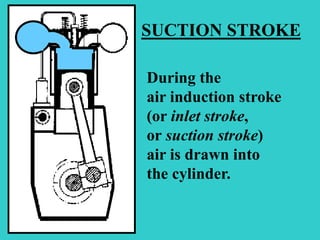
A diesel engine uses internal combustion to power ships. There are two main types of cylinder arrangements: a V-engine, where cylinders are arranged at an angle, and an inline engine, where cylinders are lined up straight. The four strokes of a diesel engine are: 1) intake stroke to draw in air, 2) compression stroke to compress the air, 3) power stroke where fuel injects and burns to push the piston, and 4) exhaust stroke to push out exhaust gases. Scavenging systems are used to remove exhaust gases from the cylinder.