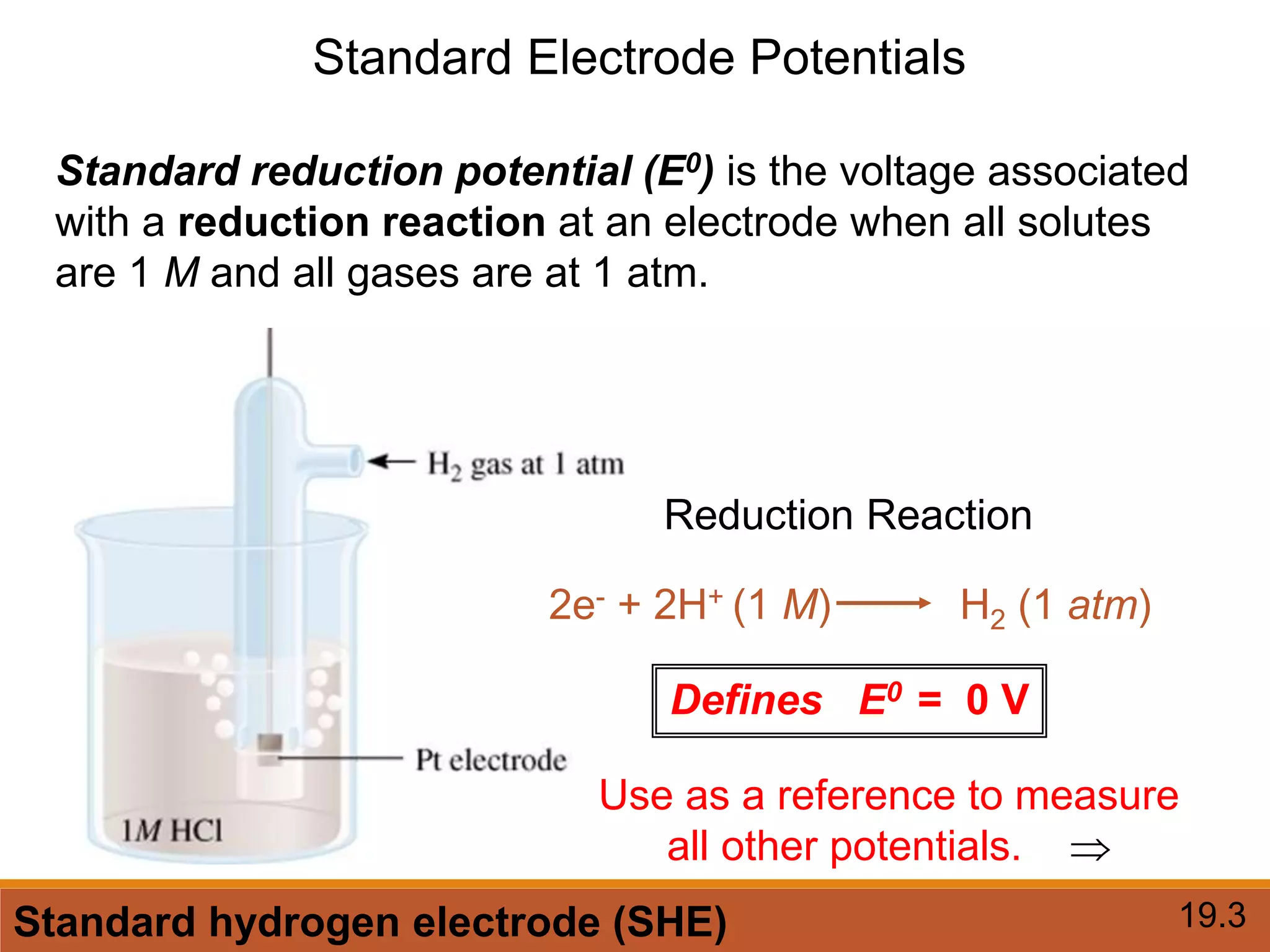
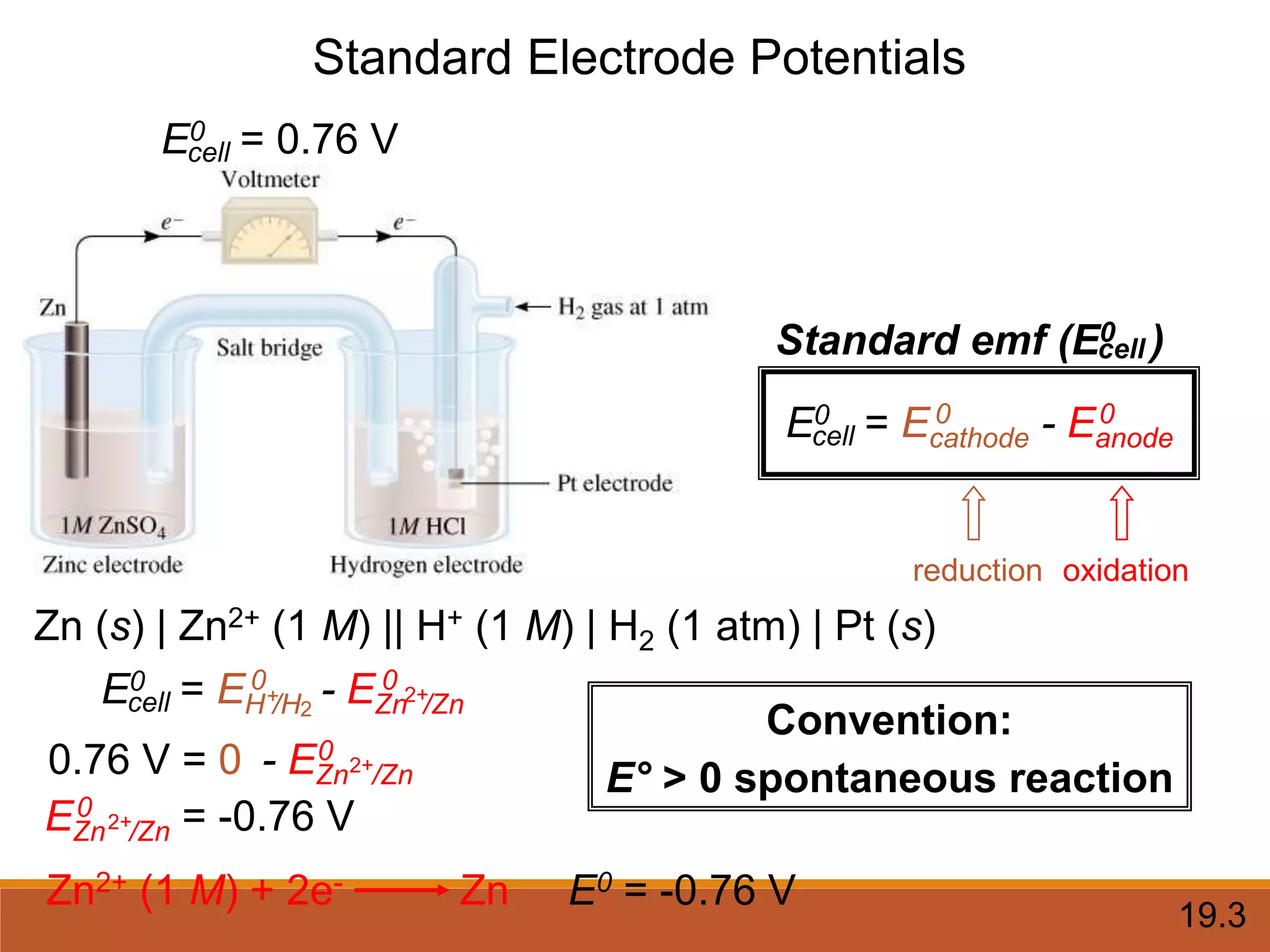
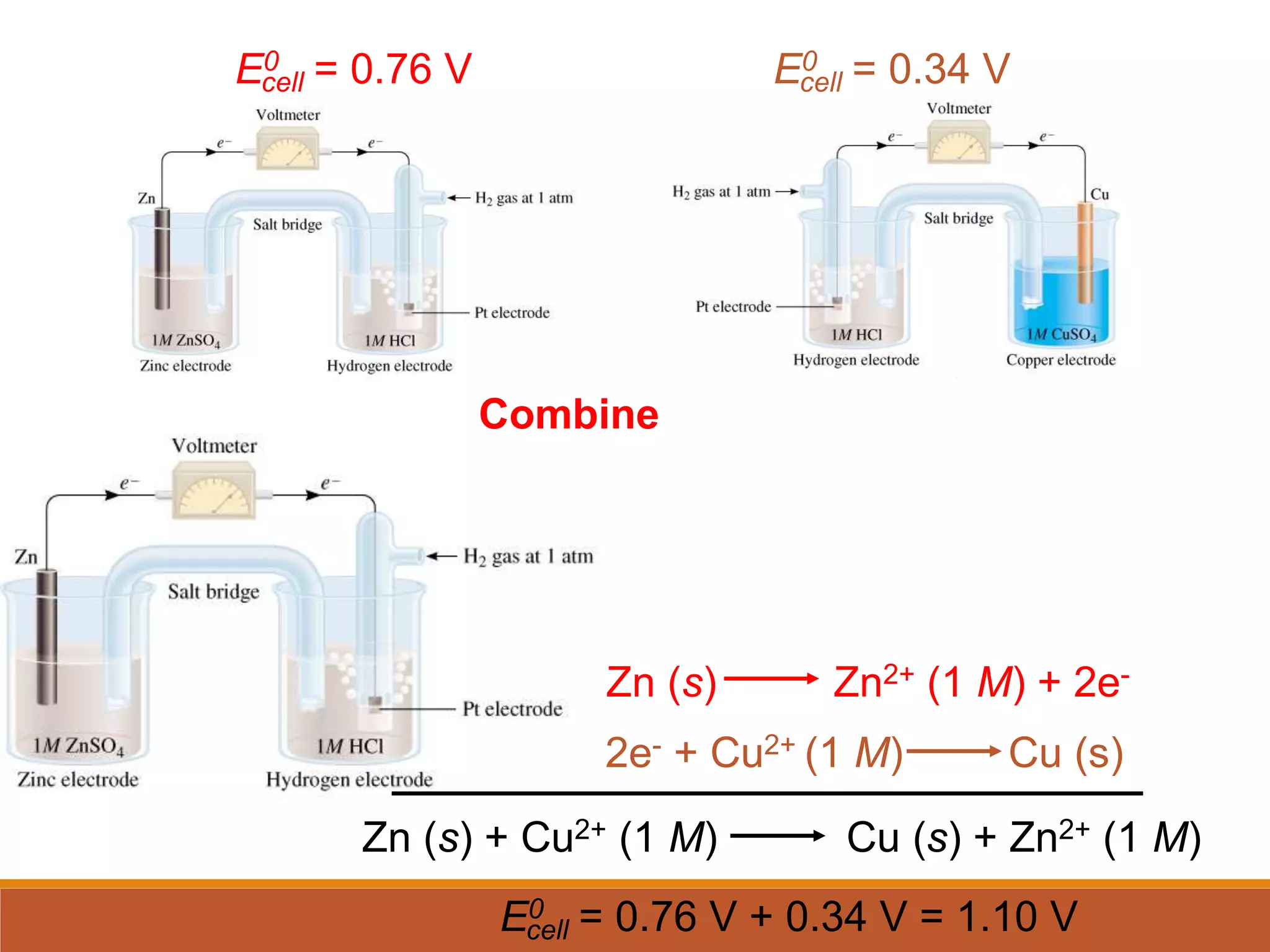
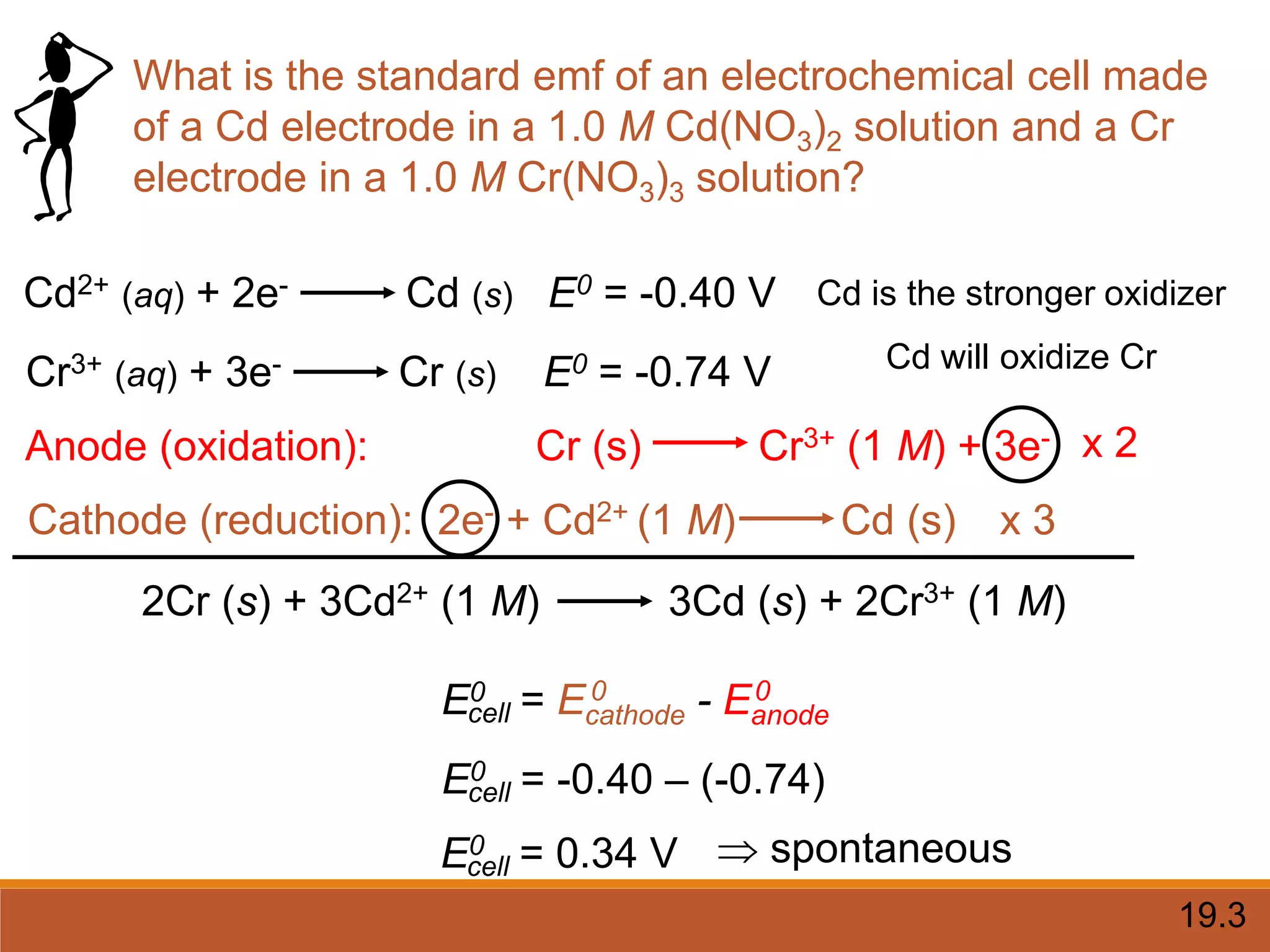
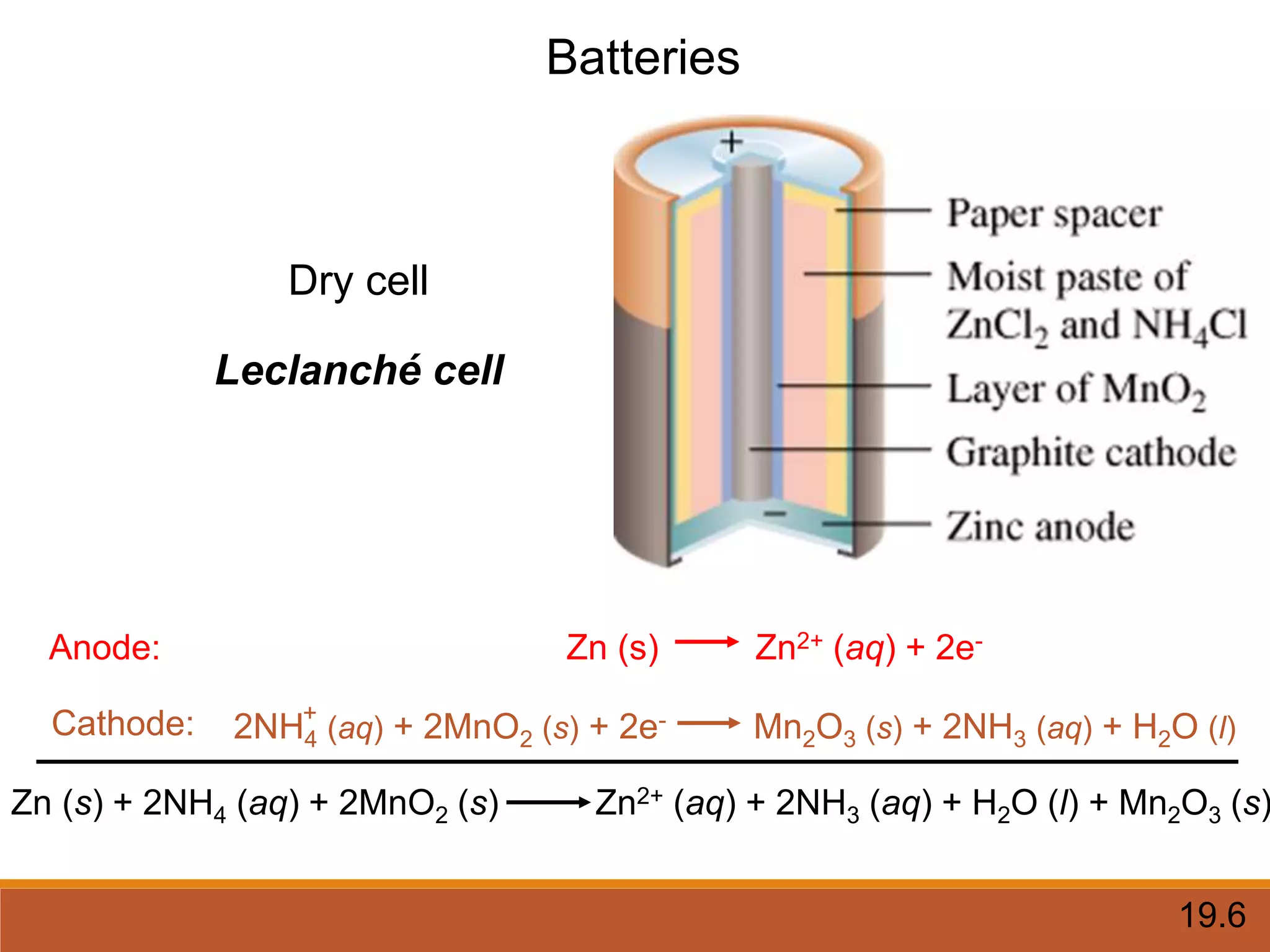
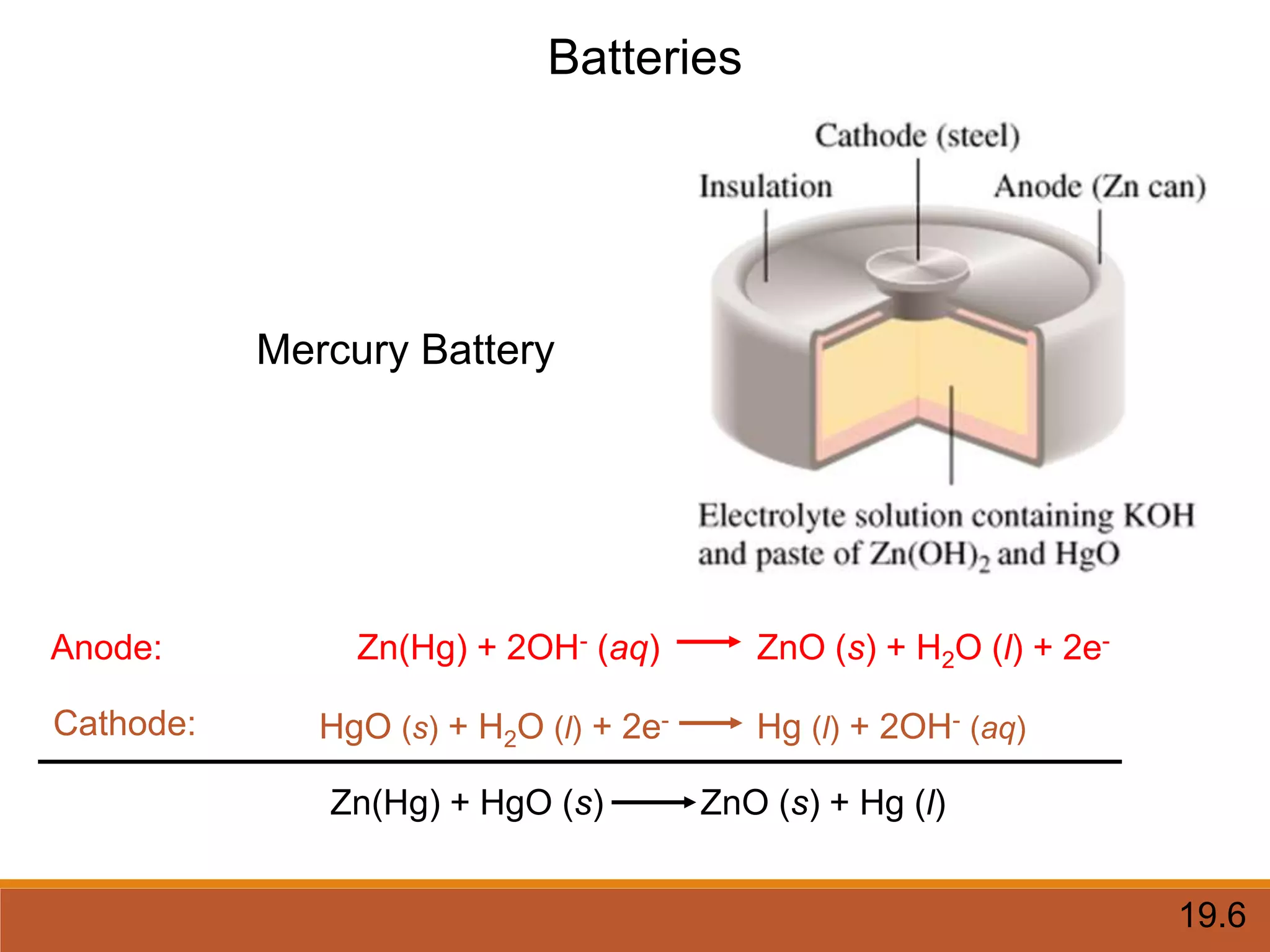
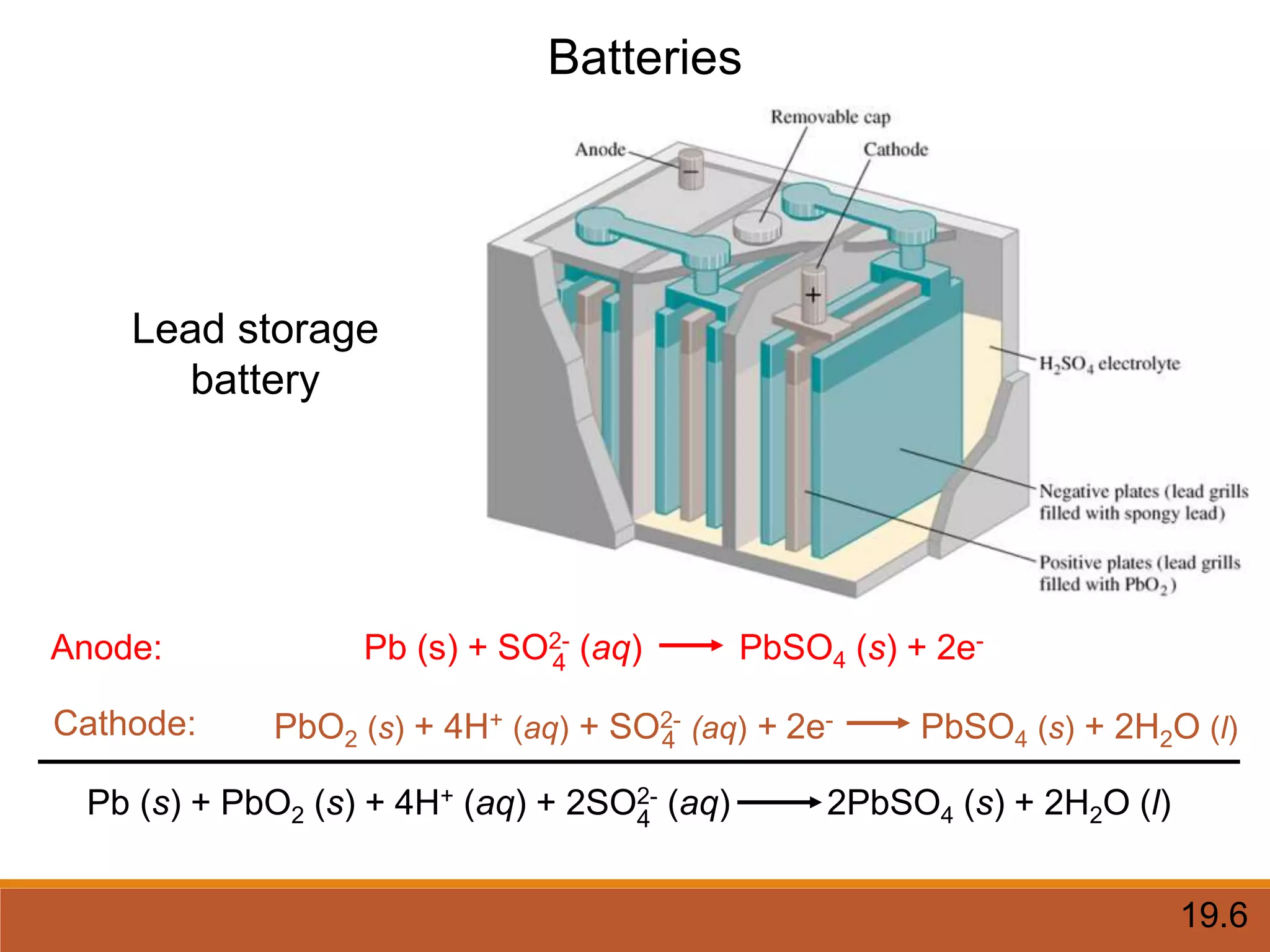
