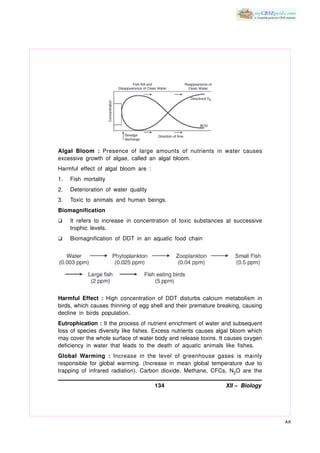
This document provides information about various environmental issues and pollution. It defines terms like pollution, pollutants, slash and burn agriculture, reforestation, effluents, CPCB, BOD, CNG, and FOAM. It describes biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and how it is a measure of organic pollution in water. It discusses the harmful effects of algal blooms, biomagnification of DDT, eutrophication, global warming, ozone depletion, and methods to control air pollution. It lists questions related to these topics at the end.