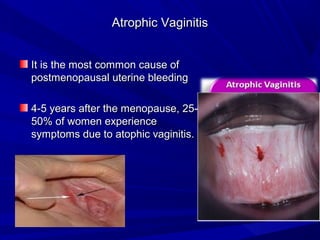
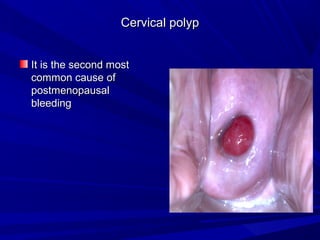
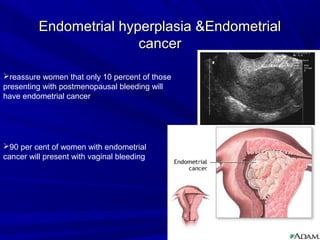
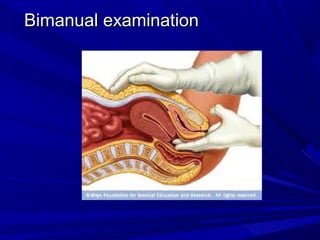
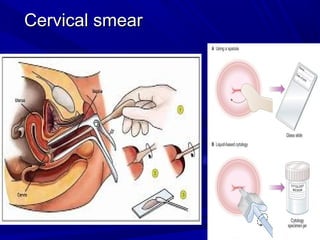
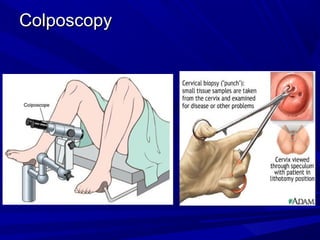
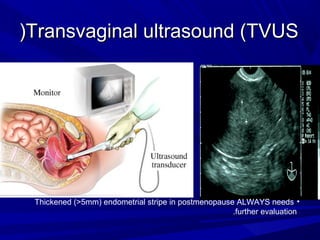
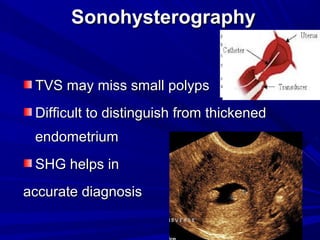
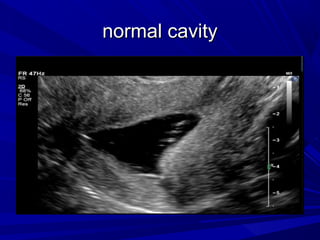
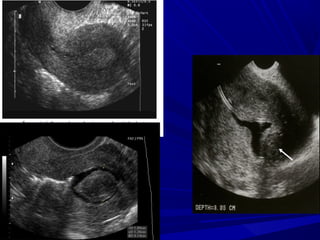
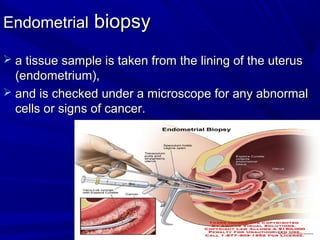
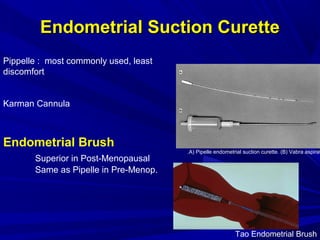
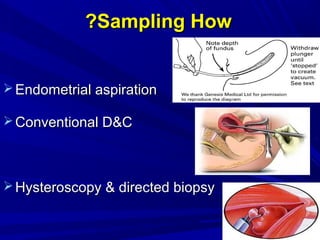
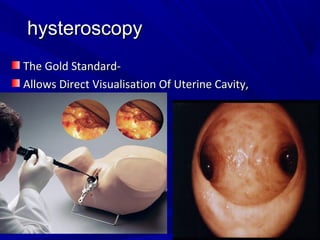
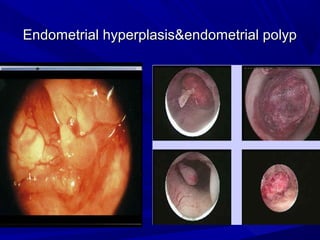
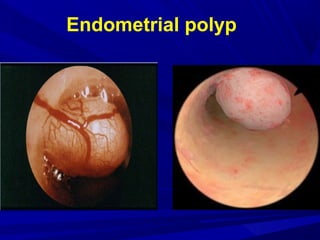
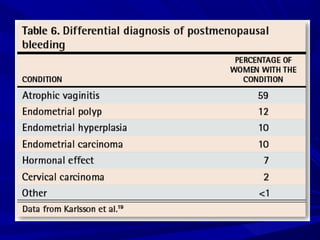
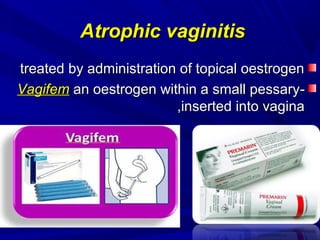
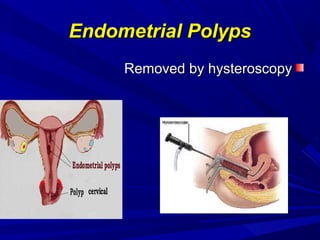
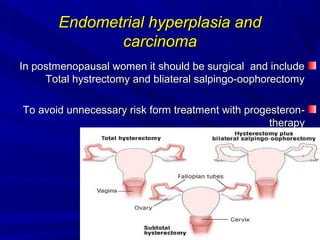
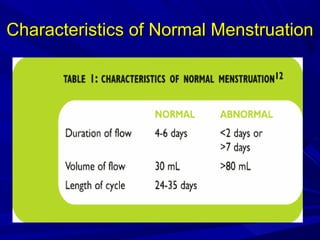
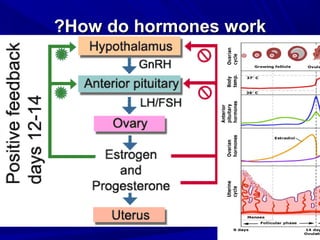
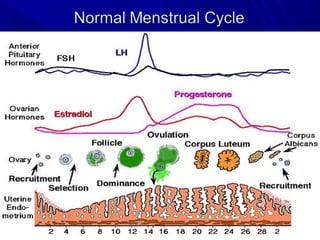
