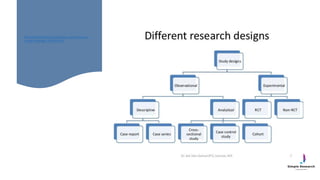
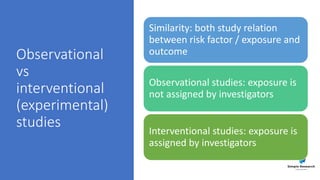
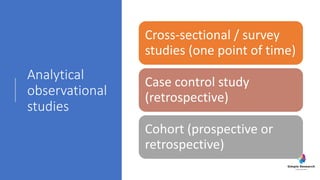
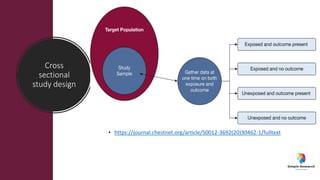
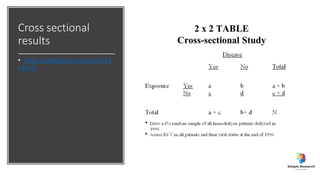
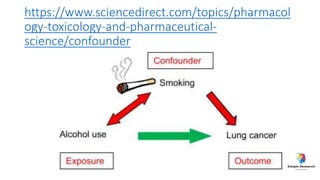
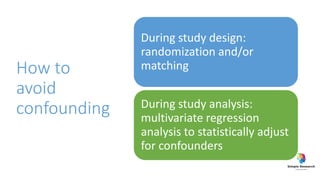
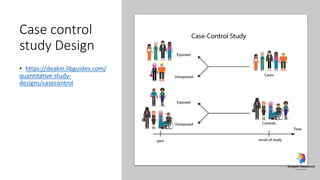
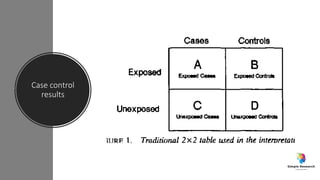
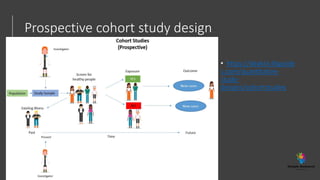
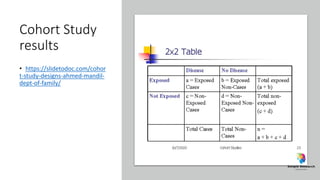
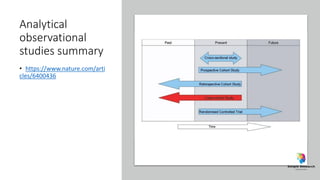
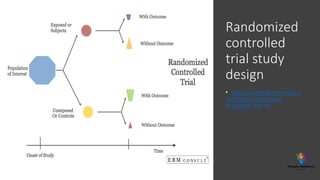
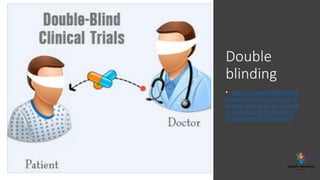
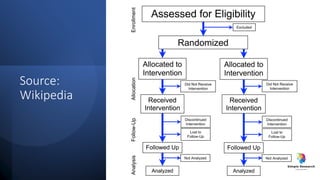
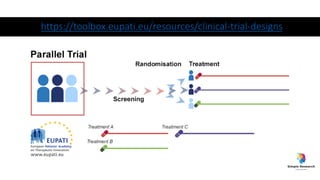
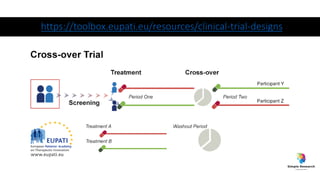
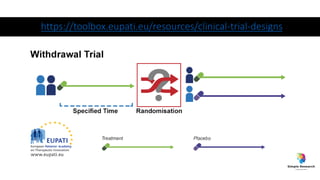
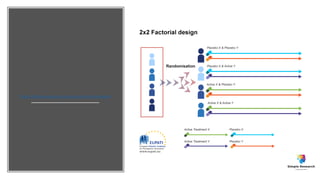
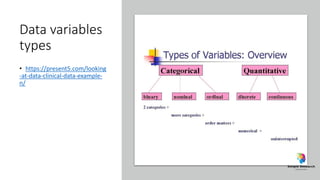
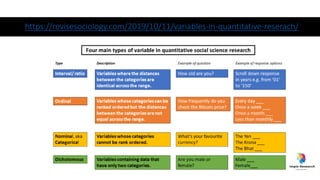
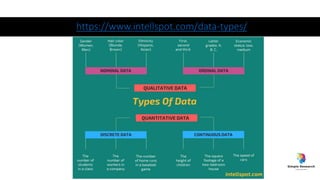
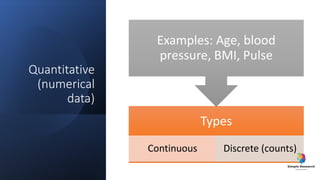
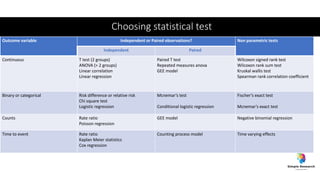
The document outlines various study designs in research, including observational, interventional, and analytical studies, along with their respective pros and cons. It highlights specific designs such as case reports, case control, cohort studies, and randomized controlled trials, emphasizing their applications and limitations. Additionally, it provides guidance on data types, variables, statistical tests, and a checklist for data analysis.