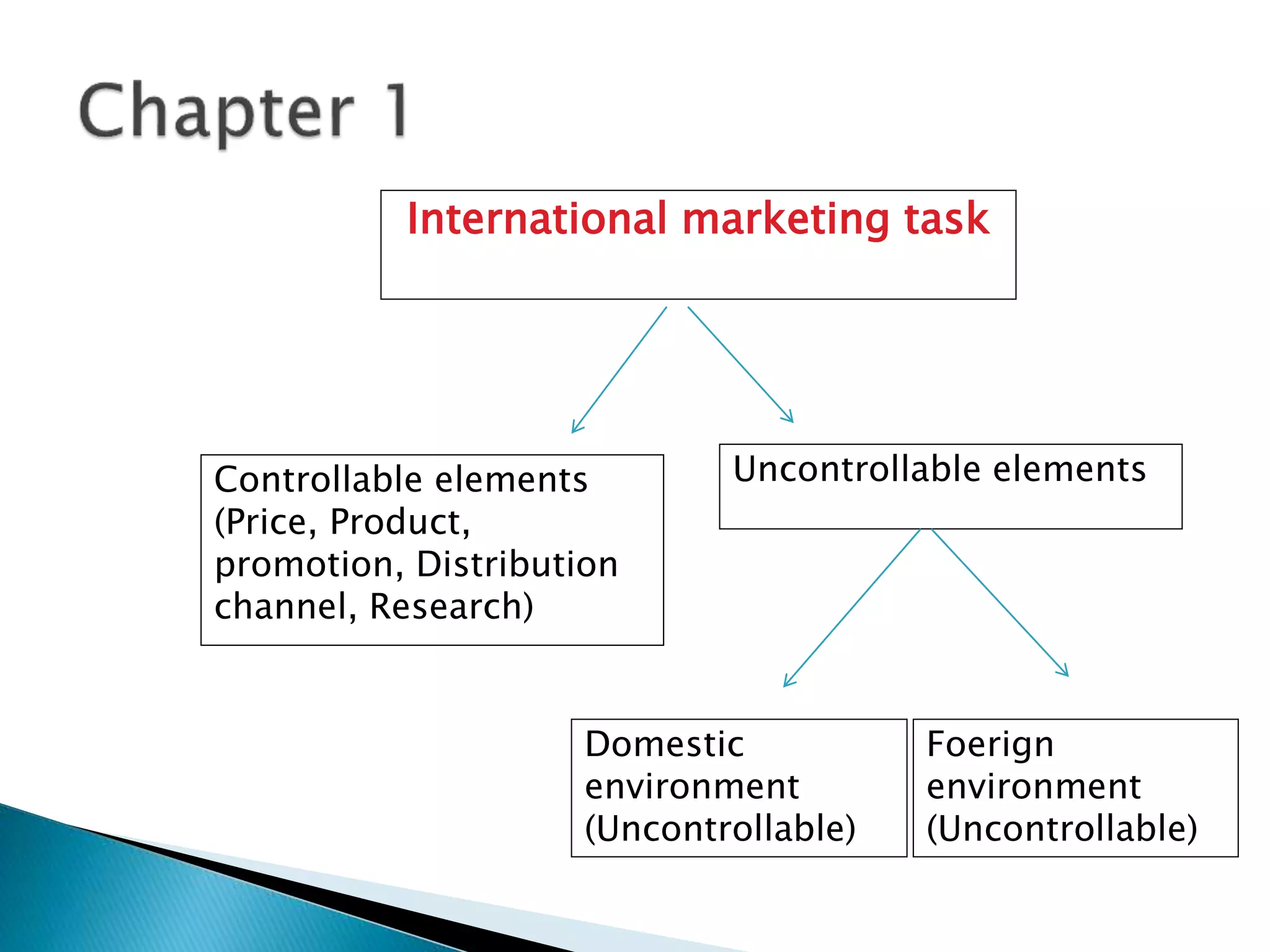
This document outlines the key topics and assignments for an international marketing course. It includes chapters from the textbook on topics like cultural dynamics, global marketing research, and international marketing management. The assignments require students to analyze controllable and uncontrollable elements of entering a new global market with a selected product, develop a cultural analysis and marketing plan, and identify an appropriate international marketing channel. Grading is based on attendance, coursework, midterm and final exams.