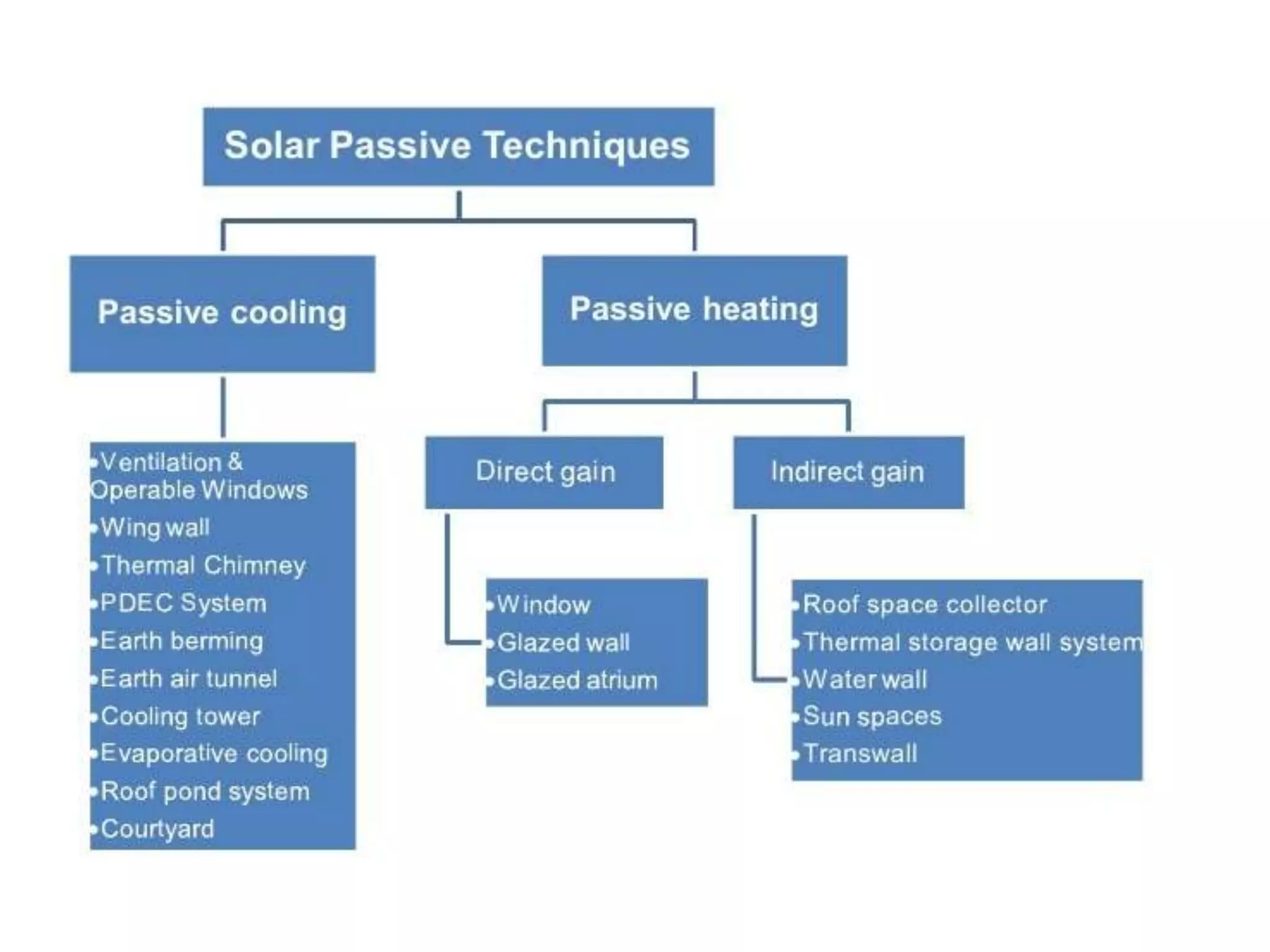
This document summarizes solar passive architecture techniques for designing energy efficient buildings. It discusses the aims of minimizing energy use and promoting renewable resources. The methodology involves researching passive features and case studies. Passive design uses natural heating and cooling through elements like south-facing glass, thermal mass, and cross ventilation. Historically, the Greeks and Romans designed cities and homes to maximize winter sun exposure. Case studies from India demonstrate current applications of passive solar techniques.