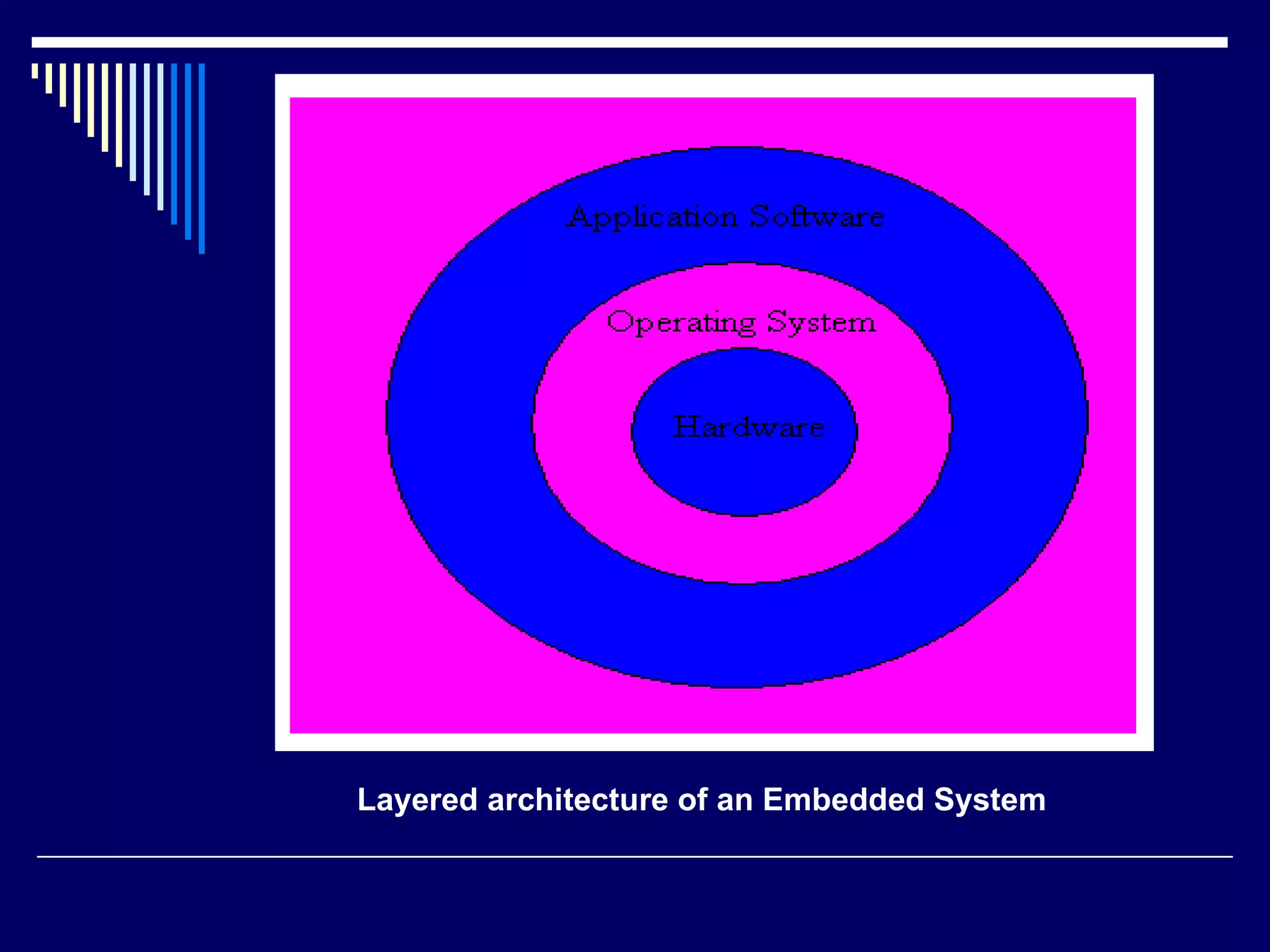
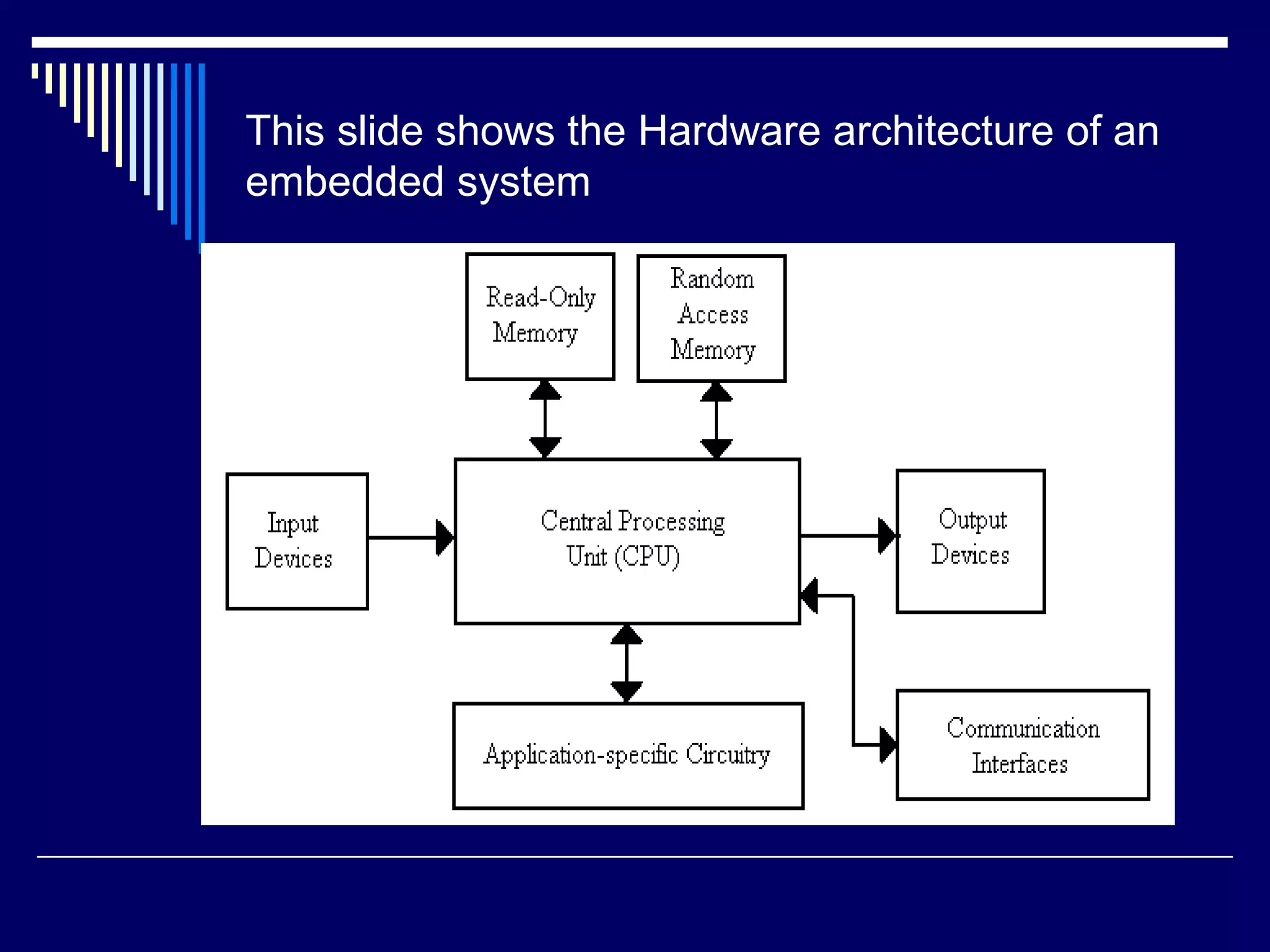
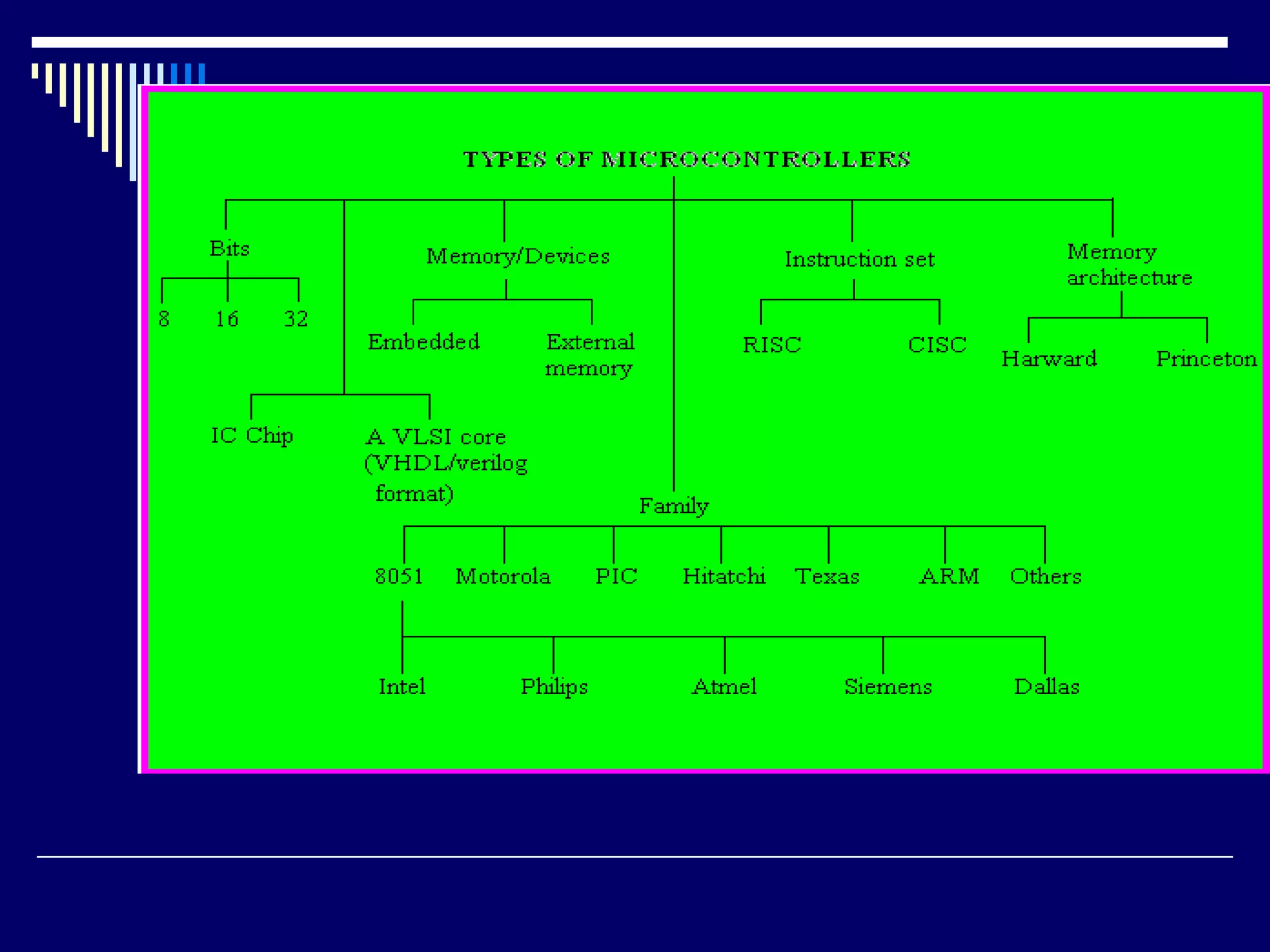
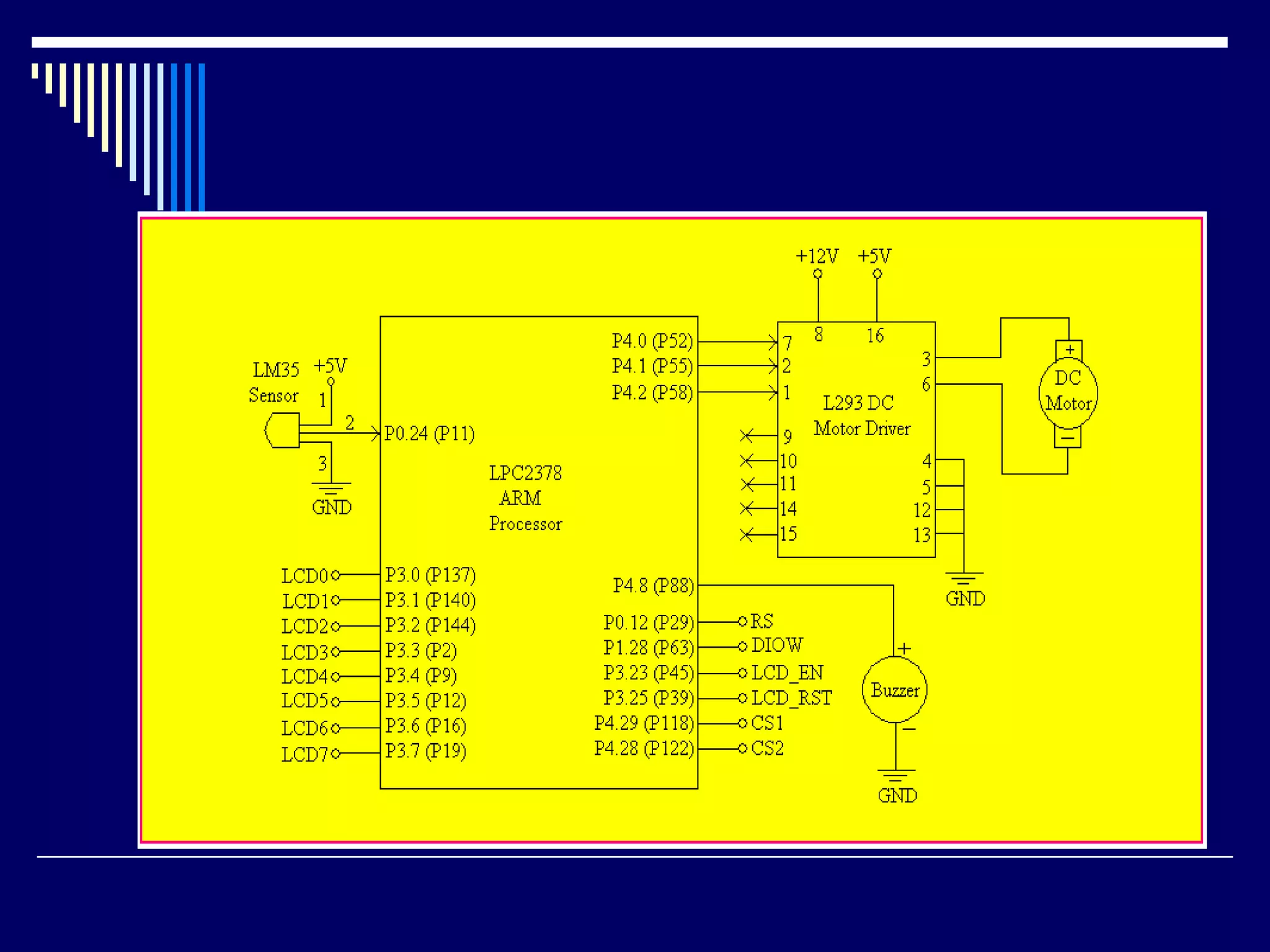
An embedded system is a computer system designed to perform dedicated functions within a larger mechanical or electrical system. It consists of a microprocessor or microcontroller and other components integrated to perform predefined tasks. Embedded systems are found in many devices like phones, appliances, vehicles etc. They are designed to perform real-time processing within strict constraints of power, size and cost. Common programming languages for embedded systems include C and C++.