11.4 sexual reproduction (1).pptx
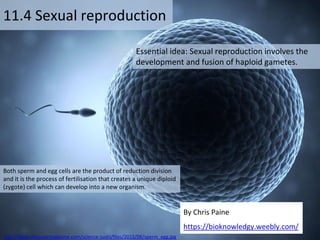
- 1. Essential idea: Sexual reproduction involves the development and fusion of haploid gametes. 11.4 Sexual reproduction By Chris Paine https://bioknowledgy.weebly.com/ Both sperm and egg cells are the product of reduction division and it is the process of fertilisation that creates a unique diploid (zygote) cell which can develop into a new organism. http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/science-sushi/files/2015/06/sperm_egg.jpg
- 2. Understandings Statement Guidance 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. 11.4.U3 Fertilization in animals can be internal or external. 11.4.U4 Fertilization involves mechanisms that prevent polyspermy. Fertilization involves the acrosome reaction, fusion of the plasma membrane of the egg and sperm and the cortical reaction. 11.4.U5 Implantation of the blastocyst in the endometrium is essential for the continuation of pregnancy. 11.4.U6 HCG stimulates the ovary to secrete progesterone during early pregnancy. 11.4.U7 The placenta facilitates the exchange of materials between the mother and fetus. 11.4.U8 Estrogen and progesterone are secreted by the placenta once it has formed. 11.4.U9 Birth is mediated by positive feedback involving estrogen and oxytocin.
- 3. Applications and Skills Statement Guidance 11.4.A1 The average 38-week pregnancy in humans can be positioned on a graph showing the correlation between animal size and the development of the young at birth for other mammals. 11.4.S1 Annotation of diagrams of seminiferous tubule and ovary to show the stages of gametogenesis. 11.4.S2 Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions.
- 4. 11.4.S2 Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions.
- 5. 11.4.S2 Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions. Structure of the mature egg Haploid (n) contains 23 chromosomes to be passed from mother to child Consists of a glycoprotein that protects the egg and prevents the entry of sperm. Not required – will break down Contains nutrients to support the early development of fertilised egg Makes the zona pellucida impenetrable to sperm (after fertilisation) to prevent polyspermy* Provides nutrients to support the early development of fertilised egg Diagram from: http://www.slideshare.net/gurustip/reproduction-ahl-1062218 Cortical granules Can you match the annotations to the labels?
- 6. 11.4.S2 Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions. Structure of the mature egg Haploid (n) contains 23 chromosomes to be passed from mother to child Consists of a glycoprotein that protects the egg and prevents the entry of sperm. Not required – will break down Contains nutrients to support the early development of fertilised egg Makes the zona pellucida impenetrable to sperm (after fertilisation) to prevent polyspermy* Provides nutrients to support the early development of fertilised egg Diagram from: http://www.slideshare.net/gurustip/reproduction-ahl-1062218 Cortical granules
- 7. 11.4.S2 Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions. Structure of the mature sperm Haploid (n), contains 23 chromosomes to be passed from father to child Contains enzymes which can digest the zona pellucida Possesses helical mitochondria which provide the ATP (energy) for swimming (and other processes) Contains protein fibres and microtubules to strengthen and allow the tail to move respectively. Can you match the annotations to the labels?
- 8. 11.4.S2 Annotation of diagrams of mature sperm and egg to indicate functions. Structure of the mature sperm Haploid (n), contains 23 chromosomes to be passed from father to child Contains enzymes which can digest the zona pellucida Possesses helical mitochondria which provide the ATP (energy) for swimming (and other processes) Contains protein fibres and microtubules to strengthen and allow the tail to move respectively.
- 9. Nature of science: Assessing risks and benefits associated with scientific research—the risks to human male fertility were not adequately assessed before steroids related to progesterone and estrogen were released into the environment as a result of the use of the female contraceptive pill. (4.8) http://www.theguardian.com/envi ronment/2012/jun/02/water- system-toxic-contraceptive-pill https://www.arhp.org/publications-and- resources/contraception-journal/august-2011 https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/12/101208125813.htm Assessing risks and benefits associated with scientific research: pollution from the female contraceptive pill Use these and other links. How serious is the pollution threat from the female contraceptive pill? Out for the count: Why levels of sperm in men are falling http://www.independent.co.uk/news/science/out-for-the- count-why-levels-of-sperm-in-men-are-falling-1954149.html Don't blame the pill for estrogen in drinking water £30bn bill to purify water system after toxic impact of contraceptive pill Birth Control Hormones In Water: Separating Myth From Fact
- 10. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm.
