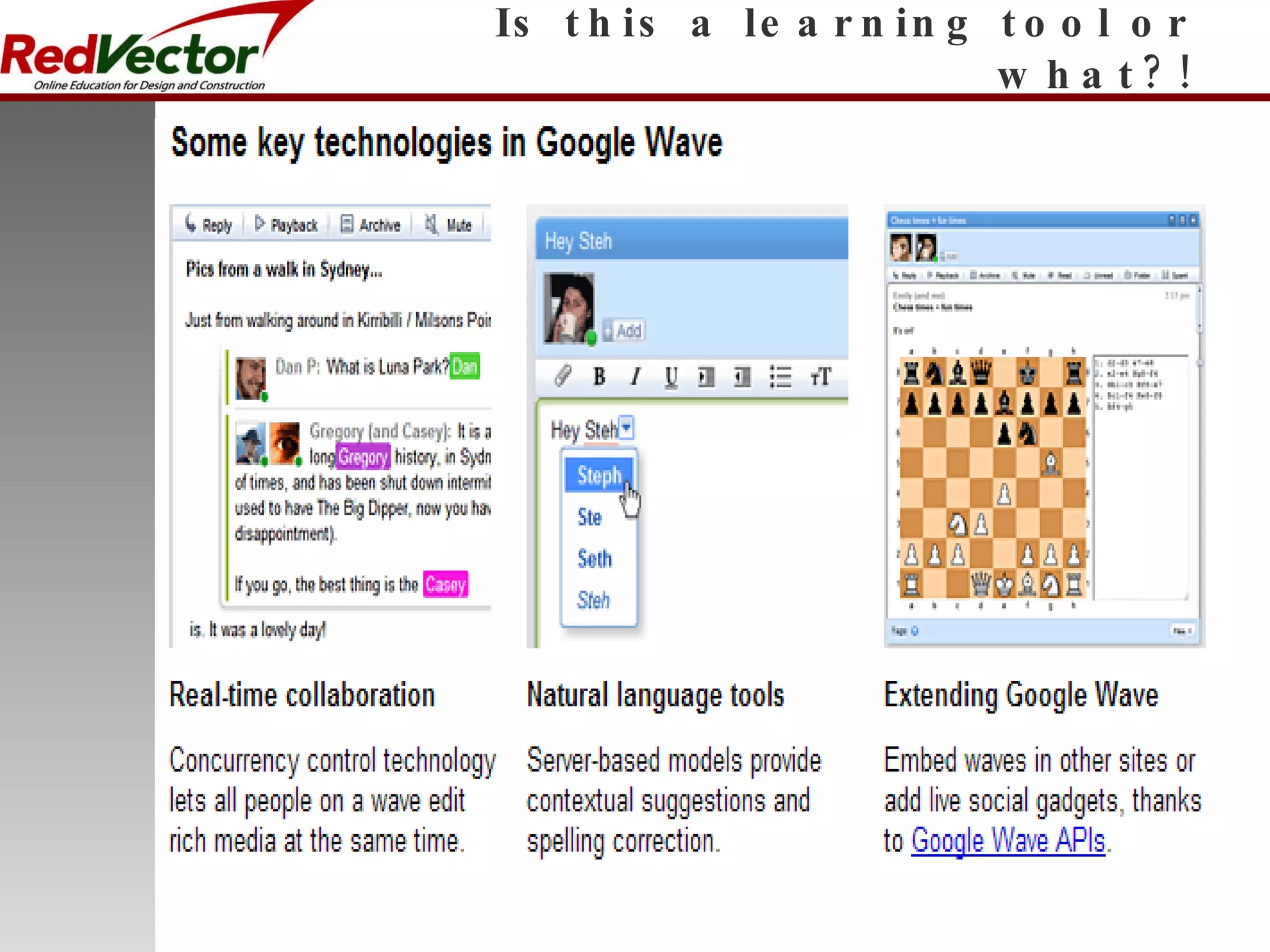
The document discusses social learning as a learning tool using social media and networking sites. It defines social learning, provides examples of social learning in the workplace, and discusses both the impacts and risks of social learning. The document examines how companies can apply social learning and provides recommendations for minimizing risks associated with social networking sites. It analyzes specific social media platforms like Twitter and their potential for social learning. The document concludes that social learning is evolving through internet technologies and that companies can gain benefits from a social learning program by committing resources and gaining leadership support.

























![How to find me Mike Vandall EVP, Business Development (813) 864-2663 [email_address] www.redvectorsolutions.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20091009socialmediaasalearningtool-12544091485046-phpapp02/75/2009-10-09-Social-Media-As-A-Learning-Tool-34-2048.jpg)