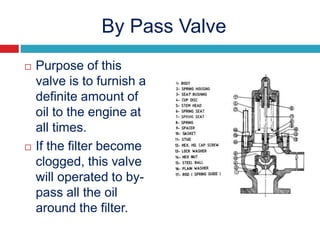
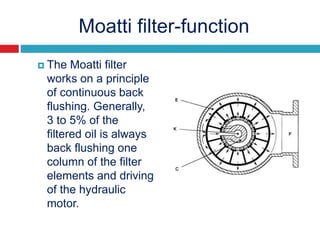
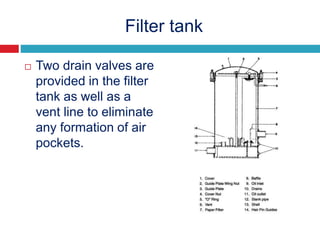
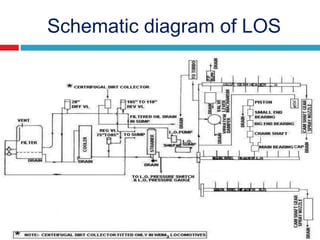
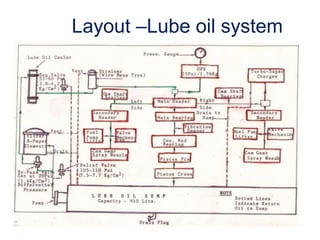
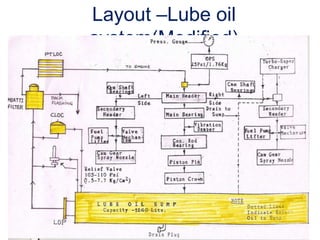
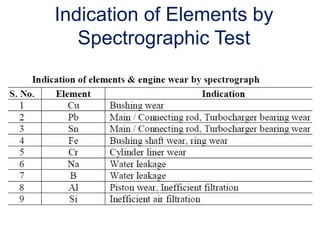
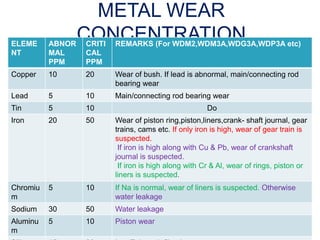
The document provides information about the components, purpose, and operation of a lube oil system for diesel engines. It includes:
- A list of the main components of the lube oil system such as the lube oil pump, filter, cooler, sump, and their purposes.
- Schematic diagrams that illustrate the layout and flow of oil through the system to lubricate parts like the main bearings, connecting rod bearings, camshaft, and more.
- Descriptions of additional components like the relief and regulating valves that control oil pressure, and the centrifugal cleaner and filter that remove contaminants from the oil.
- Troubleshooting guidance for issues involving low oil pressure,