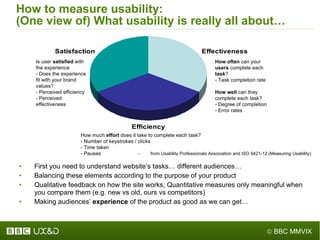
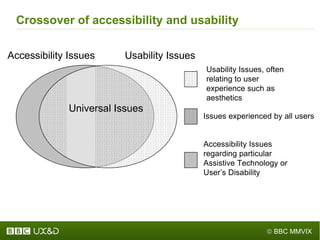
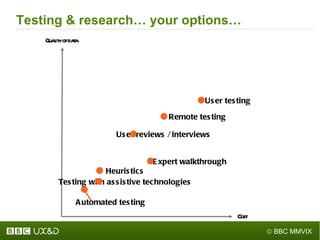
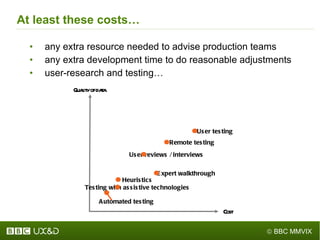
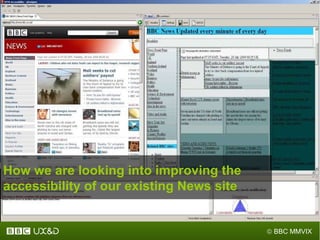
The document discusses the importance of improving accessibility in digital content, emphasizing the need for business support, guidelines, and effective governance in quality assurance processes. It outlines the significant number of disabled individuals using the internet and stresses the necessity of creating a great user experience for them, alongside usability and accessibility standards. Furthermore, it highlights the integration of accessibility into production processes, procurement, and communication with audiences to ensure inclusive digital environments.