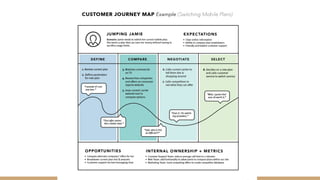
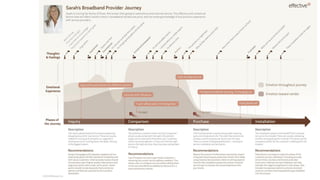
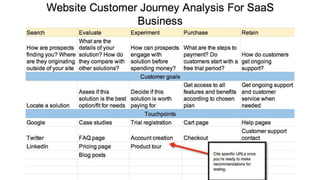
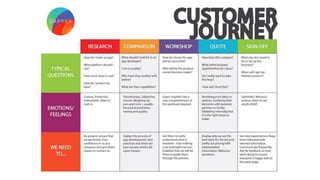
Journey mapping is a strategic tool that visualizes the process a person undergoes to achieve a goal, encompassing customer journey models and key components such as user actions, emotions, and opportunities. The mapping process involves several steps like defining objectives, profiling personas, and identifying touchpoints, with an emphasis on empathy and group participation. Ultimately, journey maps help uncover insights that can inform product management by transforming opportunities into user stories and actionable backlog items.