Embed presentation
Download to read offline




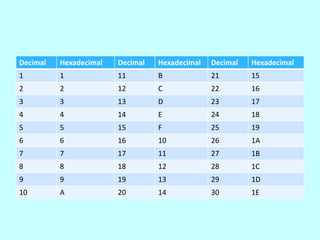
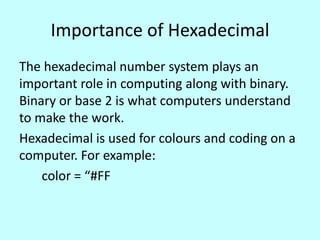
This document discusses the hexadecimal number system. It uses base 16, with digits 0-9 and letters A-F to represent values. Hexadecimal is important in computing because it connects decimal, binary, and color/coding systems. It allows counting beyond decimal 9 by replacing 9 with A, B, C, etc. up to F, at which point the next place value increases like a standard positional number system.





