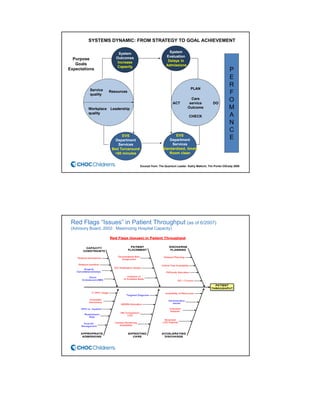
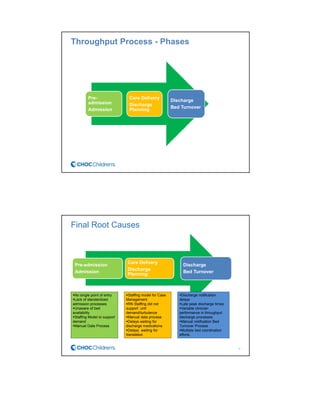
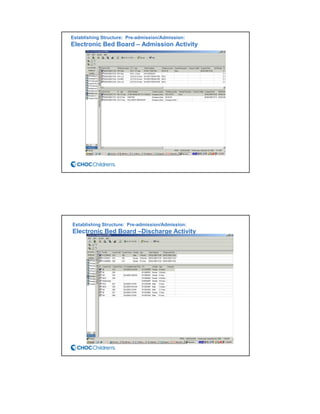
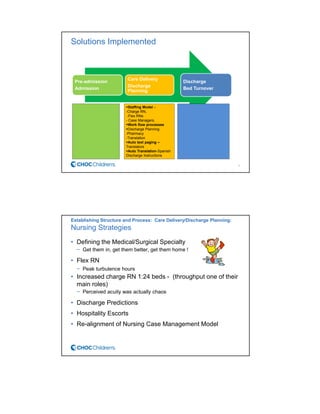
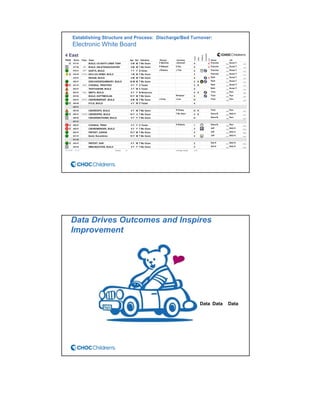
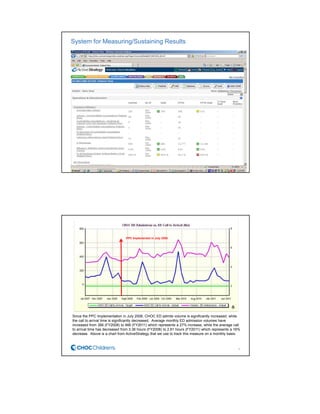
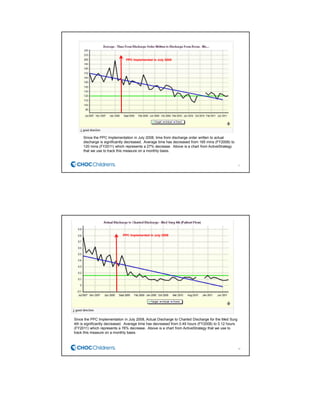
CHOC Children's Hospital implemented an interdisciplinary Patient Flow Improvement Team to address issues with patient throughput and capacity. The team developed technology-enabled solutions across the continuum of care from pre-admission to discharge. This included an electronic bed board, standardized admission processes, and automated discharge workflows. Data from the systems showed improvements such as a 27% increase in ED admissions, 76-80% faster discharge times, and an 81% reduction in cancelled admissions. The initiatives helped align practices with strategic goals of ensuring timely access to care.