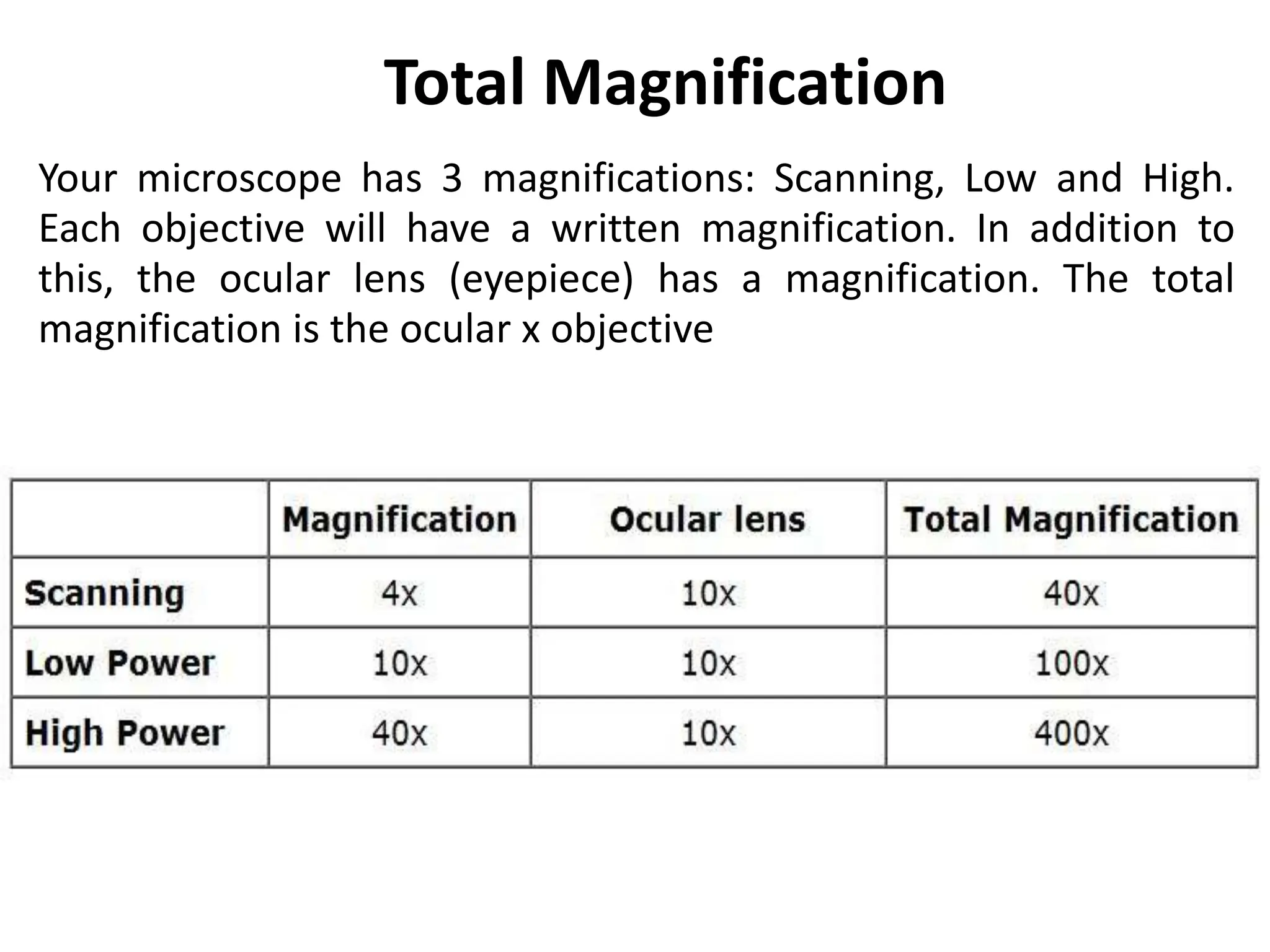
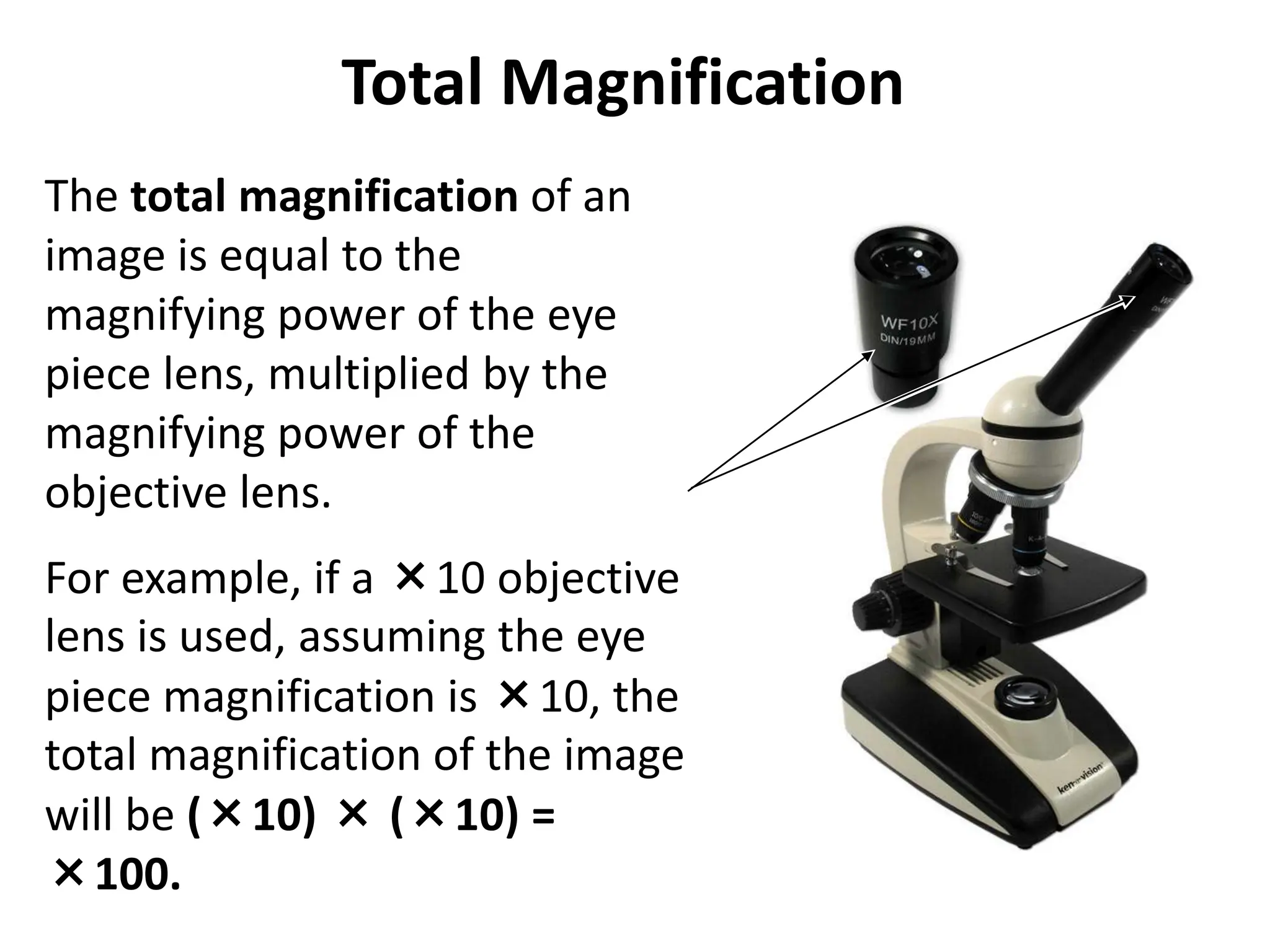
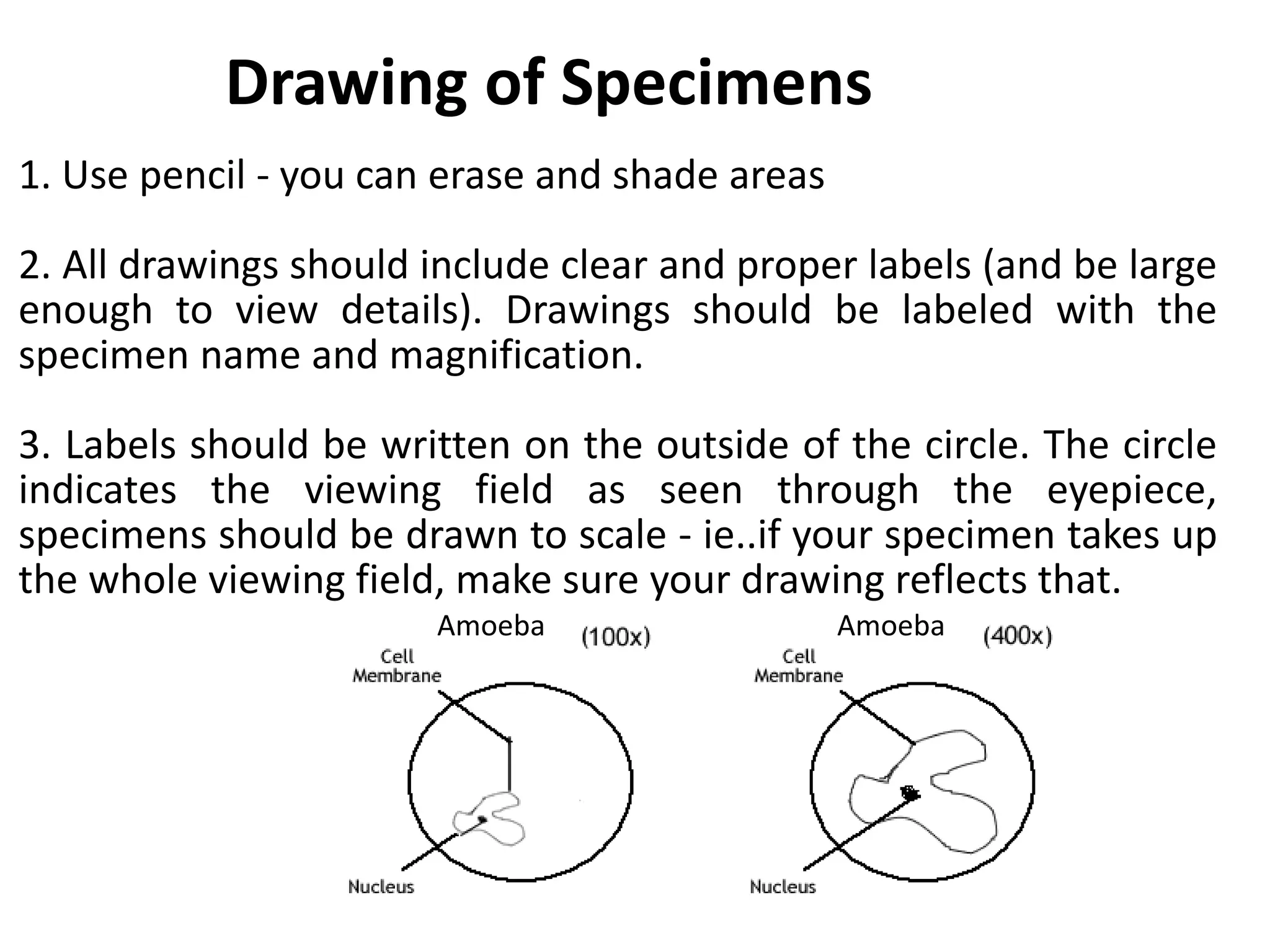
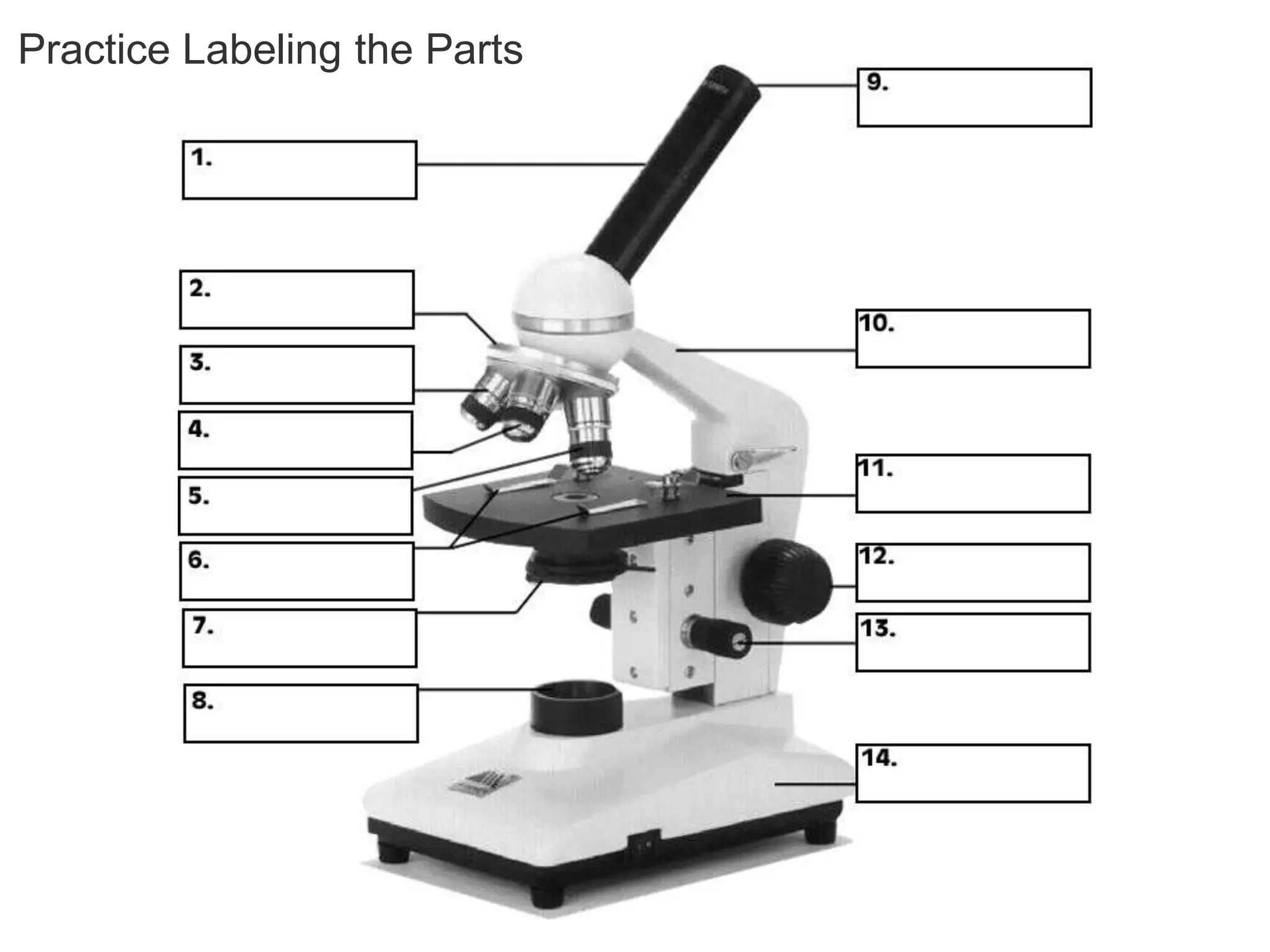
Here are the key points about types of light microscopes:
- Compound light microscopes are the most common type found in classrooms and labs. They use a system of multiple lenses (objective and eyepiece lenses) to magnify specimens. The magnification is calculated by multiplying the objective and eyepiece powers.
- Stereo microscopes are used to view three-dimensional specimens. They have two separate optical paths to provide binocular vision. This allows depth perception which is useful for tasks like dissection.
- Inverted or upside-down microscopes have their objectives below the stage to allow viewing live cell cultures or other transparent samples from below. This is important for studies of living cells and organisms without disturbing the