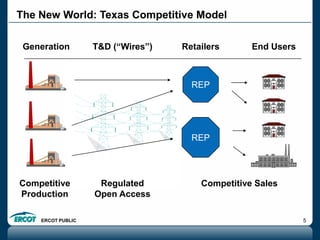
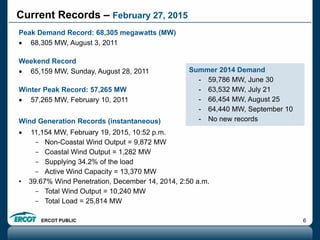
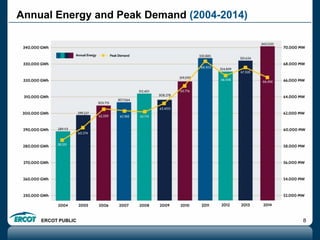
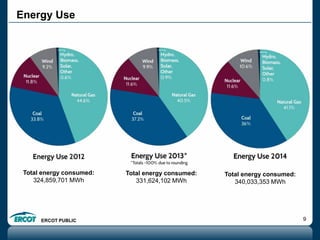
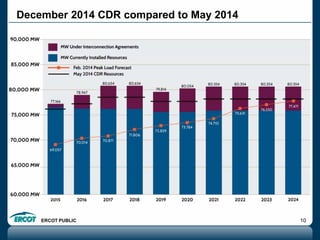
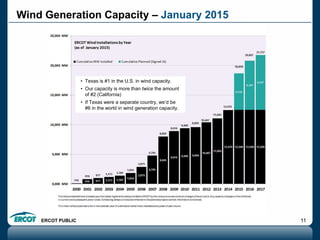
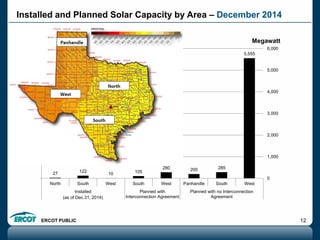
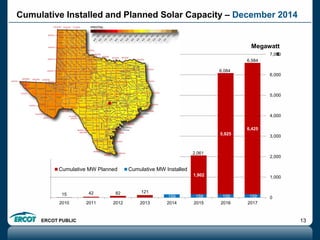
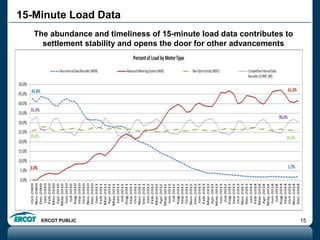
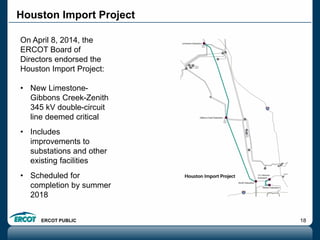
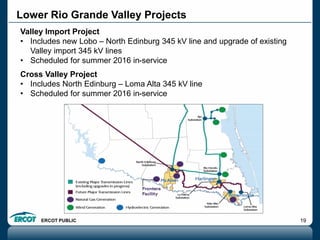
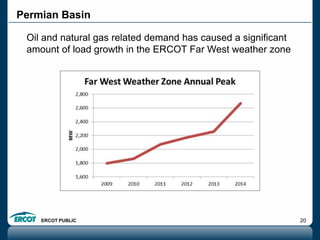
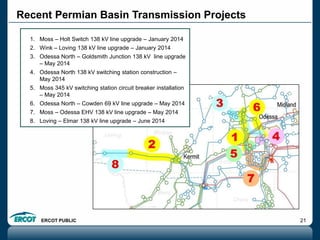
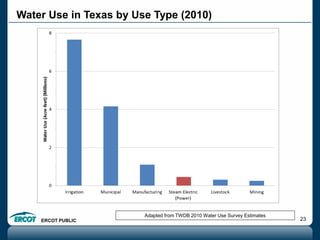
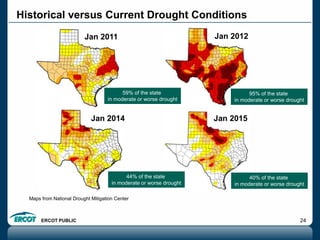
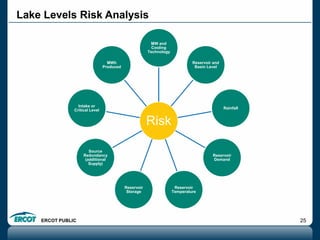
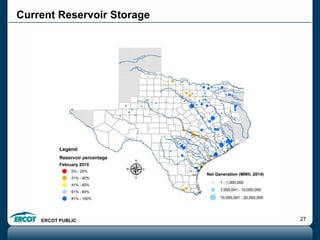
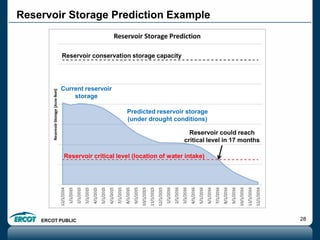
ERCOT is responsible for ensuring the reliability of the electric grid in most of Texas. It discussed several key issues including record demand levels, increasing renewable and solar capacity, potential impacts of environmental regulations which could cause many coal plants to retire, and various transmission expansion projects. It also summarized its efforts to monitor drought conditions and risks to power generation from water shortages using a predictive modeling tool.