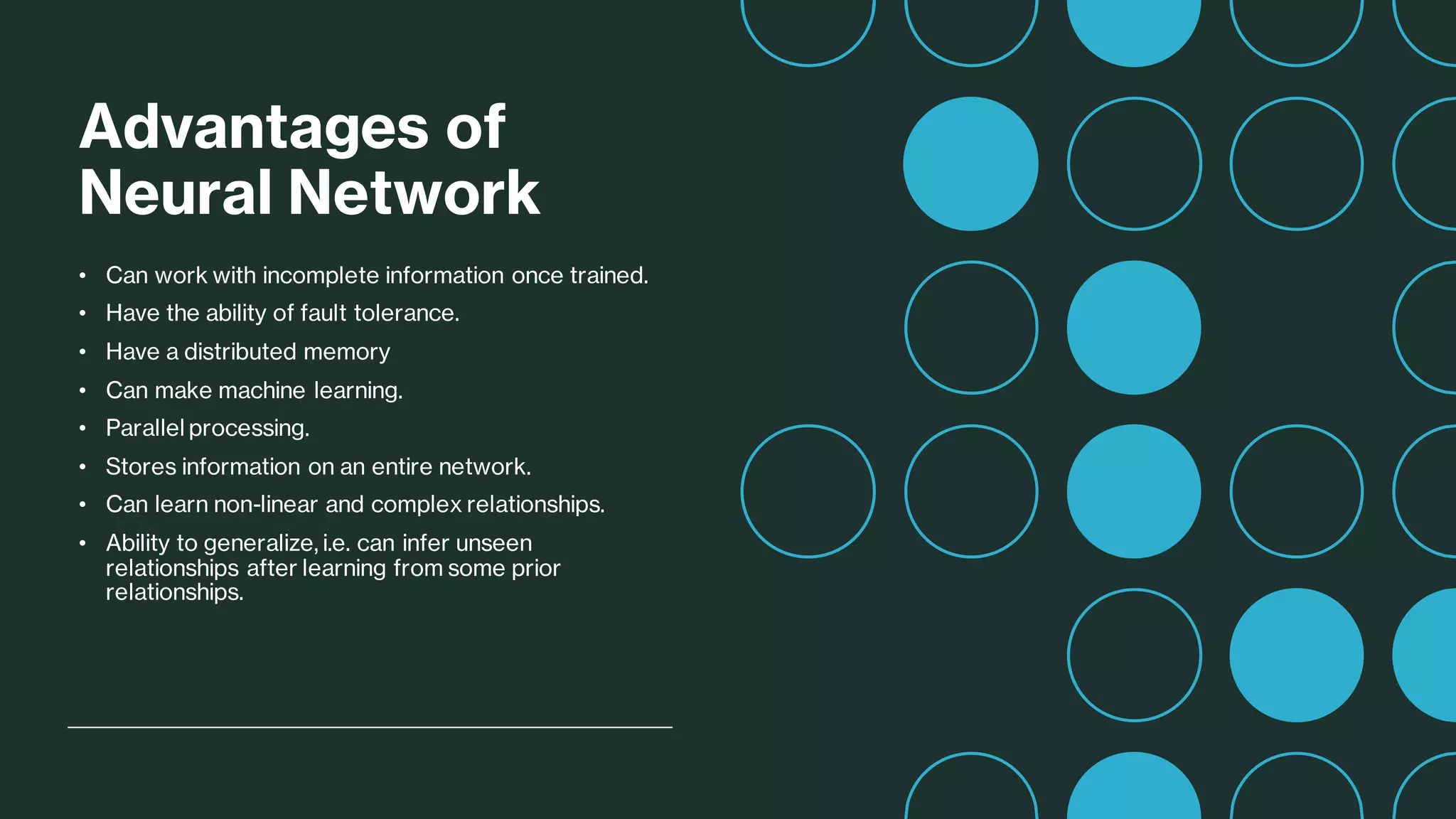
Aryan Raj, a student with roll number 18700120047 studying in CSE 1 semester 5, has chosen the topic of explaining Neural Networks in detail for his AI subject. Neural Networks are computing systems inspired by biological neural networks that can perform tasks using large amounts of data, and are called artificial neural networks. The network is trained to produce desired outputs and use different models to predict future results from data. Nodes in neural networks are interconnected similar to a human brain. There are three main types of learning in neural networks: supervised, reinforcement, and unsupervised learning. The architecture of neural networks can be single layer feedforward, multi-layer feedforward, or recurrent. Neural networks have advantages like fault tolerance, parallel processing,