This document discusses various neural network learning processes and paradigms, including:
- Error-correction learning uses a delta rule to minimize the difference between the network's output and the desired output.
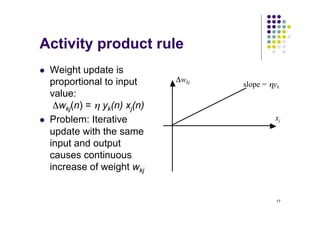
- Hebbian learning updates weights based on the activities of connected neurons, with rules like the activity product rule.
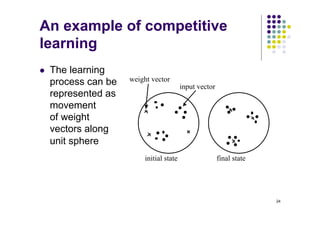
- Competitive learning is unsupervised, with neurons competing to respond to input patterns in order to classify them.
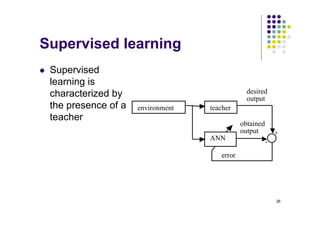
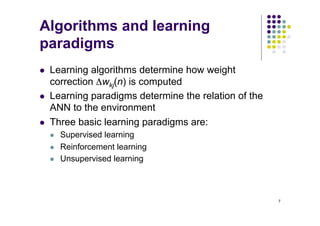
- Supervised learning uses input-output pairs from a teacher to train the network, while reinforcement learning receives a grade or reward instead of examples. Unsupervised learning has no teacher.





![10
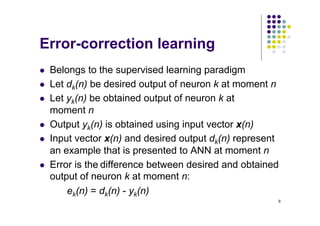
Error-correction learning
l The goal of error-correction learning is to minimize
an error function derived from errors ek(n) so that the
obtained output of all neurons approximates the
desired output in some statistical sense
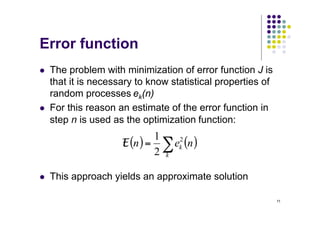
l A frequently used error function is mean square
error:
where E[.] is the statistical expectation operator, and
summation is for all neurons in the output layer
( )⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
= ∑
k
k n
e
E
J 2
2
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-learningprocess1-221102095201-85261713/85/02-LearningProcess-1-pdf-10-320.jpg)





![18
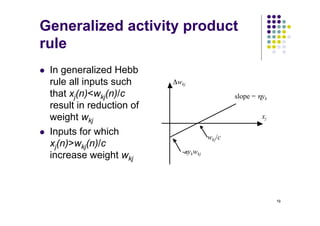
Generalized activity product
rule
l To overcome the problem of weight saturation
modifications are porposed that are aimed at limiting
the increase of weight wkj
l Non-linear limiting factor (Kohonen, 1988):
Δwkj(n) = η yk(n) xj(n) - α yk(n) wkj(n)
where α is a positive constant
l This expression can be written as:
Δwkj(n) = α yk(n)[cxj(n) - wkj(n)]
where c = η/α](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-learningprocess1-221102095201-85261713/85/02-LearningProcess-1-pdf-18-320.jpg)