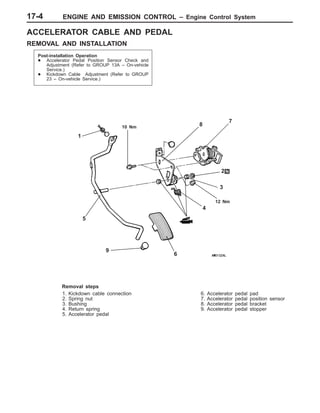
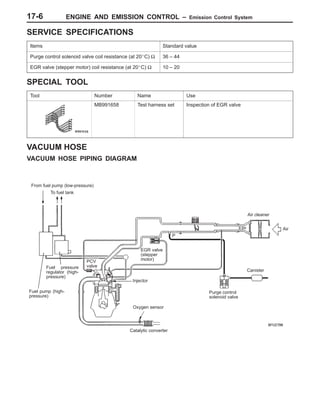
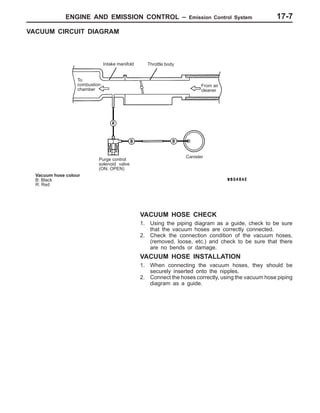
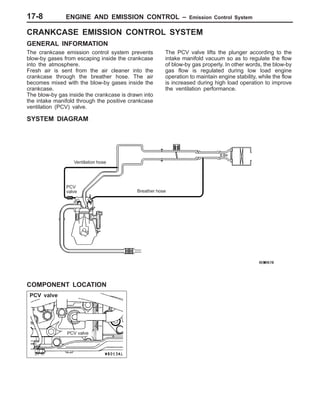
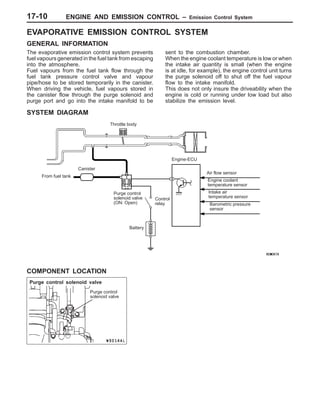
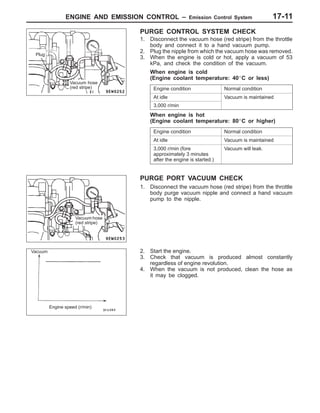
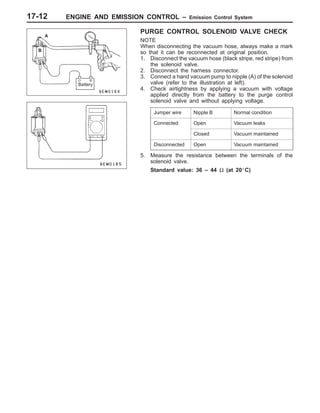
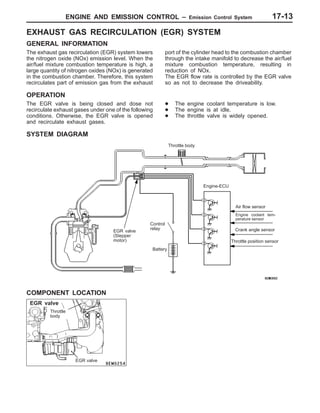
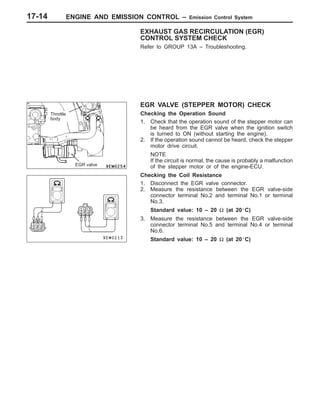
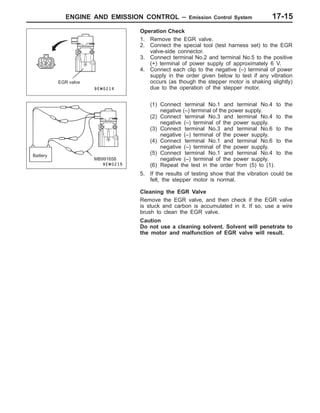
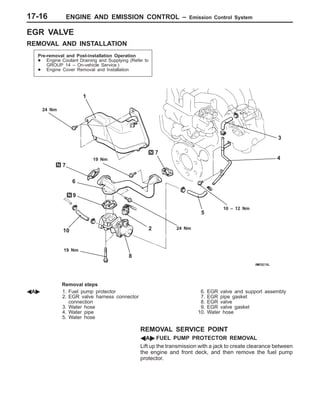
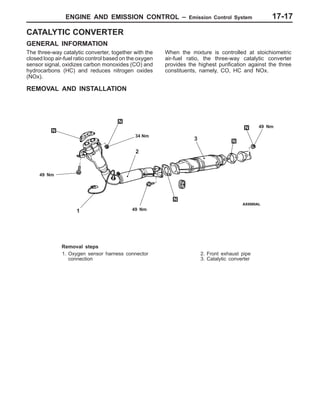
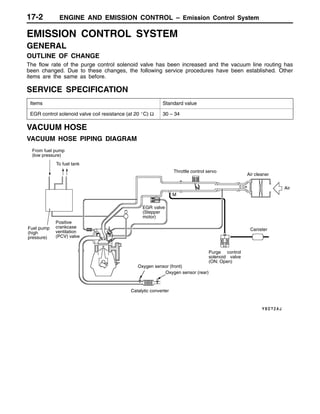
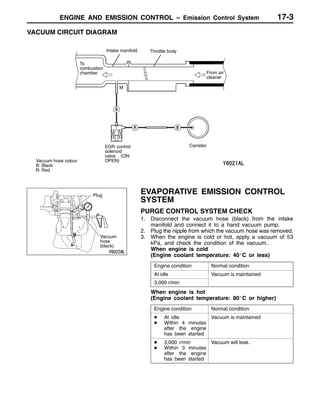
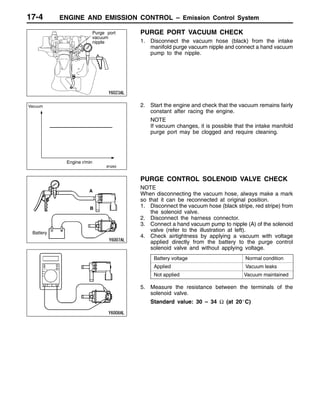
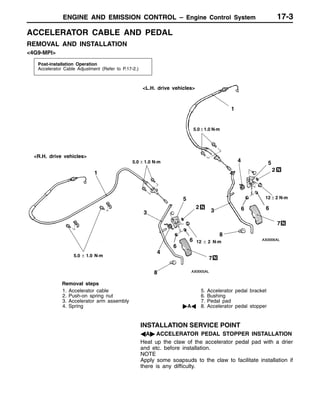
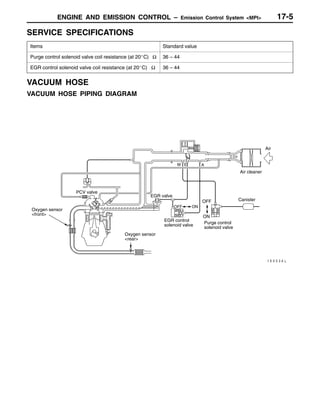