- 11. 11.4.S1 Annotation of diagrams of seminiferous tubule and ovary to show the stages of gametogenesis. divide to produce spermatocytes spermatogonia
- 12. 11.4.S1 Annotation of diagrams of seminiferous tubule and ovary to show the stages of gametogenesis. divide to produce spermatocytes spermatogonia
- 13. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/007249 5855/student_view0/chapter28/animation__spe rmatogenesis__quiz_1_.html http://www.cengage.com/biology/discipline_content/ani mations/spermatogenesis.html
- 14. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. Roles of hormones are not required, but it is interesting to note that FSH and LH have roles in males as well as females
- 15. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. contains the primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of supporting follicle cells contains the secondary oocyte, ready for ovulation outer layer of cells in the ovary
- 16. 11.4.S1 Annotation of diagrams of seminiferous tubule and ovary to show the stages of gametogenesis.
- 17. 11.4.S1 Annotation of diagrams of seminiferous tubule and ovary to show the stages of gametogenesis. contains the primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of supporting follicle cells contains the secondary oocyte, ready for ovulation outer layer of cells in the ovary
- 18. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. https://youtu.be/2-VKgdhfNpY Human ovulation captured on film:
- 19. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. Image edited from: http://www.ib.bioninja.com.au/_Media/oogenesis_med.jpeg Oogenesis production of ova (female gametes) during fetal development large numbers of oogonia are formed by mitosis. oogonia enlarge (growth) and undergo meiosis, but stop in prophase I (until puberty). They are now termed primary oocytes and are held in primary follicles. (at puberty) some follicles develop each month in response to FSH: • the oocyte completes the first meiotic division • Division of the cytoplasm is unequal creating a polar body • the secondary oocyte continues into meiosis II and halts at prophase II polar bodies eventually degenerate Secondary oocytes develop along with the follicle. When the follicle is mature it rupture to release the secondary oocyte with a small number of cells (the mature egg) into the fallopian tube. The remaining follicle cells remain in the ovary to form the corpus luteum (which secretes progesterone). The oocyte completes meiosis II (forming the ovum) if the cell is fertilized and another polar body 1 2 4 3b 5 3a
- 20. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. Oogenesis resources: http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495 855/student_view0/chapter28/animation__matur ation_of_the_follicle_and_oocyte.html http://highered.mheducation.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::6 40::480::/sites/dl/free/0072495855/63089/28_02_1.swf::Structure%2 0of%20the%20Ovary%20and%20the%20Developmental%20Sequence %20of%20the%20Ovarian%20Follicles http://www.wiley.com/college/jenkins/0470227583/ani mations/index_25_03_01.html
- 21. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. Compare and contrast the processes of spermatogenesis and oogenesis (8 marks)
- 22. 11.4.U1 Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both involve mitosis, cell growth, two divisions of meiosis and differentiation. AND 11.4.U2 Processes in spermatogenesis and oogenesis result in different numbers of gametes with different amounts of cytoplasm. Compare and contrast the processes of spermatogenesis and oogenesis Oogenesis Spermatogenesis Cell division Begin with mitosis and later on involve meiosis Growth Involve cell enlargement before meiosis Product Haploid cells (gametes) Differentiation Produce specialised gametes Location Eggs/ova produced in the ovaries Sperm produced in the testes Initiated During development of fetus During puberty Pauses During prophase I and between prophase II and metaphase II None cytokinesis Unequal, producing polar bodies Equal Number of gametes One ova, polar bodies degenerate Four sperm Release 14th day, midpoint of the menstrual cycle Continuous production, released during sexual intercourse Ceases At the menopause Continuous until death (8 marks)
- 23. 11.4.U3 Fertilization in animals can be internal or external. http://www.bio1100.nicerweb.com/Locked/media/SAVE/ch31/31_08.jpg https://i.ytimg.com/vi/q50Yphp1gzI/maxresdefault.jpg In some aquatic species fertilisation is external (e.g. fish and amphibians) ; eggs are released followed shortly by sperm. This method of fertilisation is susceptible to environmental variation and therefore animals that use it often produce large quantities of eggs and sperm to compensate for losses. Terrestrial animals (e.g. reptiles, birds and mammals) are mostly internal fertilisers to prevent dehydration of gametes or the developing embryo. Sperm is deposited into the female, in easy reach of the ova, during intercourse. Internal and external Fertilization
- 24. 11.4.U4 Fertilization involves mechanisms that prevent polyspermy. There is more to fertilisation than the fusion of the gametes http://www.abpischools.org.uk/res/coResourceImport/ modules/genome/en-flash/fertilisation.swf Why can only a single sperm fertilise an ova, what prevents polyspermy? How does the sperm penetrate the zona pellucida? What causes the pause in the ova’s meiosis process to continue?
