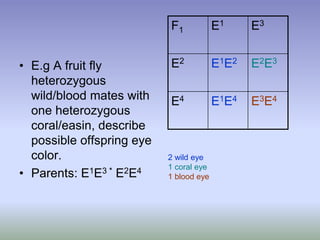
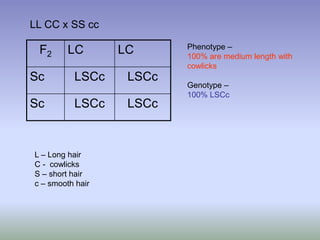
This document discusses multiple alleles and incomplete dominance. It provides examples of multiple alleles for eye color in fruit flies, represented by different alleles (E1, E2, etc.) with the smaller number being dominant. Examples are given of incomplete dominance resulting in intermediate traits, such as pink flowers from the cross of red and white flowering plants. Possible genotypes and phenotypes are described for F1 and F2 generations of crosses between parents with different trait combinations.