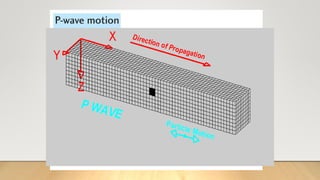
This document discusses a lesson on plate tectonics and locating the epicenter of an earthquake. The lesson objectives are to teach students how to locate an earthquake epicenter using triangulation from seismic data recorded at three stations. The document provides background on plate tectonics and earthquake terminology. It then presents a activity where students are given seismic data from three stations and asked to determine the epicenter using triangulation.