- 25. 11.4.U4 Fertilization involves mechanisms that prevent polyspermy. 1. The sperm pushes through the follicular cells and binds to receptors in the zona pellucida Fertilisation https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acrosome_reaction_diagram_en.svg 2. Enzymes are released from the acrosome and digest the glycoprotein based zona pellucida http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pat hphys/reprod/fert/fert.html
- 26. 11.4.U4 Fertilization involves mechanisms that prevent polyspermy. 1. The sperm pushes through the follicular cells and binds to receptors in the zona pellucida Fertilisation https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acrosome_reaction_diagram_en.svg 2. Enzymes are released from the acrosome and digest the glycoprotein based zona pellucida 2. The membranes of the sperm and the ova fuse this stimulates: a. By exocytosis cortical granules (vesicles) release proteases (enzymes) into the zona pellucida causing the zona pellucida to ‘harden’ and become inpenetrable to (subsequent) sperm, preventing polyspermy. a. An influx of Ca2+ into the ova which prompts the completion of meiosis II http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hb ooks/pathphys/reprod/fert/fert.ht ml
- 27. 11.4.U4 Fertilization involves mechanisms that prevent polyspermy. 1. The sperm pushes through the follicular cells and binds to receptors in the zona pellucida Fertilisation https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acrosome_reaction_diagram_en.svg 2. Enzymes are released from the acrosome and digest the glycoprotein based zona pellucida 2. The membranes of the sperm and the ova fuse this stimulates: a. By exocytosis cortical granules (vesicles) release proteases (enzymes) into the zona pellucida causing the zona pellucida to ‘harden’ and become inpenetrable to (subsequent) sperm, preventing polyspermy. a. An influx of Ca2+ into the ova which prompts the completion of meiosis II 4. The nucleus of the sperm cell is deposited into the ova’s cytoplasm and subsequently fuses with the ova’s nucleus forming a diploid zygote (cell).
- 28. 11.4.U5 Implantation of the blastocyst in the endometrium is essential for the continuation of pregnancy. Blastocyst formation occurs in the fallopian tubes and uterus prior to implantation. When the blastocyst reaches the uterus, it will embed itself in the endometrium. Once implanted the developing embryo will gain nutrients and oxygen from the endometrium tissue fluid which is supplied, in turn, by a the endometrium’s capillary network. http://www.ib.bioninja.com.au/_Media/blastocyst_med.jpeg http://www.as.wvu.edu/~sraylman/physiology/cleavage_impl ant.swf Implantation of the blastocyst A ball of cells called a morula form after a series of mitotic divisions The ball of cells continues to divide, but unequally forming a fluid-filled cavity in the middle - this is now termed a blastocyst which consists of: • Inner mass of cells (develops into the embryo) • Outer layer (develops into the placenta) • A fluid filled cavity
- 29. 11.4.U6 HCG stimulates the ovary to secrete progesterone during early pregnancy. So can you explain why during pregnancy … … menstruation ceases? … no further mature eggs are released? (think about what you know from 6.6)
- 30. 11.4.U6 HCG stimulates the ovary to secrete progesterone during early pregnancy.
- 31. 11.4.U8 Estrogen and progesterone are secreted by the placenta once it has formed. *The placenta takes over the hormonal role of the corpus luteum at about week ten of the pregnancy: • HCG initially maintains the corpus luteum • Estrogen maintains the lining of the uterus • Progesterone maintains the endometrium and prevents contractions *
- 32. 11.4.U7 The placenta facilitates the exchange of materials between the mother and fetus. Chorionic villi increase surface area for exchange of substances Placental (chorionic) cells secrete hormones, e.g. HCG, oestrogen and progesterone.
- 33. 11.4.U9 Birth is mediated by positive feedback involving estrogen and oxytocin. The process of birth is stimulated by the rise in estrogen levels. As estrogen increases it is no longer inhibited by progesterone and therefore it initiates contracting in the (smooth) muscular wall of the uterus. The contractions stimulate stretch receptors signal the brain to release oxytocin from the pituitary gland. Oxytocin also stimulates the muscle of the uterine wall and contractions to grow stronger. The contractions again stimulate stretch receptors causing more oxytocin Contractions continue for short time after birth to eject the placenta. As the stretch receptors are no longer stimulated oxytocin levels fall and contractions cease. Positive feedback Hormonal control of birth
- 34. 11.4.A1 The average 38-week pregnancy in humans can be positioned on a graph showing the correlation between animal size and the development of the young at birth for other mammals. http://jeb.biologists.org/content/208/9/1731 The graph shows the relationship between (adult) body mass and gestation period (pregnancy) in a range of mammals. (g) (days) Adult size and development of newborn young in mammals Altricial mammals give birth to relatively helpless, incompletely developed offspring. Precocial mammals give birth to offspring that are mobile and able to defend themselves. These are in reality extremes on a scale. Although there is a definite positive correlation between body mass and gestation period there are mammals with the same gestation period but widely varying body masses (by an order greater than 103). The general rule is that animals with a long gestation periods give birth to offspring who are more developed at the time of birth. humans
- 35. Bibliography / Acknowledgments Bob Smullen