Embed presentation
Download to read offline
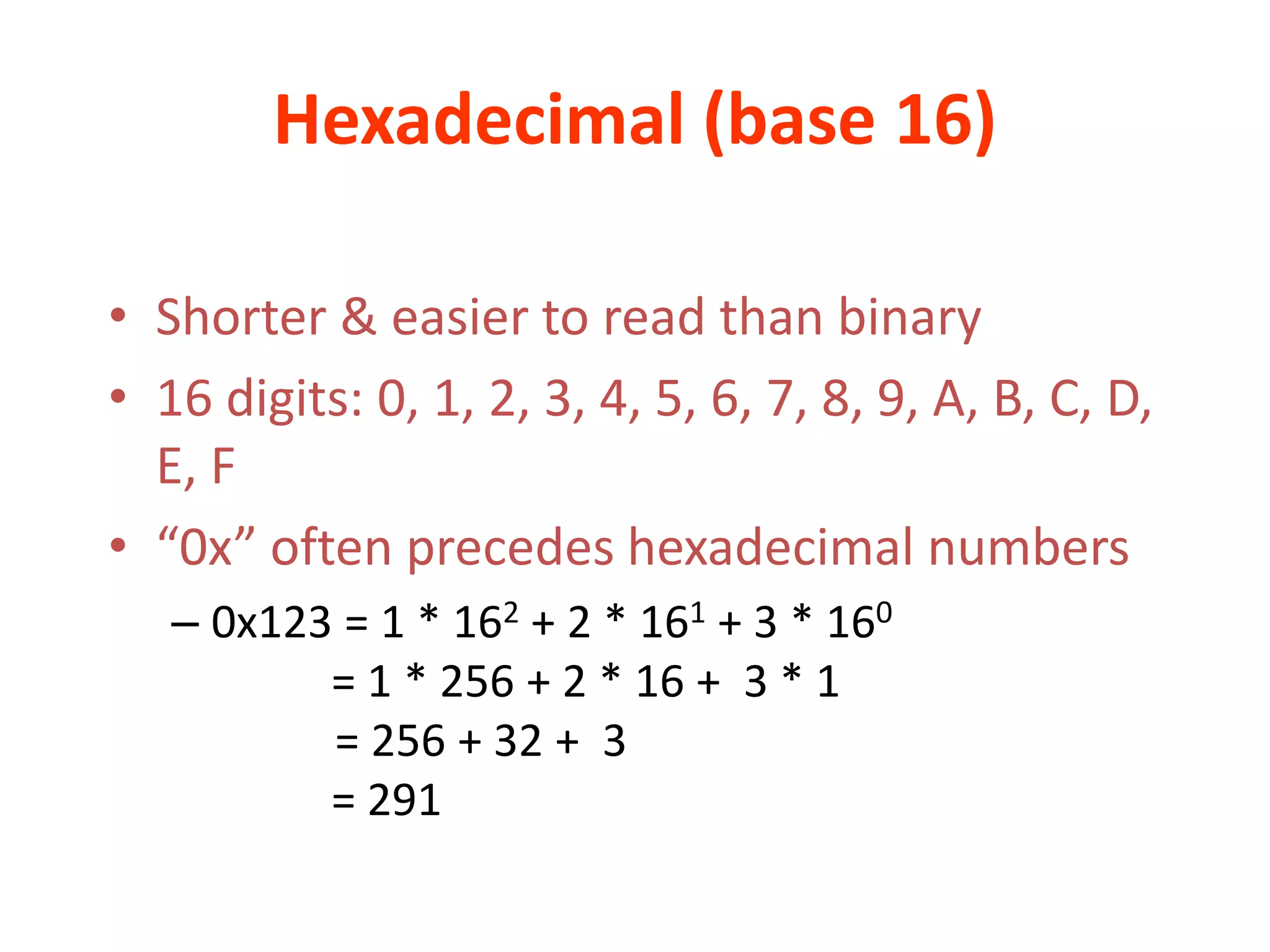


Hexadecimal is a base-16 number system represented by the digits 0-9 and A-F, that is shorter and easier to read than binary. It is often used to display computer memory addresses and RGB color values. In hexadecimal, each position represents a power of 16 and the value of a number is the sum of each digit multiplied by its place value, such as 0x123 equaling 291 in decimal. Other number systems like base 13 also represent values as the sum of each digit multiplied by its place value raised to the corresponding power.


