The document provides a tutorial on developing iOS mobile applications, specifically focusing on making network requests using NSURLConnection and handling JSON data. It details the implementation of the NSURLConnectionDelegate protocol and the conversion of JSON to Foundation objects using NSJSONSerialization. The document also compares JSON with XML, highlighting JSON's advantages in readability and speed.







![- (IBAction)btnFetchData1:(id)sender {
NSURLRequest
*theRequest=[NSURLRequest
requestWithURL:[NSURL
URLWithString:@“http://google.com"]];
NSURLConnection *con =
[[NSURLConnection alloc]
initWithRequest:theRequest delegate:self];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-objective-csession7-170502155743/85/07-objective-c-session-7-8-320.jpg)




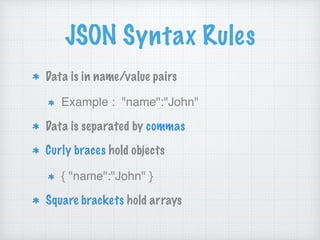
![JSON vs XML
JSON Example
{"employees":[
{ "firstName":"John", "lastName":"Doe" },
{ "firstName":"Anna", "lastName":"Smith" },
{ "firstName":"Peter", "lastName":"Jones" }
]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-objective-csession7-170502155743/85/07-objective-c-session-7-14-320.jpg)




![id json = [NSJSONSerialization
JSONObjectWithData:dataObject
options:0 error:nil];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-objective-csession7-170502155743/85/07-objective-c-session-7-20-320.jpg)