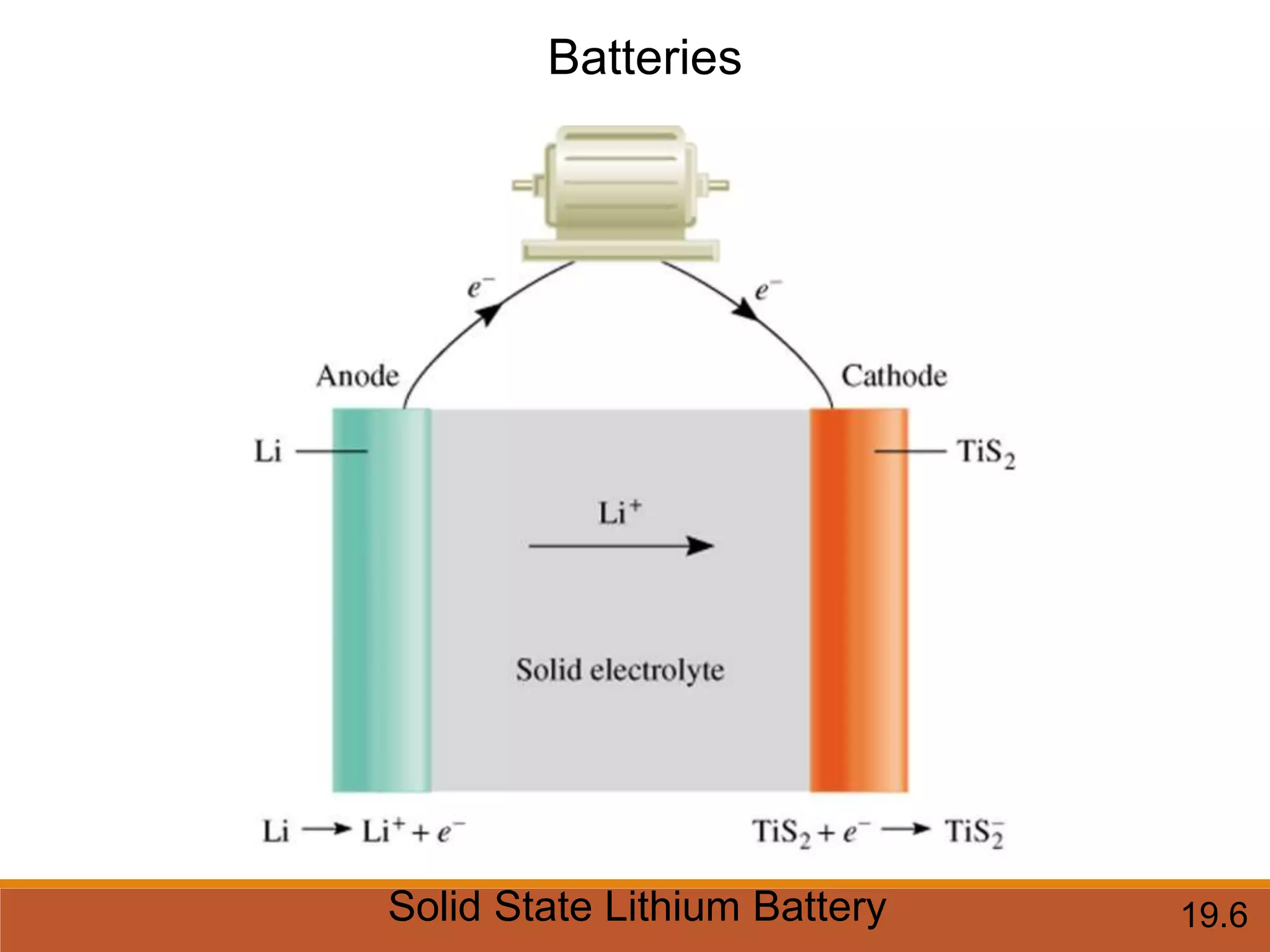
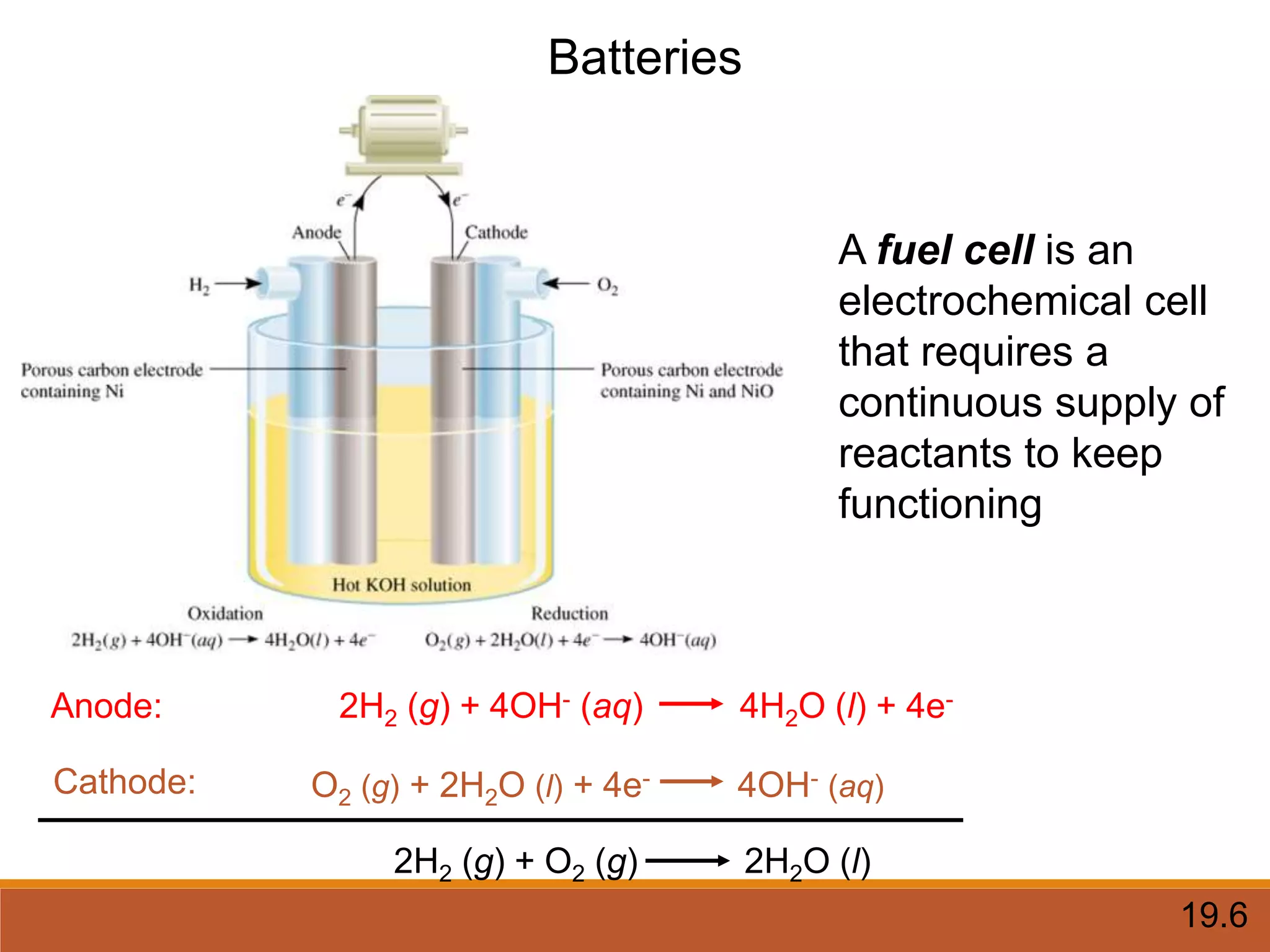
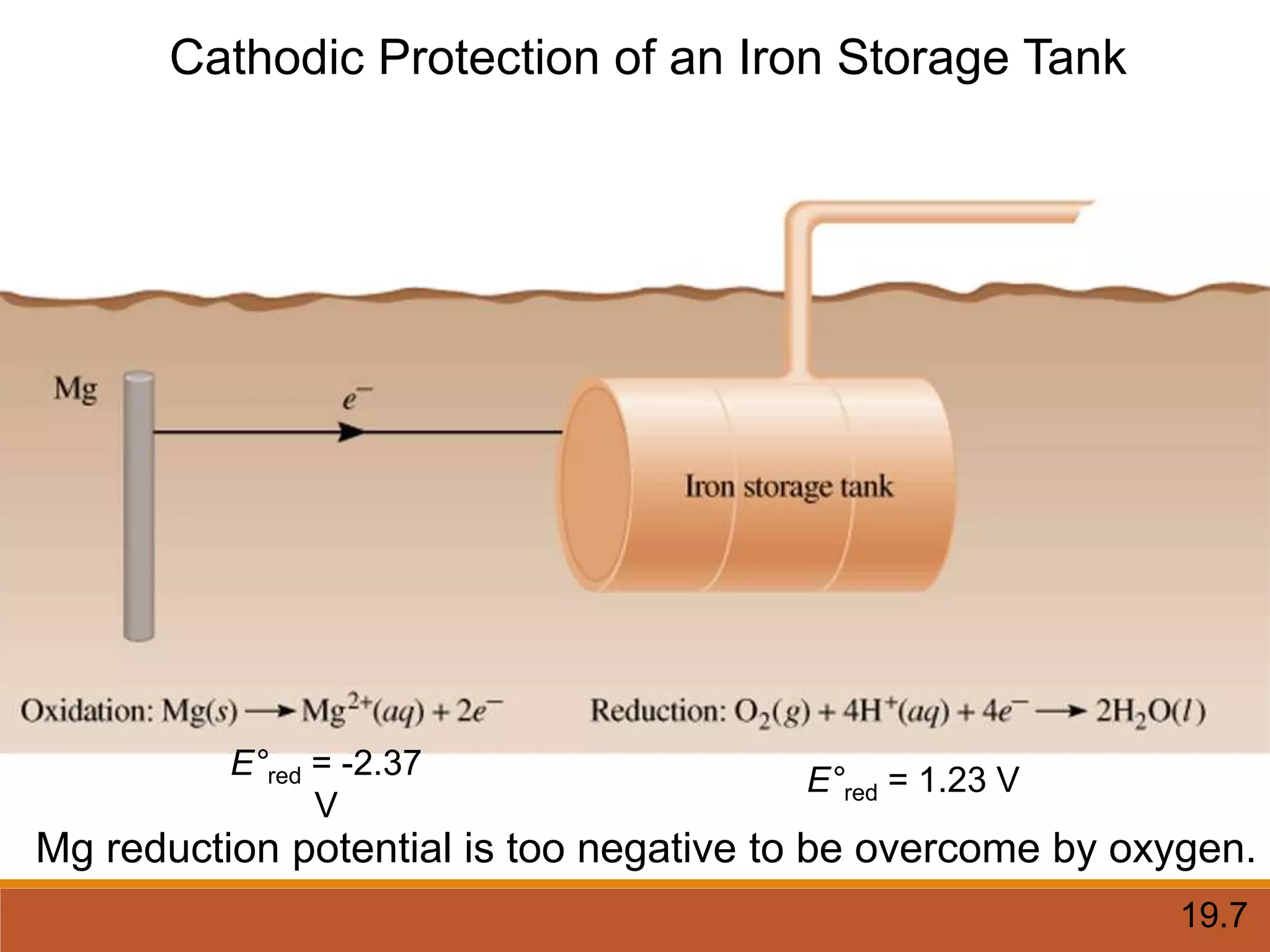
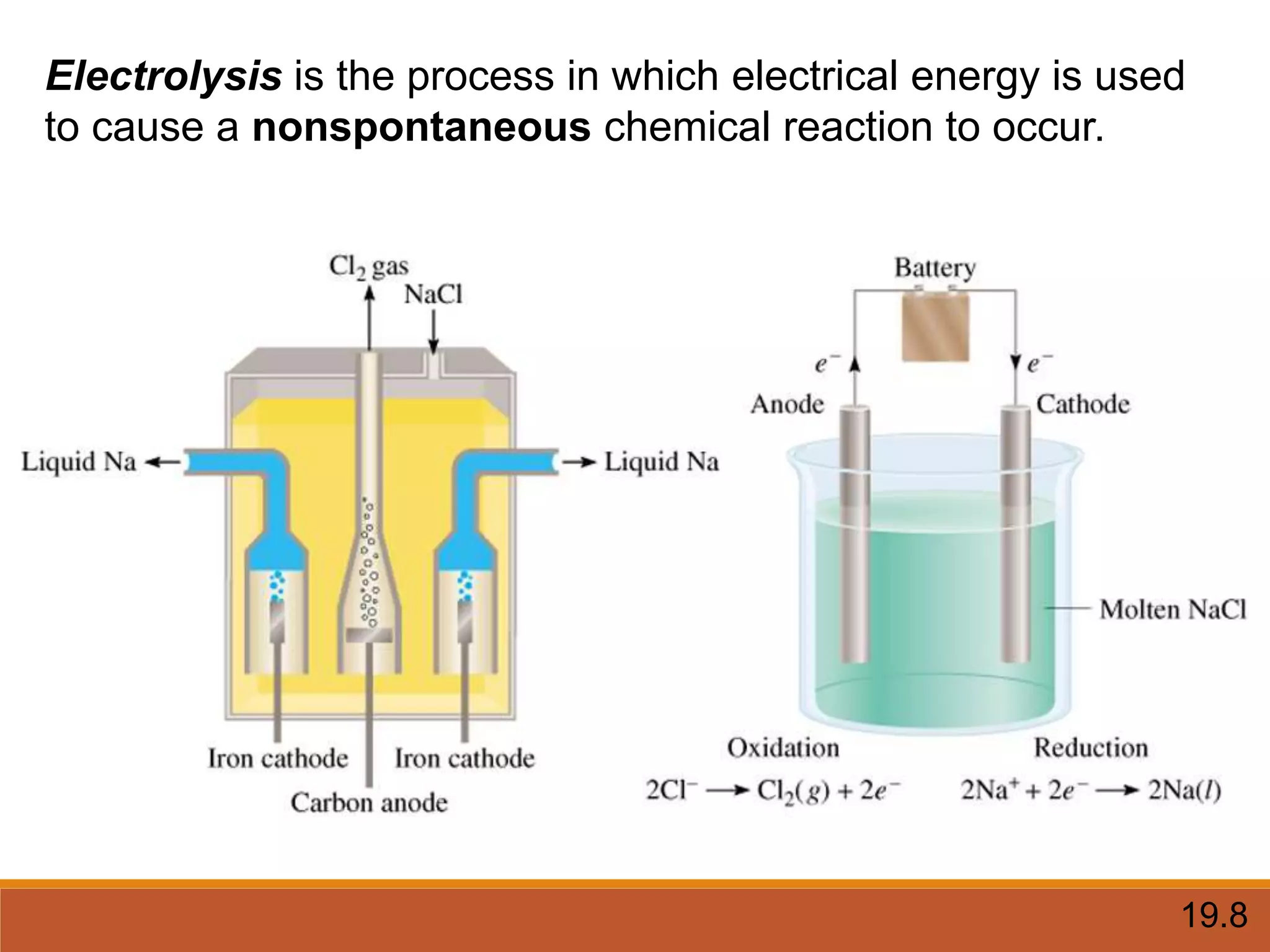
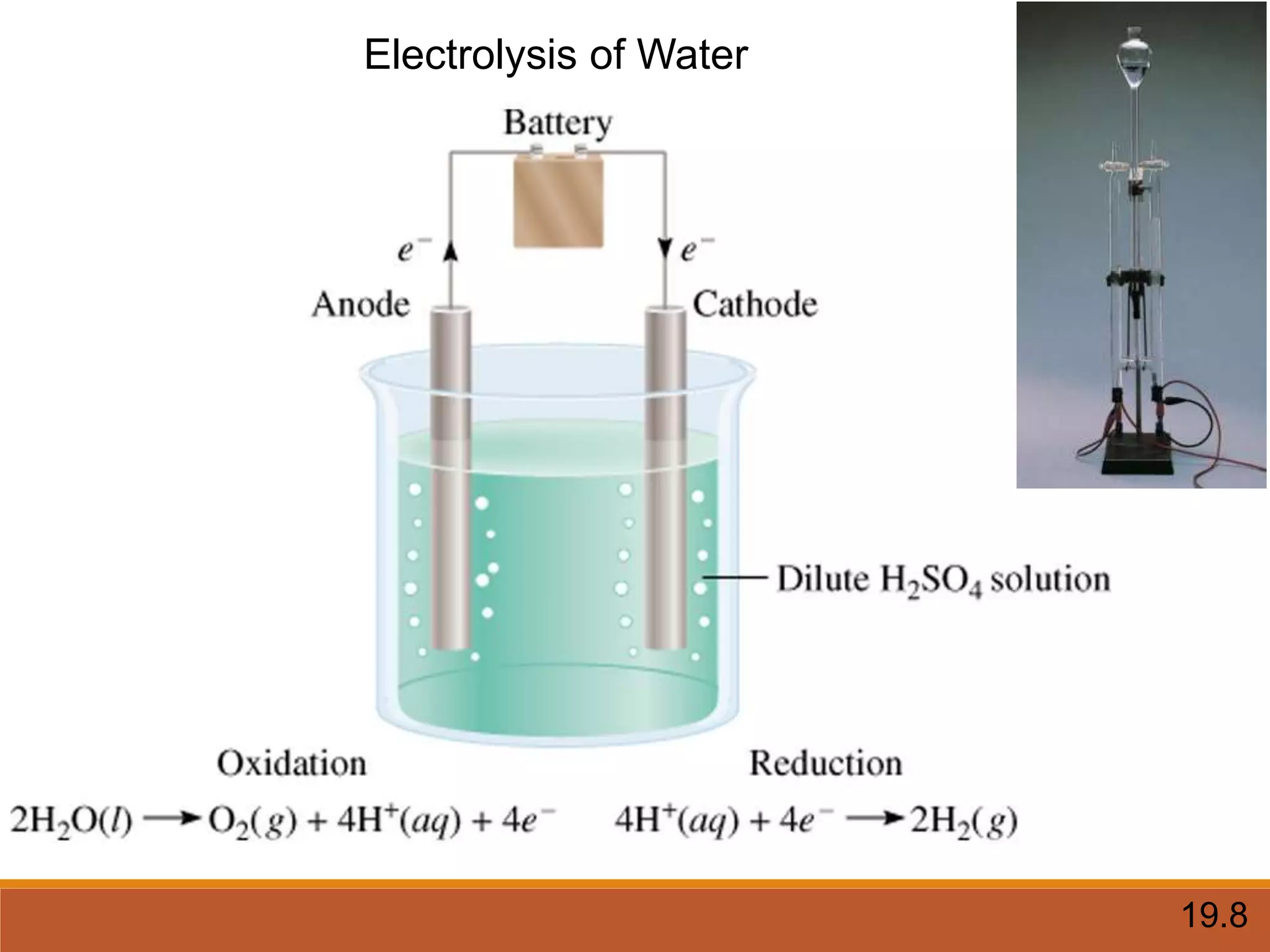
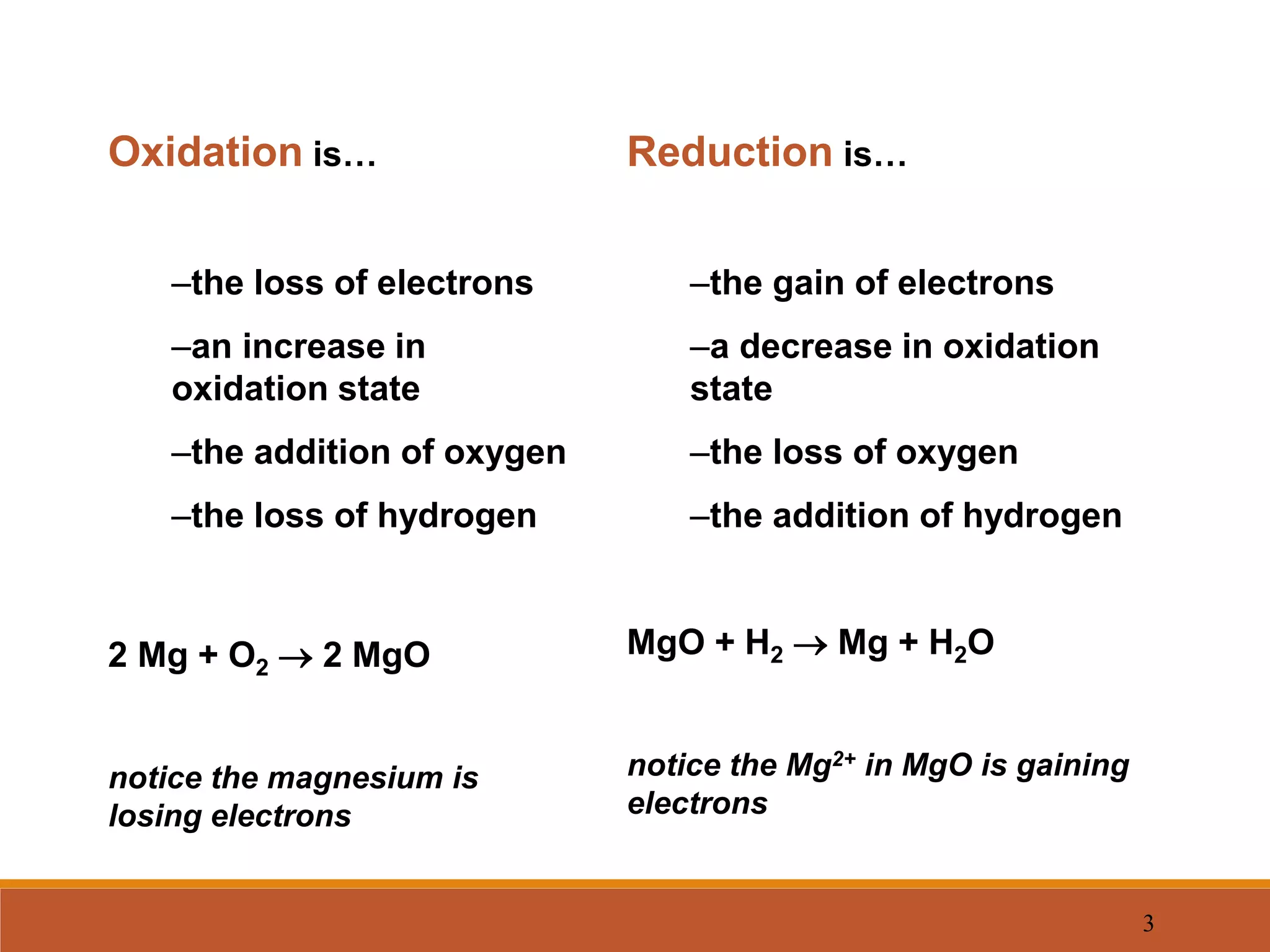
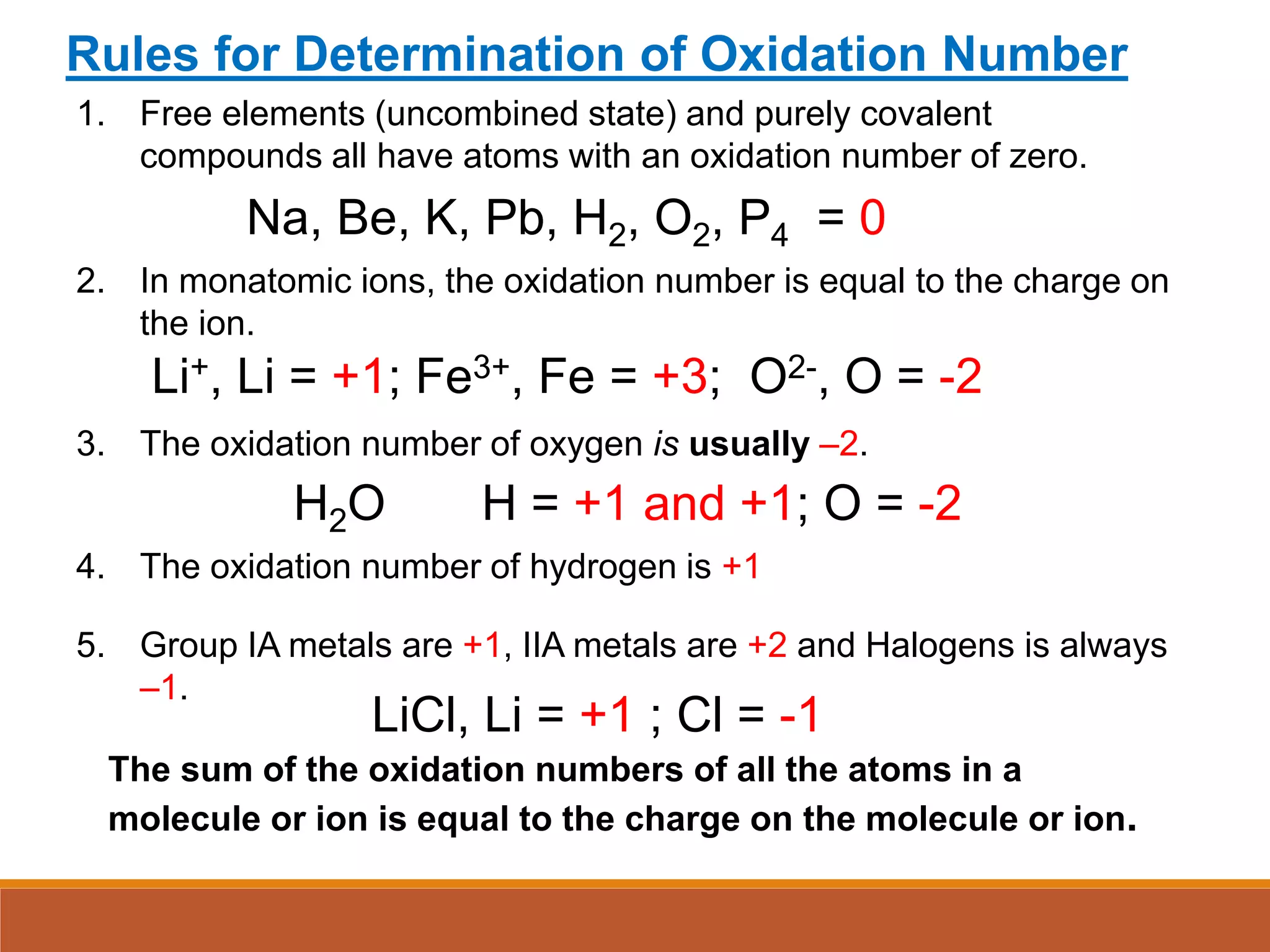
