This document discusses JSON and Java integration using Jackson. It provides an introduction to JSON, its syntax and compatibility with other languages. It then covers how to use Jackson annotations to serialize and deserialize Java objects to and from JSON. The document also discusses JSON parsing, schema, and how to integrate JSON with Java technologies like MuleSoft.



![JSON Compatibility
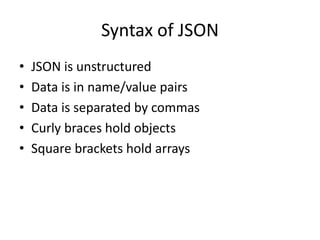
• Array
– ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday“]
– "employees":[
{"firstName":"John", "lastName":"Doe"},
{"firstName":"Anna", "lastName":"Smith"},
{"firstName":"Peter","lastName":"Jones"}
]
• Object
– { “firstname": “Santhosh ", “lastname": “Gowd”} All data
types are intuitive and similar to other programming
languages
• Also compatible with other languages like C, C++, C#,
ColdFusion, Python and many more.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f18df389-ca75-4bed-9f90-7f55adf6f119-151020111437-lva1-app6892/85/Java-JSON-Jackson-6-320.jpg)