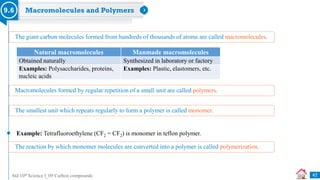
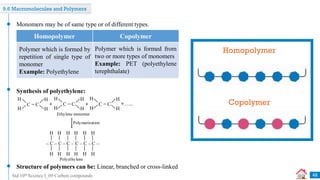
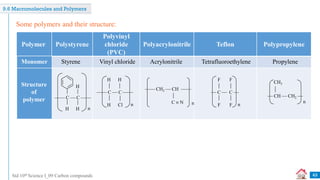
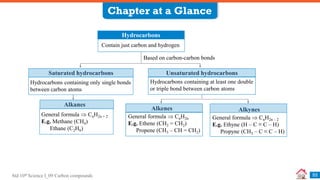
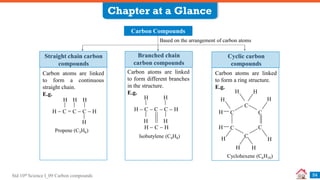
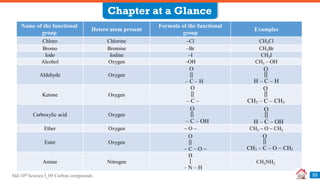
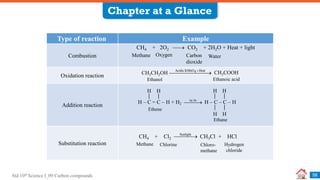
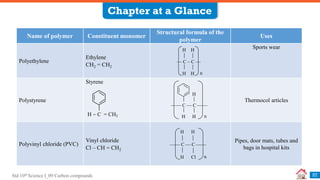
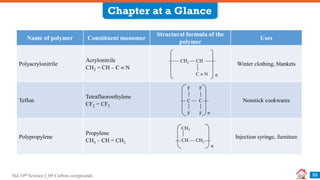
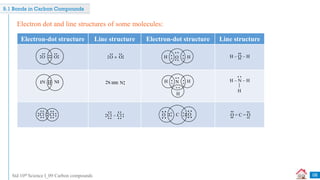
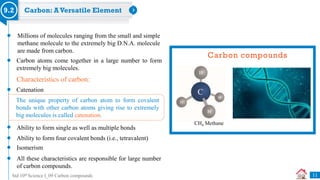
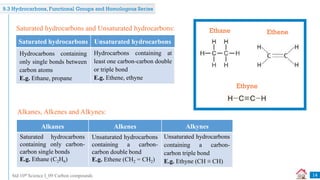
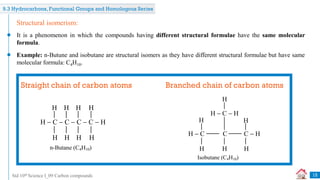
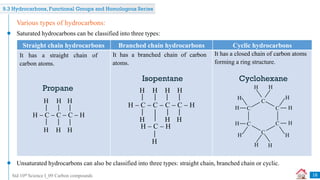
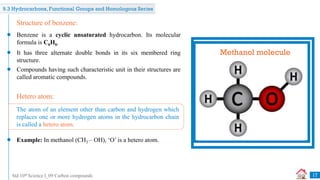
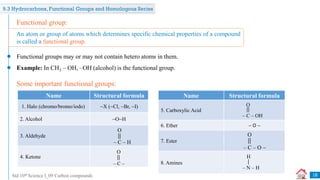
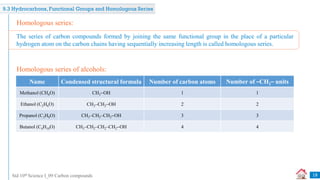
Carbon compounds can be classified based on their structure and bonding. The document discusses carbon bonding and different types of carbon compounds including hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated or unsaturated, and as alkanes, alkenes or alkynes depending on the presence of single, double or triple carbon-carbon bonds. Functional groups and homologous series are also introduced. Nomenclature of carbon compounds using IUPAC and common systems is explained.