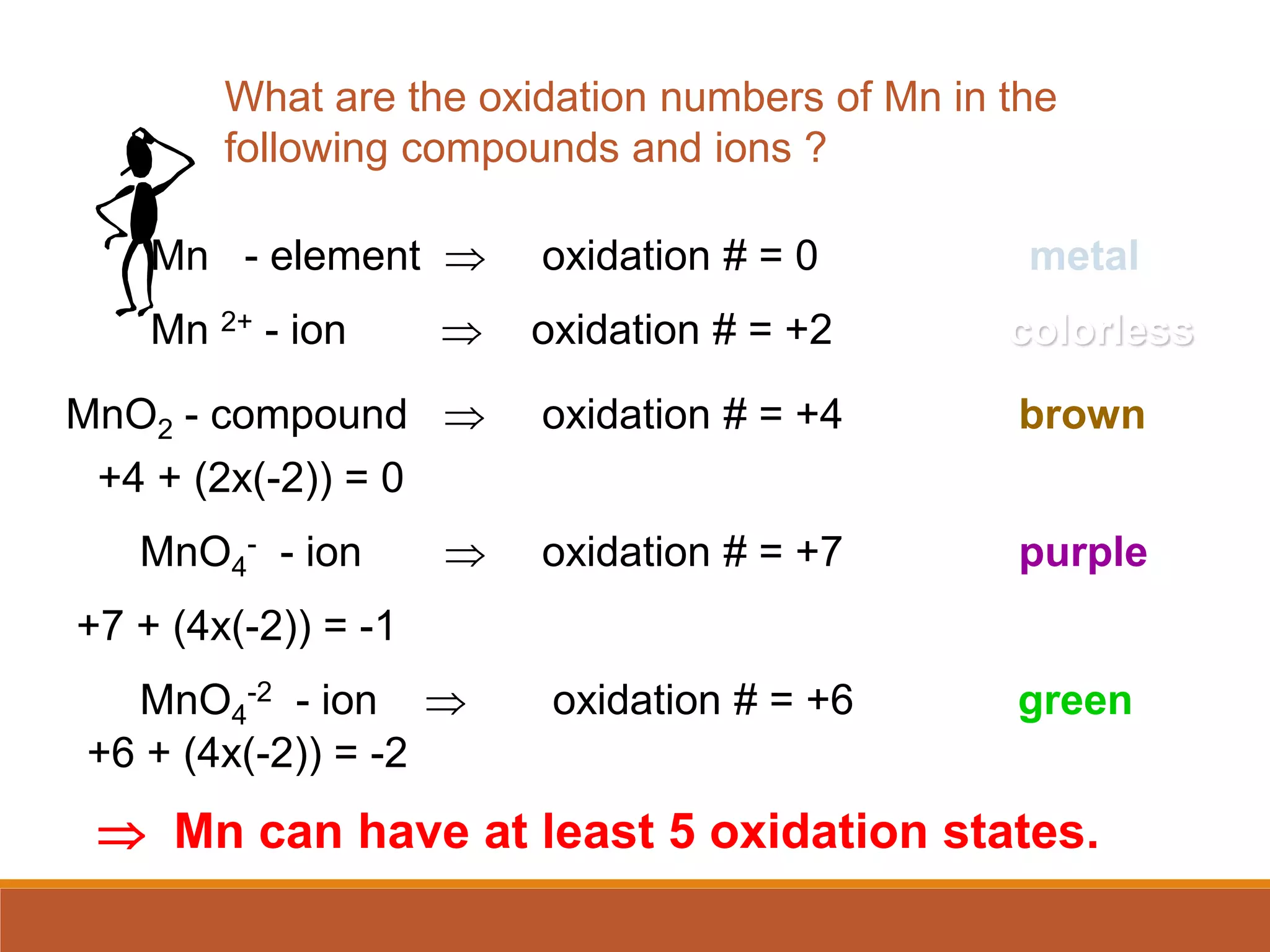
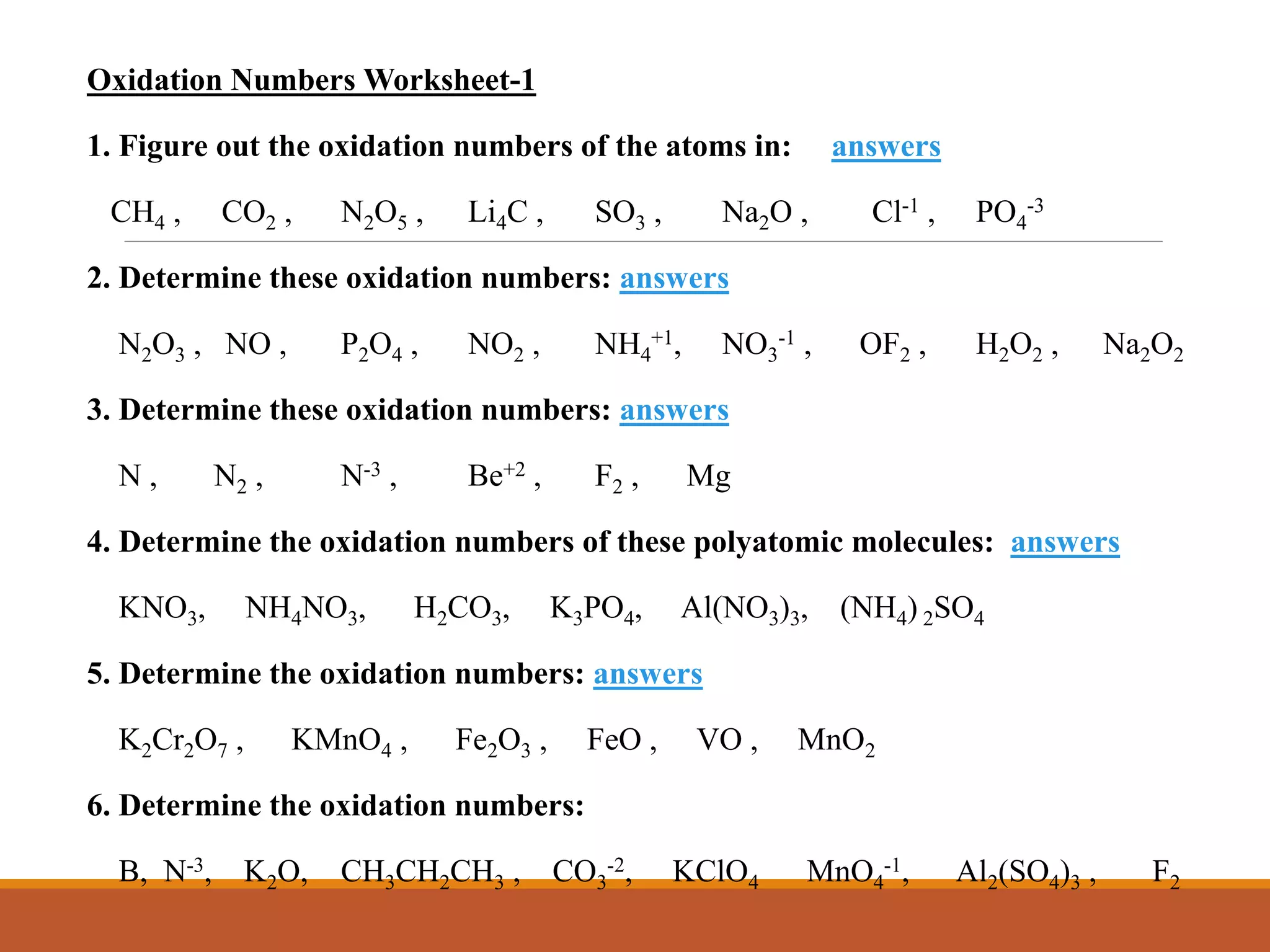
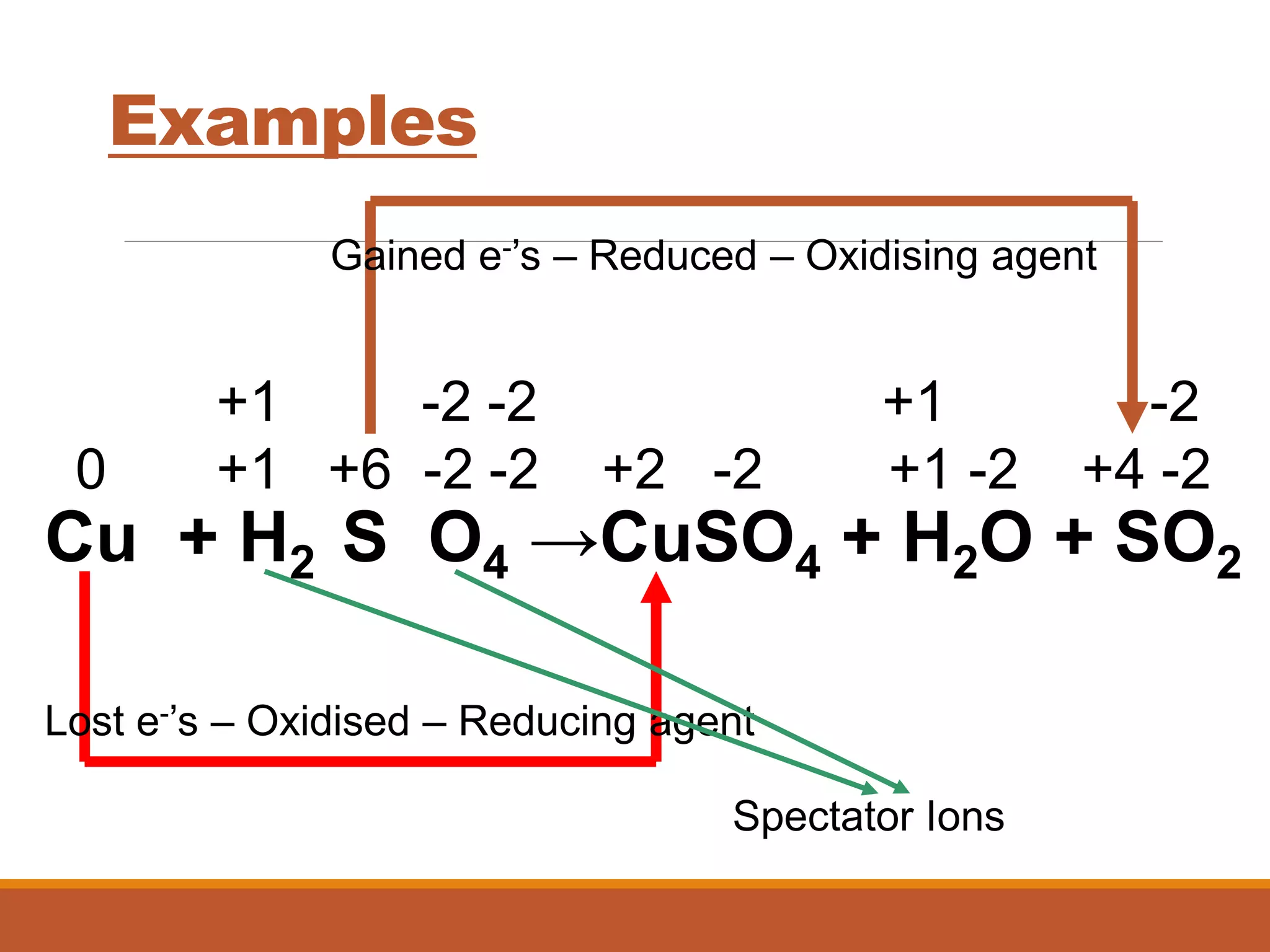
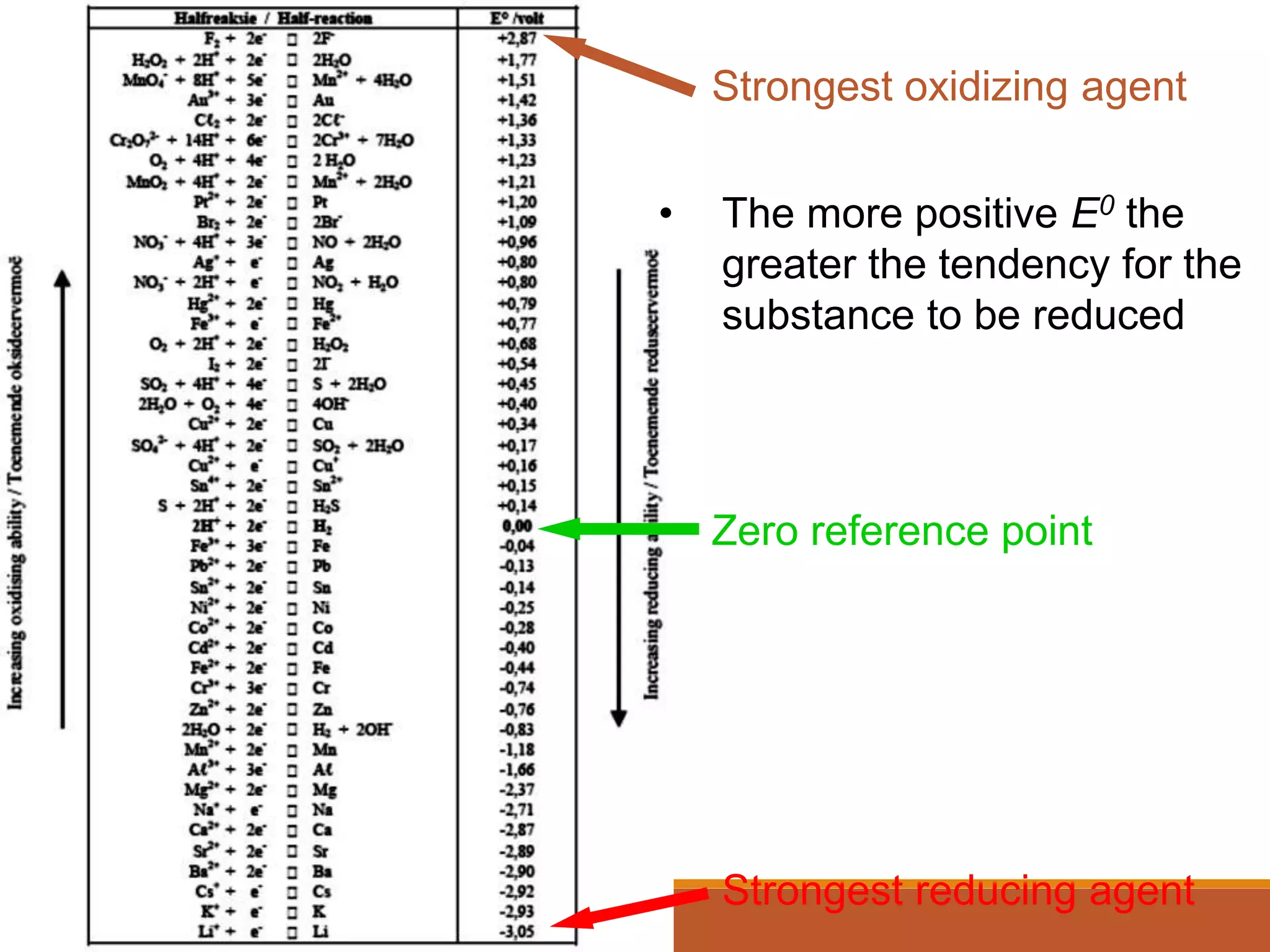
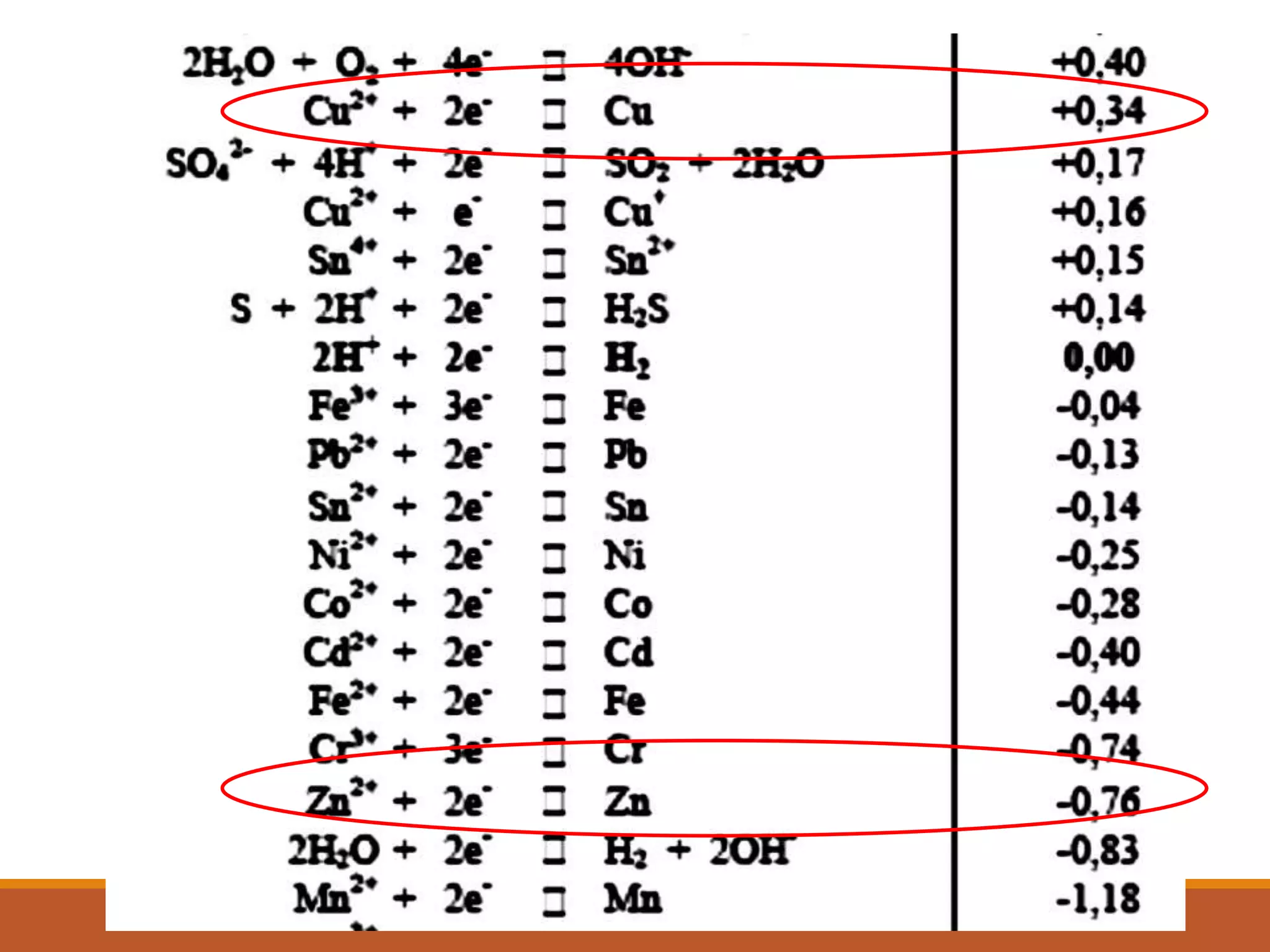
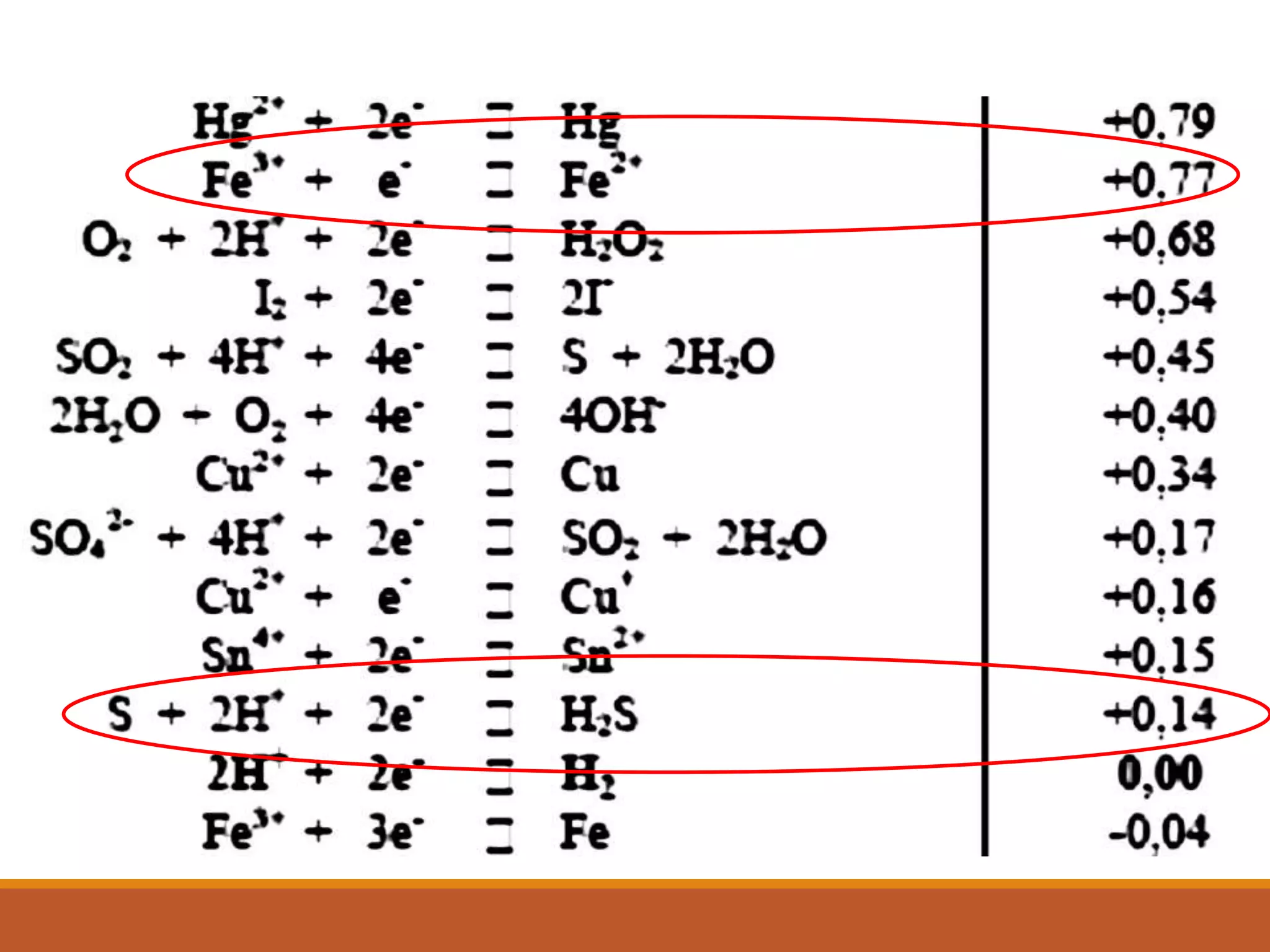
