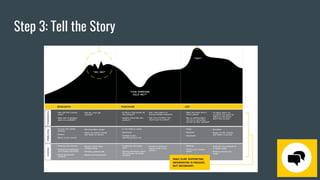
The document outlines the process of experience mapping, which involves researching and visually mapping out the holistic journey a customer takes to achieve a goal. The process has four steps: 1) uncover customer behaviors, thoughts, and feelings through research; 2) collaboratively chart the customer journey; 3) tell the story of the journey through a visual map; and 4) use the map to improve customer experience and prioritize opportunities. Done correctly, experience mapping provides insights into how customers interact with a brand across different channels and touchpoints over time.