![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
10
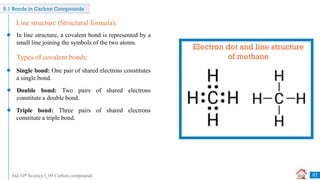
Draw an electron-dot structure of methane. [Dec 2020] [1 Mark]
Q
H
C H
H
H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-10-320.jpg)





![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
23
Complete the analogy:
Alkene : C = C :: Alkyne: _______. [Mar 2020] [1 Mark]
Q
C ≡ C
Answer the following questions: [Mar 2020] [3 Marks]
i. Define hydrocarbons.
ii. Name the types of hydrocarbons.
iii. Name two carbon compounds used in day-to-day life.
Q
Keywords: i. Compounds which contain carbon and hydrogen
ii. Saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons
iii. a. Cooking gas: (Propane + Butane)
b. Detergent: Sodium dodecylbenzene sulphate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-23-320.jpg)
![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
24
Draw the structural formula of C3H8. [Dec 2020][1 Mark]
Q
Define homologous series. [Dec 2020] [1 Mark]
Q
Keywords: series of carbon compounds, same functional group, sequentially increasing length of carbon chain
H – C – C – C – H
H H
H H
H
H
Complete the following flowchart and write the general formula of alkane: [Jul 2019] [2 Marks]
Q
i.
CH4 C3H8 C5H12
ii. The general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2.
CH4 C3H8 C5H12
C2H6 C4H10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-24-320.jpg)
![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
25
Write the names of first four members of homologous series of alcohols. [Mar 2019] [2 Marks]
Q
Homologous
series of alcohols
Propanol
Methanol
Ethanol Butanol
Homologous
series of alcohols](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-25-320.jpg)
![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
26
Complete the following table: [Mar 2020] [3 Marks]
Q
Straight chain of carbon compound Structural formula Molecular formula Name
C CH4 Methane
CC i iii Ethane
CCC ii C3H8 v
CCC C iv vi
H C H
H
H
H
H C C C C H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
i.
ii.
iii. C2H6
iv. C4H10
v. Propane
vi. Butane
H C C – H
H
H H
H
H C C – C – H
H
H H H
H
H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-26-320.jpg)



![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
32
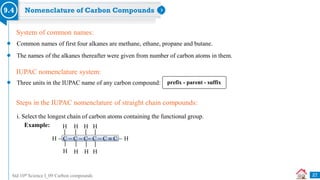
Write the IUPAC names of the following structural formulae. [Dec 2020] [1 Mark each]
i. CH3CHOHCH3
ii. CH3CH2COOH
iii. CH3COCH2CH3
Q
i. Propan-2-ol
Complete the following table: [Mar 2019] [3 Marks]
Q
i. Ethene
Sr. No. Common Name Structural Formula IUPAC Name
1. Ethylene CH2 = CH2 i
2. ii CH3COOH Ethanoic acid
3. Methyl alcohol iii Methanol
ii. Propanoic acid
iii. Butanone
ii. Acetic acid
iii. CH3OH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-32-320.jpg)







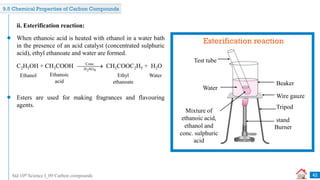
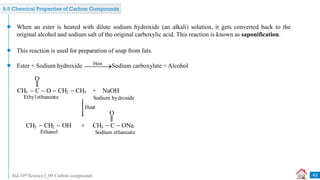

![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
45
Combustion of coal in air is a _______ reaction. [July 2019] [1 Mark]
Q
combination
A displacement
B
decomposition
C double displacement
D
The melting point of pure ethanoic acid is _______. [Dec 2020] [1 Mark]
Q
17°C
A 19°C
B
15°C
C 27°C
D](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-45-320.jpg)
![Std 10th Science I_09 Carbon compounds
Previously Asked Board Questions
46
Match the pairs: [July 2019] [2 Marks]
Q
(i – b), (ii – c)
Group ‘A’ Group ‘B’
i. Ethanol a. Hydrogen peroxide
ii. Methane b. Tincture iodine
c. Biogas
d. Non-stick cookware
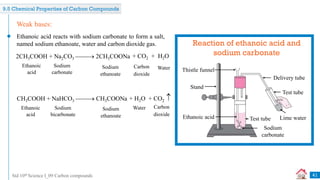
What is meant by vinegar and gasohol? What are their uses? [July 2019] [3 Marks]
Q
Keywords: Vinegar: 5-8% aqueous solution of ethanoic acid
Use: preservative
Gasohol: petrol + ethanol
Use: fuel](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09carboncompounds-230125092637-88447ed0/85/09-Carbon-Compounds-ppsx-46-320.jpg)