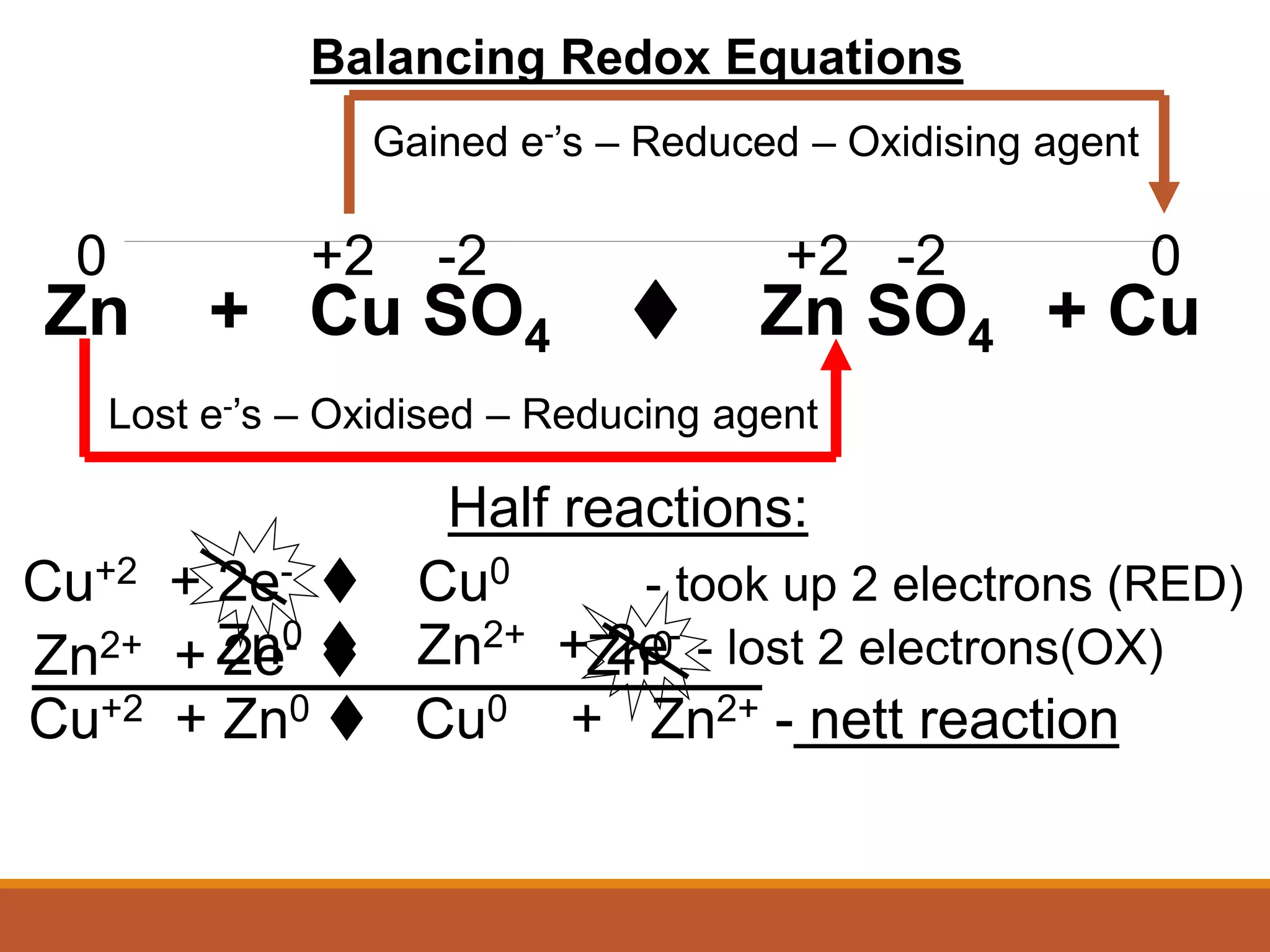
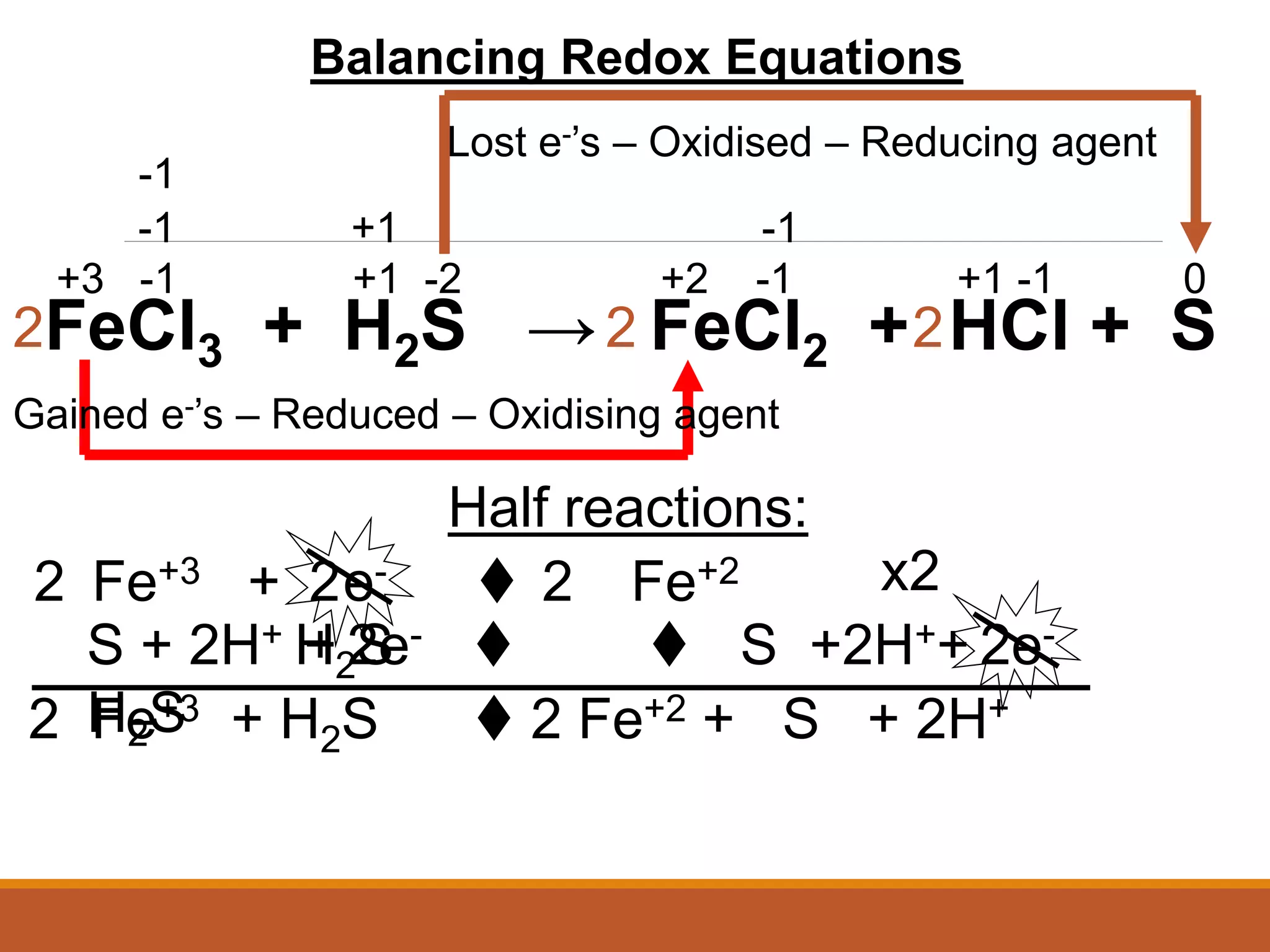
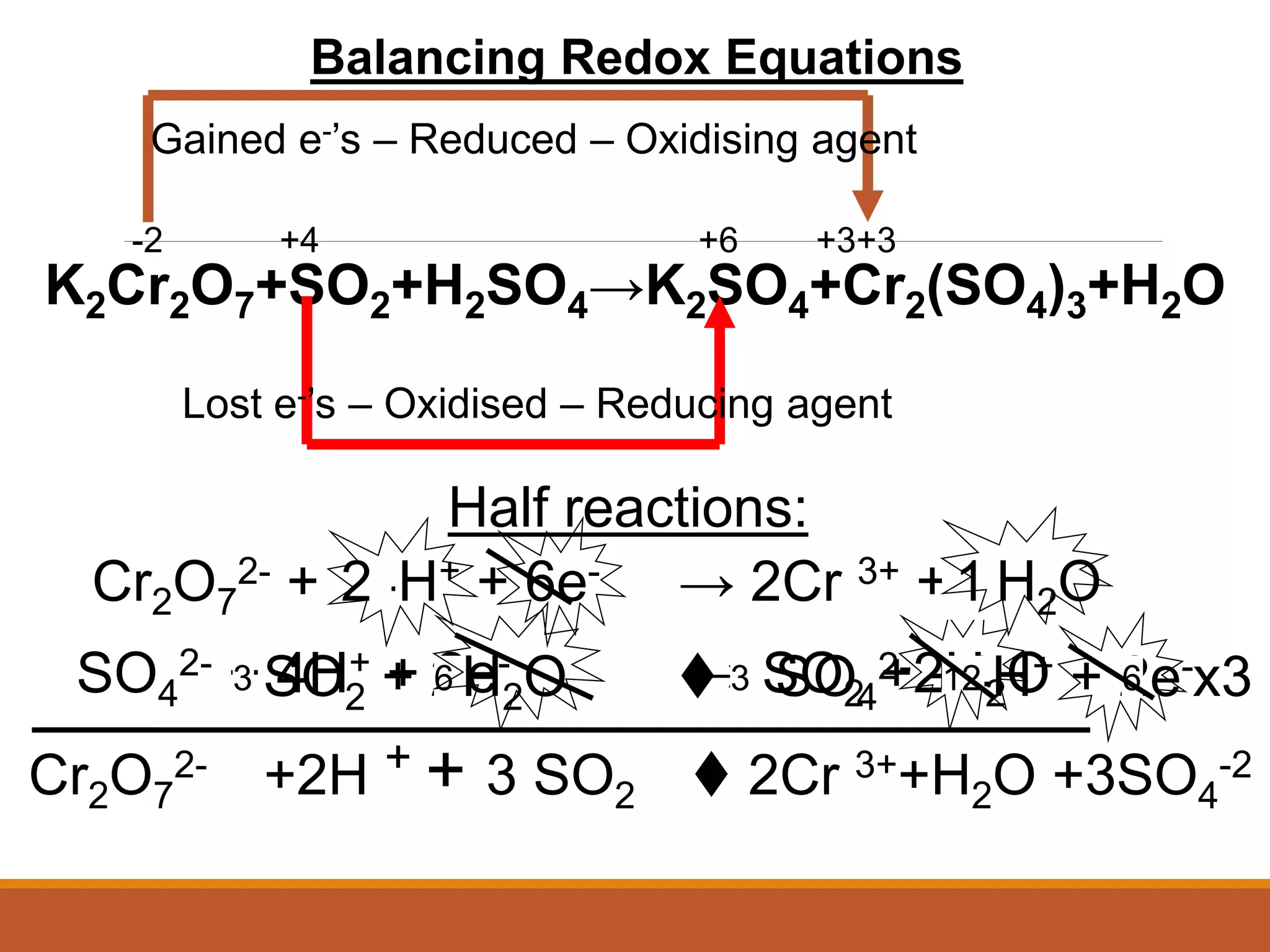
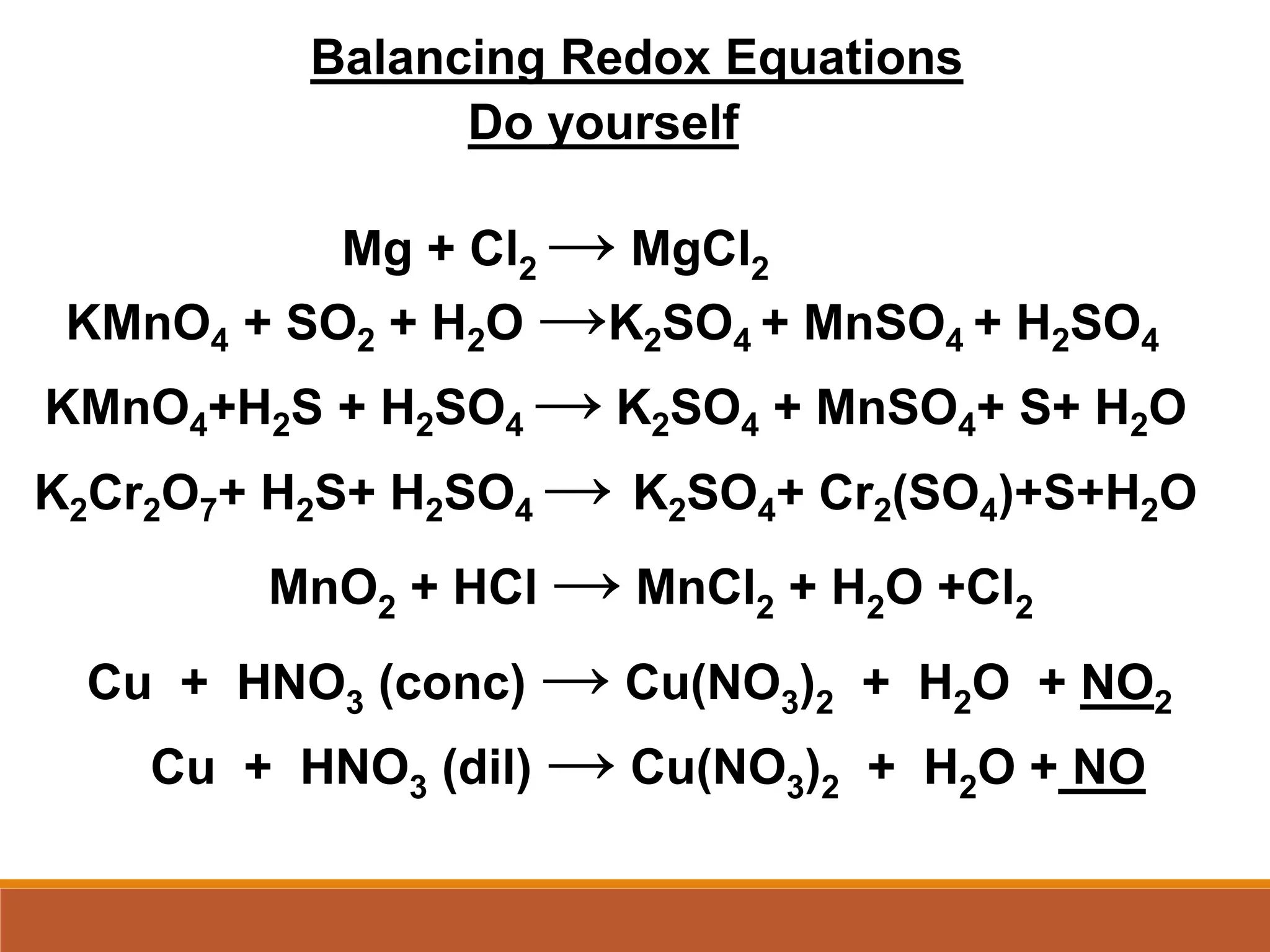
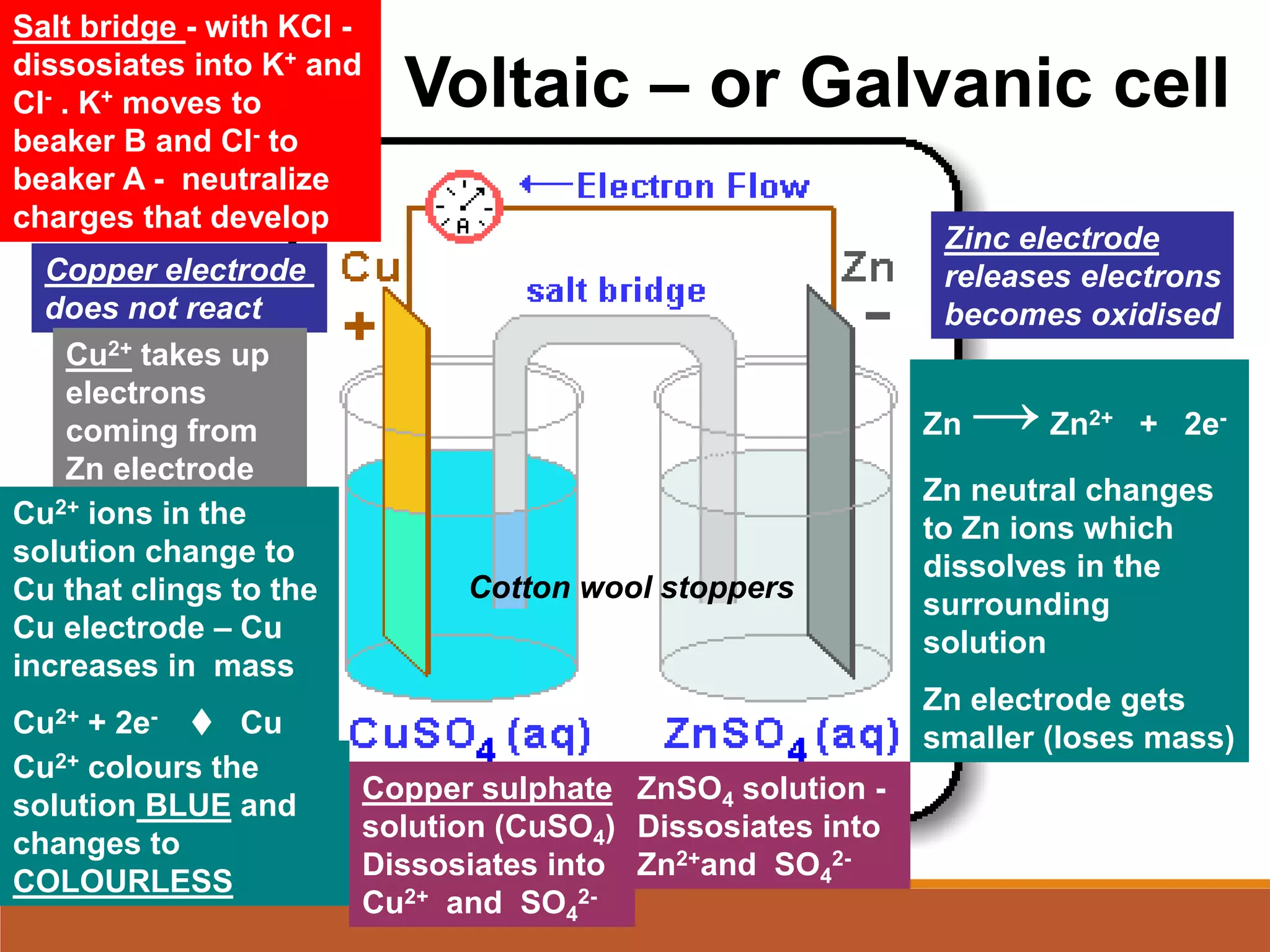
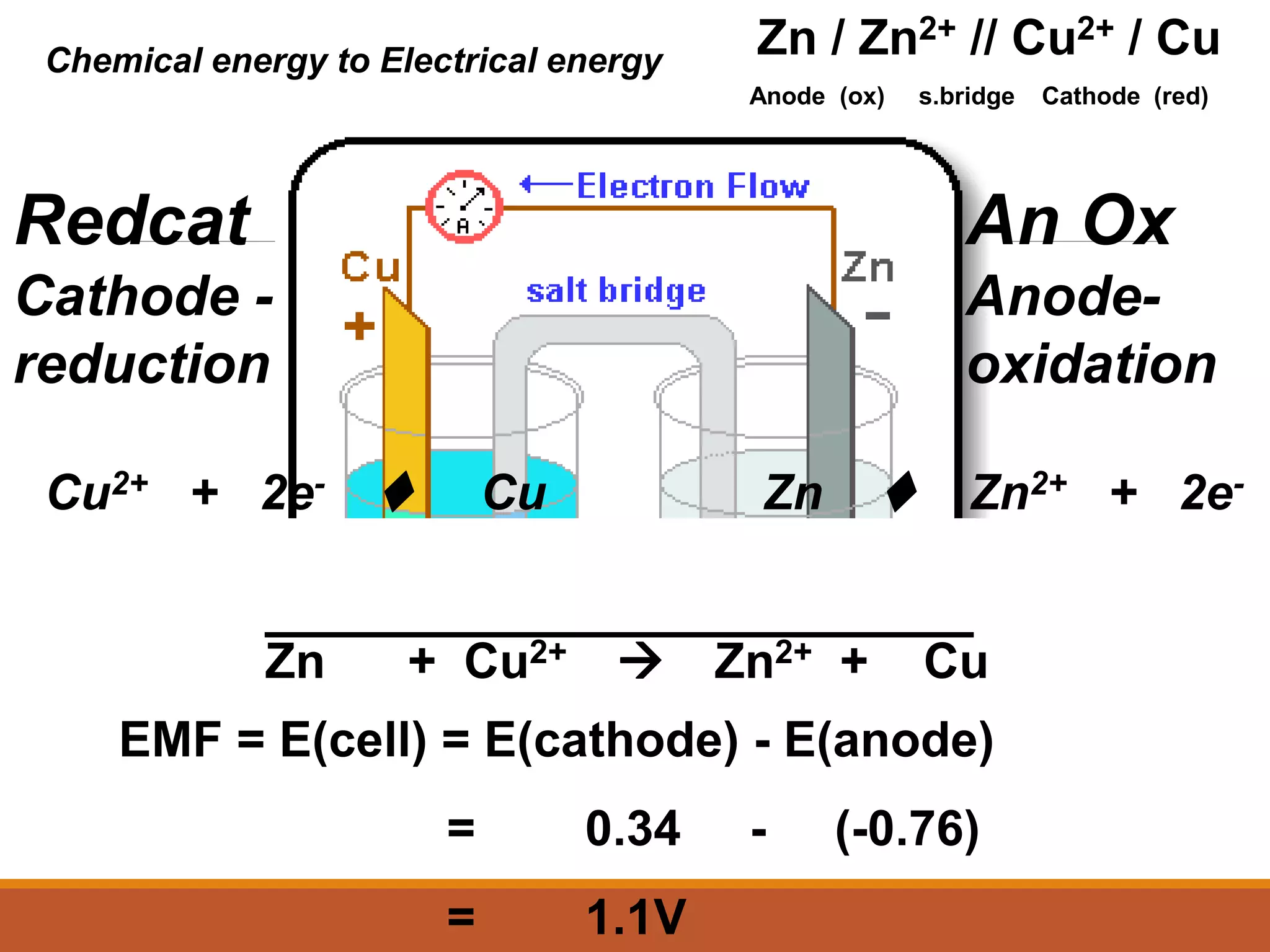
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between reactants. In an electrochemical cell, a spontaneous redox reaction occurs between two half-cells separated by a salt bridge. In the oxidation half-reaction, electrons are lost at the anode. In the reduction half-reaction, electrons are gained at the cathode. The standard electrode potential (E0) of a half-reaction indicates its tendency to be reduced or oxidized relative to the standard hydrogen electrode. The cell potential (Ecell) is equal to the cathode potential minus the anode potential and determines if the cell reaction is spontaneous.







![Electrochemical Cells
19.2
The difference in electrical
potential between the anode
and cathode is called:
• cell voltage
• electromotive force (emf)
• cell potential
Cell Diagram
Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Cu (s) + Zn2+ (aq)
[Cu2+] = 1 M & [Zn2+] = 1 M
Zn (s) | Zn2+ (1 M) || Cu2+ (1 M) | Cu (s)
anode cathode
Use || to separate half cells
Use | to separate reactants/phases in each half cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230425094425-3ba684d8/75/1-redox-reactions-summary-presentation-ppt-30-2048.jpg)