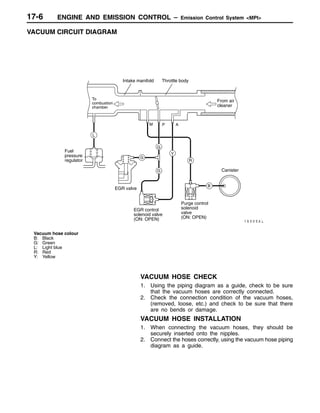
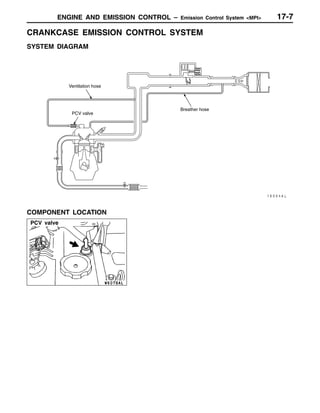
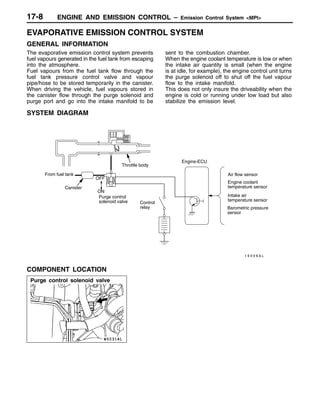
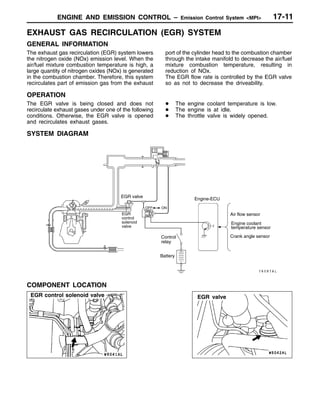
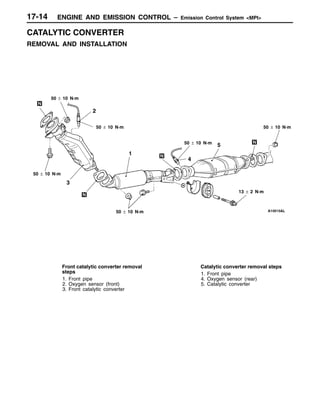
This document provides information about engine and emission control systems, including specifications, diagrams, component locations, and inspection procedures. It covers the crankcase emission control system, evaporative emission control system, exhaust gas recirculation system, and catalytic converter. Check procedures are described for the accelerator cable, positive crankcase ventilation system, purge control system, and exhaust gas recirculation valve. Specifications and diagrams are provided for reference.