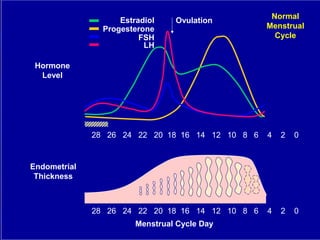
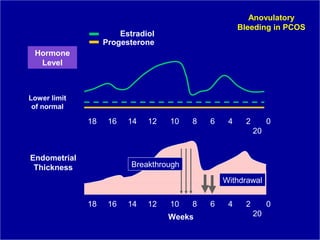
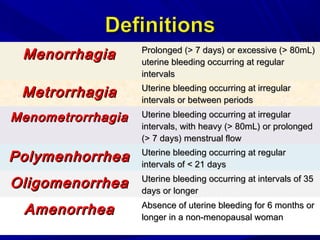
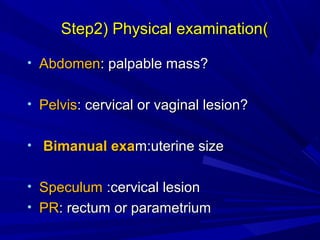
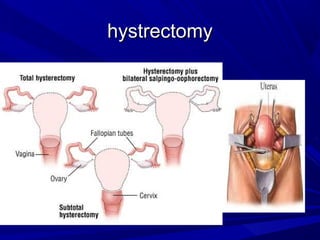
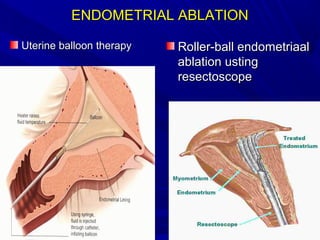
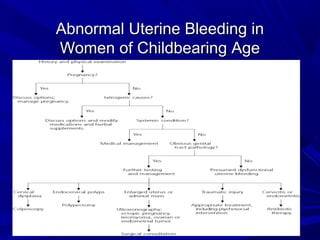
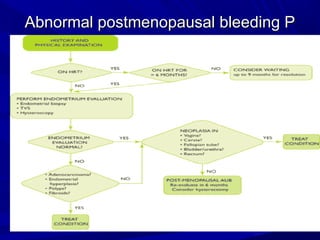
Vaginal bleeding that occurs after menopause requires evaluation to determine the cause. The most common causes are atrophic vaginitis, use of estrogen therapy, and endometrial polyps. Less common but important to identify or rule out are endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Evaluation involves history, physical exam, ultrasound of the pelvis, and endometrial biopsy to diagnose the source of bleeding and guide treatment. Management depends on the identified cause, such as using local estrogen for atrophic vaginitis, removing polyps surgically, or having a hysterectomy for cancer.