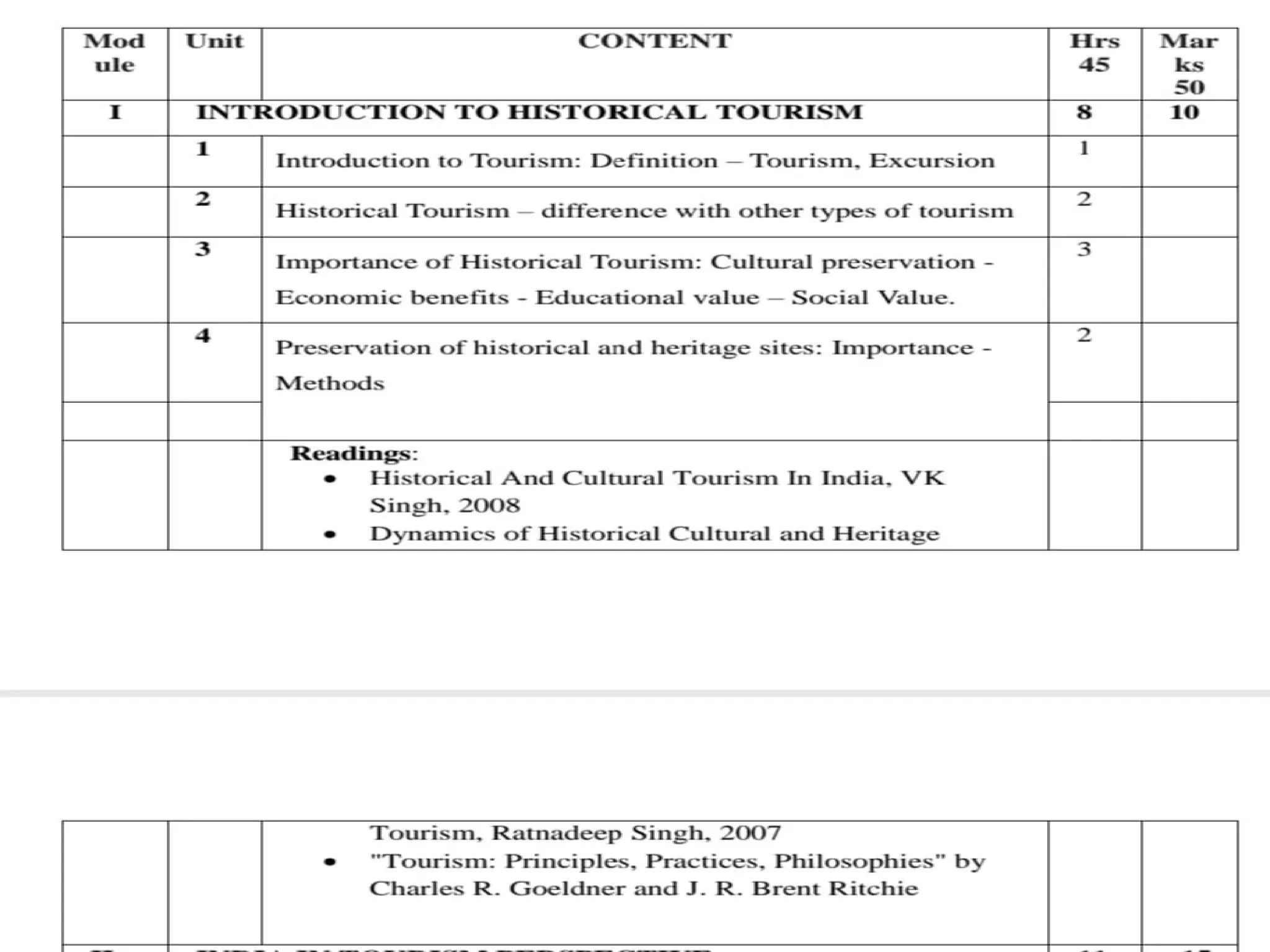
The document provides a comprehensive overview of historical tourism, defining tourism as the temporary movement of people to destinations outside their usual environment for leisure or business. It outlines various definitions from the League of Nations to the UNWTO, highlighting the industry's importance in economic growth and employment. The text also distinguishes between tourism and excursions, emphasizing the different purposes, durations, and scopes of each.